Knowledge-Grounded Dialog Generation
Current approaches to dialog generation using external knowledge.

What is dialog generation, and where is it used
Dialog generation (or dialogue generation) is the process of generating automatic text response as a reaction to the text input provided by a user. It is widely used in chatbots and virtual assistants. Real-life uses range from well-known all-purpose assistants like Siri, Alexa, Cortana, etc., to the more specialized ones like dialog agents helping lonely people. We see the practical use of automatically generated dialogs in such industries as tech, medtech, fintech, sales automation, and first-line technical support.
How does dialogue generation work
Popular language models like GPT-2, XLNet, T5, etc., allow producing coherent, good-looking text. But, unfortunately, the end result is lacking common sense and factual knowledge.
Classic models store knowledge in an implicit way as the parameters of a neural network. This means that:
- To store more knowledge, even larger networks need to be used (and they are already enormous).
- To update knowledge, the whole network needs to be re-trained.
- There is no confidence in the correctness of the end result as models can “hallucinate" and say things that aren't true, making slight factual mistakes — for example, confusing dates and numbers.
As seen in the scheme below, knowledge-grounded dialog generation adds the step on which relevant knowledge is introduced into the process to help generate a relevant response.
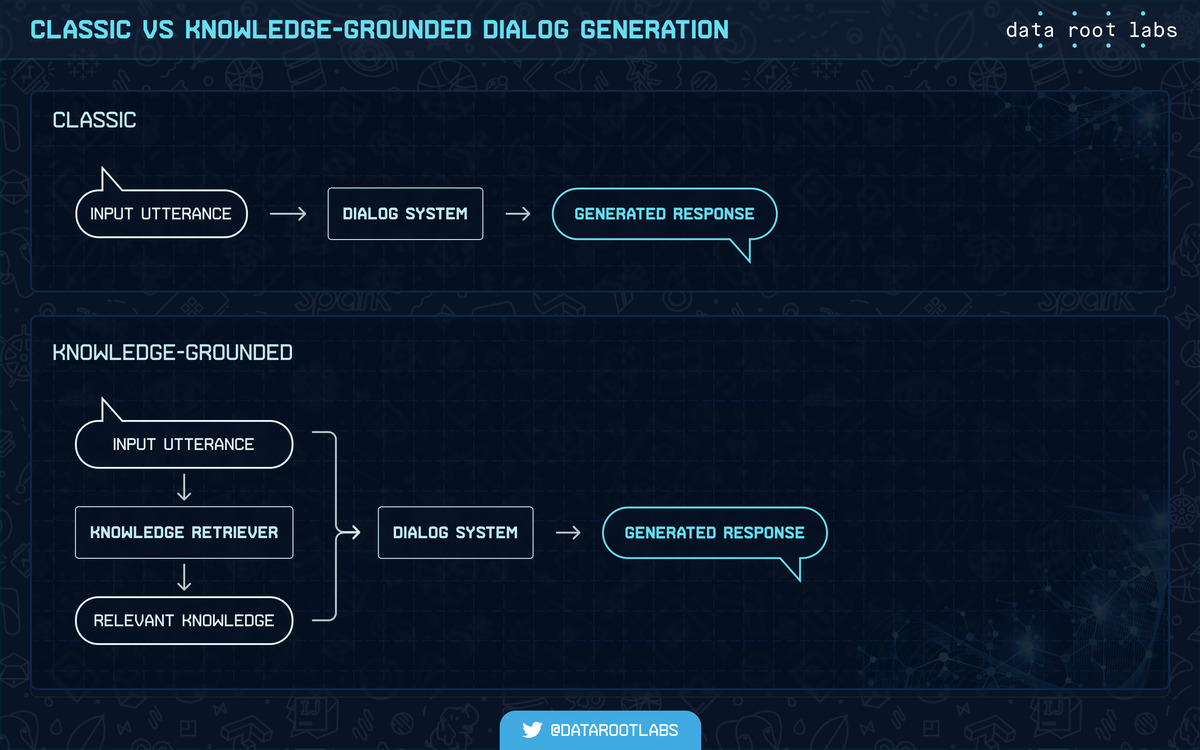
Classic vs knowledge-grounded dialog generation.
What is the best approach to knowledge-grounded dialog generation?
