AI in Dating: Can Artificial Intelligence Algorithms Help You Find Love?
How modern dating services leverage AI for more efficient, fun, and safe matchmaking.

The $3 billion+ Online Dating industry has seen a rise of all kinds of apps for all kinds of dating: traditional, long term dating, hook-ups, gay, lesbian, queer, group, "friends of friends", Ivy League, DNA, astrology - you name it! In fact, online dating apps are becoming so popular that over 50% of couples will meet online by 2031 according to eHarmony.
Hundreds of millions of users hooked on apps allow dating companies to accumulate incredible amounts of data. This data advances the artificial intelligence technology behind dating services enabling not only AI matchmaking but also a more secure and enjoyable online experience.
AI Innovation in Dating Industry
Inside: AI + Dating landscape featuring 50 companies.
But, can AI algorithms help us find love? Can they go a step further and replace a human being as a partner in a relationship? In this article we analyze how far technology has come in helping us meet "our" people, find love, and feel less lonely.
Take a look at our AI In Dating Innovation Landscape which includes 50 rising startups as well as mature companies that leverage AI to make dating more efficient, fun, and safe.

AI in Dating Industry Innovation Landscape 2021
So, how exactly do companies use AI to change and improve the way people meet? Let's look at the few use cases among mature dating companies and startups.
Relevant matches.
In-app user behavior data enriched by the profile data provides food for the machine learning algorithms that learn to provide increasingly more relevant and curated matches. The complexity of such matchmaking has gone much further than "swiping right" for the desirable looks in nearby locations.
Now many companies tune the algorithms to account for personality traits, music taste, beliefs, attitude, and much more.
Thus, Coffee Meets Bagel connects individuals with a "friend-of-a-friend" match every day. The company's matching algorithm runs on a deep neural network and uses a "blended" method. Nine models rate the matches, and the system goes through all and comes back with a converged score. Men receive up to 21 matches — or "bagels" — a day to decide on, while women receive 4.
Hinge is positioning itself as a service that helps you get off dating apps soon. Its Most Compatible feature uses machine learning and the Gale-Shapley algorithm to send daily recommendations for people based on user's past behavior within the app. In 2018, Hinge launched another feature called "We Met," where matched users were prompted to answer a brief private survey on whether the pair met up offline. This step serves as a feedback loop to teach its matching algorithms what makes up successful matches offline over time.
Tinder allegedly used to assign each user an "ELO" score that defined the quality and quantity of your profile. The score was calculated bases on the numbers of right swipes, Left/Right swipe ratio, quality of profile, things you show or tell in your profile that can be interpreted by the algorithms as traits, moods, and intentions, and messaging activity.
Tinder then recommended people with the same score as a proxy for compatibility. Currently, the company has switched to the TinVec approach which embeds users’ preferences into vectors leveraging a large number of swipes by Tinder users.
Badoo has recently introduced the feature of finding a celebrity lookalike in the app’s database. The Lookalike feature allows users to upload the photo of the desired celebrity (or any person, like your ex) and the service presents you the ones that resemble your choice the most.
Making people meet offline.
With so much activity online, it is easy to forget about the reason (at least the initial concept) behind online dating - meeting a person offline. To get people to meet in person, some companies leverage artificial intelligence to encourage meetings in real life and act as a dating coach.
For example, eHarmony plans to release an AI-enables feature that would encourage users to suggest meeting in person after they have been interacting online for a while. On the other hand, Loveflutter suggests places to go on a first date that are equidistant from both people's homes using information from Foursquare.
Improving in-app experience by minimizing unsolicited content.
Not everyone plays by the rules once you have million people using AI in online dating apps. Unwanted and abusive content, online stalking, and too many messages are annoying byproducts of popular online platforms.
To monitor user-uploaded content and filter out anything related to politics, pornography, or other sensitive topics, Blued, a mobile-based gay social app, runs AI on users' conversations to detect rule breakers. Bumble, an app that challenges female users to make the first move, recently launched Private Detector, a safety feature that uses AI to detect the sending of unsolicited pictures (with 98% of accuracy), giving users the choice to either open and view this content, or avoid it.
Similarly, a faith-based app Muzmatch which caters to single Muslims introduced the obscenity filter (haram detector) built on machine learning coupled with member feedback to detect Haram (impermissible) content.
Securing online dating space.
To protect user's safety, many services have introduced security features powered by AI to minimize spam and ban scammers. S’More that links people intellectually rather than superficially has developed an AI algorithm that confirms that your uploaded photos are: 1) real and of you; 2) are current; 3) are not overly altered. The app also introduced a behavioral score to control bad behavior and abusive content.
Lovoo developed an intelligent, continuously improving Anti-Spam program. The program automatically and semi-automatically recognizes spam, scam, and fake profiles and fights them with the power of machine learning.
A gay social network, Hornet with over 30 million users, is using an AI verification process to curb catfishing. The app examines user-activity to establish if the person is trustworthy and genuine. In addition, Hornet will be the first of the major gay social networks to let people earn a badge of authenticity.
The dating app's algorithms will decide on who gets a badge based on how they interact with the community.
NLP for a better match and date facilitation.
While some apps don't and won't access messages, others use that content to deliver better matches and a more enjoyable experience. Crushh and Mei Messaging App use AI to analyze texting relationships and habits to deliver actionable insights to users around the world. Loveflutter plans to analyze chats between its users to determine their compatibility and suggest when they should meet.
AIMM takes it a step further. This first fully conversational AI-based app is using the latest facial recognition and a fully conversational design. AIMM asks you a series of questions and listens to your voice to determine your best match. Then the dating app algorithms will start introducing matches one at a time and then will help set up a time for a phone call between you and your match. It coaches users through a first phone call, gives advice for the first date, and even provides feedback afterward.
Finding a scientific match with genomics and behavioral science.
For those who believe that genes largely determine our love life, DNA matching is already a thing. DNA Romance uses AI to match users with potential partners based on their genes by forecasting "chemistry" between single individuals online. You can send your sample for analysis to find the best match from the scientific perspective.
eHarmony's "affinity" process generates behavioral data using machine learning models to ultimately offer more personalized recommendations to its users. A relatively new entrant to the market, the Canadian app Say Allo uses a continuous learning algorithm and compatibility index based on Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT).
Exotic use cases: astrology, music, games, and video.
Finally, some companies have taken to less traditional methods of paring humans. Zotality, for example, employs proprietary AI to merge NASA's planetary data with insights of astrologers for compatibility matching. Tastebuds let you meet like-minded people who share your love for music. Desire features AI-based love games for both long-term relationships and new couples. The app analyzes users’ thinking styles, decision-making processes, and behavior to create intelligent game dynamics tailored to the partners’ desires, for both rekindle cooling relationships and boost satisfaction for new couples.
SLIDE, a video-first dating app enables users to effectively find matches and ‘test the waters’ with others. SLIDE AI feature allows users to select several profiles to analyze and generate their ideal match and then customizes matches based on that ideal.
In the table below, we summarize some of the dating app startups using AI to advance online dating.
| Company | HQ / year founded | Amount Raised, $ | Investors | What they are doing |
| 6Degrees | Canada / 2020 | — | — | 6Degrees was launched during the pandemic to bring people together while staying apart. It uses a Machine Learning program developed by the University of California (powered by a Euclidean