In this article, we’re considering and comparing document-grounded (document-based) and knowledge graph grounded approaches while also touching upon non-dialog text generation from knowledge graphs. None of these approaches presents an ultimate silver-bullet solution. However, each of them has advantages that could outweigh the cons for a given use case at hand. And each of these solutions improves text generation by adding external knowledge.
To select the correct approach for you, you need to be guided by what you are trying to build and how you are trying to help your client. So while this article won’t provide you with a clear-cut answer to what kind of approach will work best for you, we’ve gone through a considerable number of current scientific whitepapers regarding different types of knowledge-grounded dialogue generation. We also briefly covered non-dialog text generation with the help of knowledge graphs and a few popular datasets. All of this should allow you to find the approach that will work best for you.
Document-grounded dialog generation
The document-grounded dialog generation approach uses a certain document to create the response based on the contents of this document and the user’s query. It adds relevant textual documents as model input — usually, excerpts from Wikipedia articles are used.
All of the papers with this approach (including the ones listed below) assume that a document is provided, which is usually the case in datasets. The most frequently used datasets are:
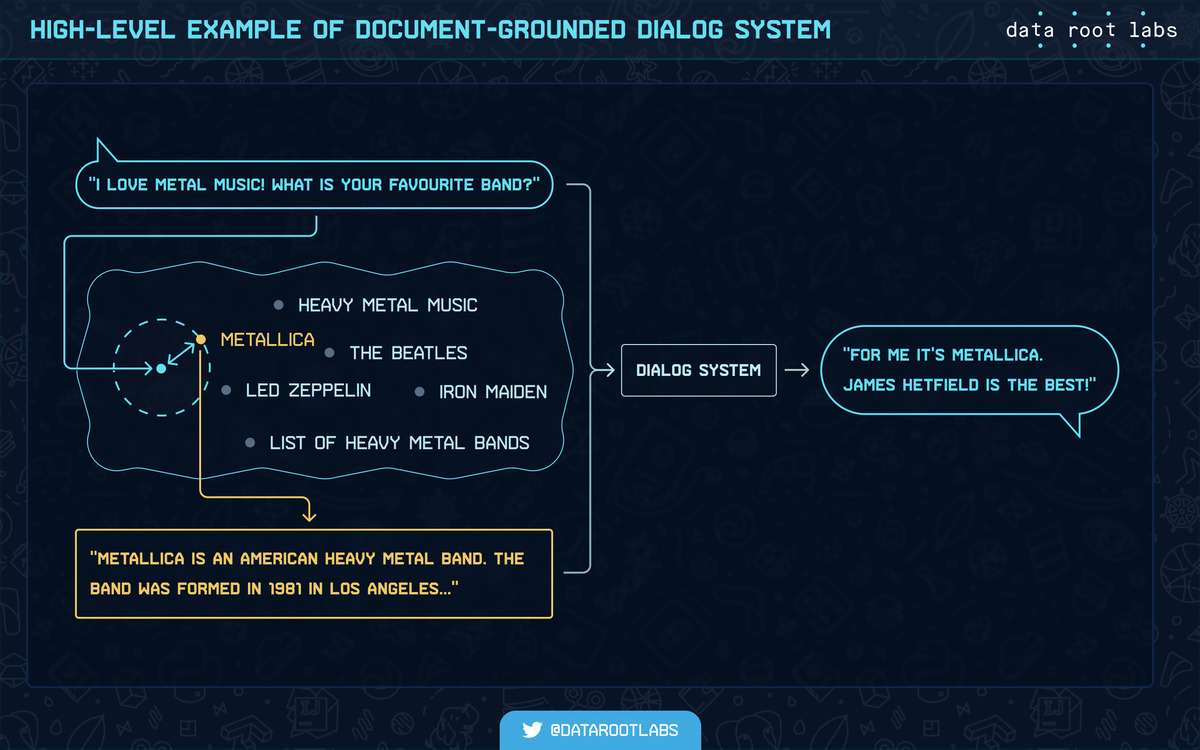
High-level example of document grounded dialog system.
| Title | Description | Contents |
A large dataset with conversations grounded using the knowledge retrieved from Wikipedia articles. | 1365 discussion topics, 202,000 utterances | |
A dataset that contains movie chats. Each response is explicitly generated by copying and/or modifying sentences from unstructured background knowledge such as plots, comments, and movie reviews. | 90,000 utterances from 9,000 conversations | |
A dataset based on Wikipedia articles about popular movies. It provides a relevant chat history while generating responses and also provides a source of information that the models could use. | 4112 conversations with an average of 21.43 turns per conversation (per-utterance documents) |
To be able to use the datasets in production, a separate document retriever is necessary. Classic retrievers were made using TF-IDF and BM25. But recently, methods with dense vector representations started to outperform TF-IDF and BM25 retrievers. Such new methods are, for example, Google’s ORQA and Facebook’s DPR, which formerly were mainly applied in question-answering context and not used for dialog generation.
We have studied numerous scientific articles that cover document-grounded dialogue generation. And these are the selected papers that we find to be useful for you. The papers are presented in order of relevance (most notable first), with our own opinionated summary for each in the “Concept” column:
| Title | Concept | Source code | Framework / Model backbone | Dataset(s) |
Part of BlenderBot 2.0. Converts dialog context into a query for a search engine. Then, all the retrieved documents are used in the Fusion-in-Decoder scheme. New dataset was used for supervised training of all the components. | PyTorch / Transformers | WoW, WoI (Wizard of Internet) | ||
Knowledge-Grounded Dialogue Generation with Pre-trained Language Models (2020) | Utilizes knowledge selection module to fit the input — dialog context and external knowledge — into the GPT-2 length constraints. For training, reinforcement, and curriculum learning with warm-up on pseudo ground-truth selected knowledge is used. No training script and no retriever are available for this approach. However, a checkpoint is provided. | PyTorch / Transformers | WoW, CMU_DoG | |
Difference-aware Knowledge Selection for Knowledge-grounded Conversation Generation (2020) | Computes explicit differential information between the selected knowledge candidates and the knowledge from previous turns to be used for knowledge selection later. | PyTorch / RNN | WoW, Holl-E | |
DukeNet: A Dual Knowledge Interaction Network for Knowledge-Grounded Conversation (2020) | Uses dual learning for simultaneous unsupervised learning of knowledge shifter and posterior knowledge tracker, which is used only during training. The initial knowledge tracker used during inference is trained via posterior. | PyTorch / RNN | WoW, Holl-E | |
Incremental Transformer with Deliberation Decoder for Document Grounded Conversations (2019) | Uses an Incremental Transformer for incremental encoding of utterances with knowledge and Deliberation Decoder for two-step decoding — one for text coherence and the other for knowledge correctness. | PyTorch / Transformers | CMU_DoG | |
RefNet: A Reference-aware Network for Background Based Conversation (2020) | Dynamically switches between generative and extractive methods during the response generation to combine the best of two worlds. | Tensorflow / RNN | Holl-E | |
Sequential Latent Knowledge Selection for Knowledge-Grounded Dialogue (2020) | Treats selected knowledge as a latent variable for end-to-end sequential knowledge selection and response generation, with copy mechanism. | Tensorflow / Transformers, RNN | WoW, Holl-E | |
Selects global knowledge utterances. Next, on each generation step, it can select local knowledge — tokens from global knowledge. | PyTorch / RNN | Holl-E |
Knowledge graph grounded dialog generation
The knowledge graph grounded dialog generation approach adds a relevant chunk of a large knowledge graph or a single triple from it as model input. The main knowledge graphs used in knowledge graph grounded approaches are ConceptNet, ATOMIC, Freebase, with the main dialog source being Reddit.
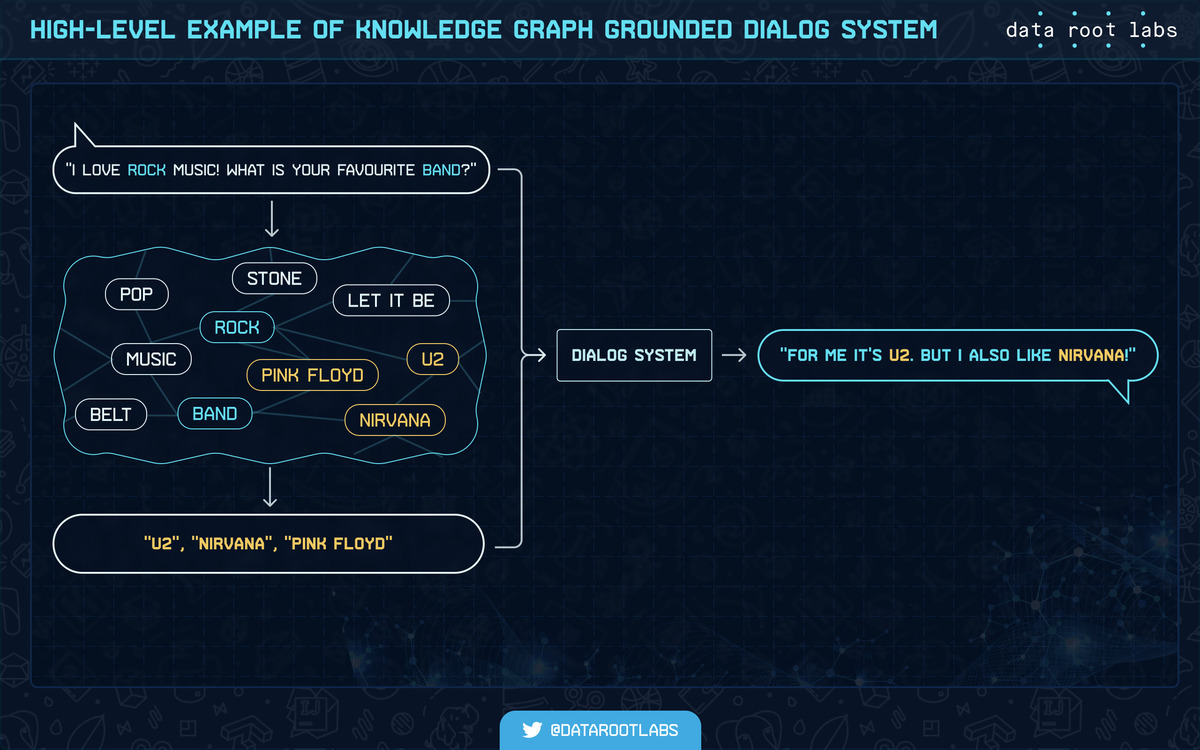
High-level example of knowledge graph grounded dialog system.
These are the selected papers that propose knowledge graph grounded approaches. They are also chosen and annotated by us in the "Concept" section and are presented in order of relevance:
| Title | Concept | Source code | Framework / Model backbone | Dataset(s) / Knowledge graph |
Commonsense Knowledge Aware Conversation Generation with Graph Attention (2018) | A classic work on combining dialog generation with external commonsense knowledge. One of the first works of this kind. Its official codebase is written in Python 2; however, there is an unofficial implementation that utilizes Python 3. | @thu-coai/ccm unofficial | Tensorflow / RNN | Reddit / ConceptNet |
Can be viewed as further development of CCM. The knowledge fact set is retrieved from the graph and ranked by felicitous fact recognizer. The results are later used by a triple decoder, which can either copy words from context, subgraph, or select them from the vocabulary. | Tensorflow / RNN | Reddit, Weibo / ConceptNet | ||
Grounded Conversation Generation as Guided Traverses in Commonsense Knowledge Graphs (2020) | Augments response generation with a chunk of the commonsense knowledge graph. It starts with entities found in the previous utterance and grows a subgraph by adding 1- and 2-hop concepts, which form the inner and the outer flow and are used separately. | PyTorch / RNN | Reddit / ConceptNet | |
Predicts triple from knowledge graph for language model conditioning and diffuses the triple into a distribution over facts. Since the generator requires discrete fact for conditioning, this approach integrates non-differentiable sampling from the distribution via four different schemes, including latent variable and Gumbel-softmax approaches. The triple decoder can sample tokens from three distributions — fixed vocabulary, conditioning triple, and dialog context. | Tensorflow / RNN | Some chinese dataset from Weibo / ConceptNet | ||
Improving Knowledge-aware Dialogue Generation via Knowledge Base Question Answering (2020) | Uses separately trained knowledge-base question-answering model for dialog generation. | Tensorflow / RNN | Reddit / ConceptNet and FB2M (Freebase) | |
A dialog dataset annotated with a large-scale knowledge graph alongside a graph walker model. | No implementation code for the baseline model exists; there is only data / RNN | New dataset / Freebase subset | ||
Proactive Human-Machine Conversation with Explicit Conversation Goa (2019) | A dialog dataset in Chinese with dialogs over a knowledge graph + a baseline model. | PaddlePaddle / Transformers, RNN | Original Chinese dataset — DuConv / Small knowledge graphs from the dataset | |
DyKgChat: Benchmarking Dialogue Generation Grounding on Dynamic Knowledge Graphs (2019) | A dialog dataset with dialogs from two Chinese and English-language sitcoms (“Friends”) alongside dynamic knowledge graphs and a baseline model for new tasks. | Tensorflow / RNN | Own data based on “Friends” TV series and a Chinese sitcom / Small dynamic knowledge graphs from the dataset |
Non-dialog text generation from knowledge graphs
Even though we focus on dialog generation in this article, there are a number of text2text problems that can also benefit from external commonsense knowledge, for example — story generation. The results of these tasks can be transferred to dialog generation, and this poses an interesting research direction. All the tasks here are sequence-to-sequence text generation, just like the main dialog generation problem. By solving one problem, the approach can often be applied to similar problems.
The selected papers that propose non-dialog text generation with knowledge graphs are also chosen and annotated by us in the "Concept" section and are presented in order of relevance:
| Title | Concept | Source code | Framework / Model backbone | Dataset(s) / Knowledge graph |
KG-BART: Knowledge Graph-Augmented BART for Generative Commonsense Reasoning (2020) | Knowledge-graph augmented pretrained language model. It is trained on concepts-to-text task, which later can be transferred to other problems, including dialog generation. | PyTorch / Transformers | CommonGen / ConceptNet | |
Language Generation with Multi-Hop Reasoning on Commonsense Knowledge Graph, 2020 | At its core, this is the Seq2Seq approach that uses commonsense knowledge graph ConceptNet. The subgraph with mentioned entities is extracted and enriched with adjacent nodes. The node and relational embeddings are computed via graph network and later are scored using context embedding. During generation, the gate mechanism can select these entities as tokens based on the computed score. | PyTorch / Transformers | ROC stories / ConceptNet | |
Text Generation from Knowledge Graphs with Graph Transformers, 2019 | A new dataset consisting of scientific texts, paired with knowledge graphs for data-to-text task + Transformer model. | PyTorch / Transformers | New dataset — AGENDA / Graphs from dataset | |
A Knowledge-Enhanced Pretraining Model for Commonsense Story Generation, 2020 | — | Tensorflow / Transformers | ROC stories / ConceptNet, ATOMIC | |
Knowledge Graph-Augmented Abstractive Summarization with Semantic-Driven Cloze Reward, 2020 | — | PyTorch / Transformers | NYT, CNN/DM / Graphs built using StanfordNLP and OpenIE | |
Story Ending Generation with Incremental Encoding and Commonsense Knowledge, 2018 | — | PyTorch / RNN | ROC stories / ConceptNet |
More daily dialogue datasets and additional information
It’s also worth introducing you to several new, purely-dataset papers and a knowledge graph paper with no baseline models. These papers can be as important as the dialog-generation approaches that were covered above.
| Dataset name | Source code |
Topical-Chat: Towards Knowledge-Grounded Open-Domain Conversations (2019) | |
@MEDIA-DIALOG/interview-media-analysis, kaggle @shuyangli94/interview-npr-media-dialog-transcripts | |
Last but not least, we recommend checking out the 2020 survey paper “Towards information-rich, logical text generation with knowledge-enhanced neural models” that covers the knowledge-enhanced text generation systems, the state of the research that deals with these systems, and suggests new research directions.
Knowledge-Grounded Dialogue Generation: Summary
The process of generating dialogues that are both accurate and usable for real-life applications (virtual assistants, intelligent chatbots, etc.) requires using relevant external knowledge. The main existing approaches to internet-augmented dialogue generation are:
- Document-grounded dialog generation
- Knowledge graph grounded dialog generation
There are advantages and disadvantages to each approach, depending on your end goal. Which is why in this article we’ve covered dozens of research papers that present their own take on knowledge-grounded dialogue generation, adding a short summary for each. Remember that no single approach is perfect and consider your initial goal when selecting the approach to use. Hoping that this overview will make it easier for you.
Have an idea? Let's discuss!

Talk to Yuliya. She will make sure that all is covered. Don't waste time on googling - get all answers from relevant expert in under one hour.





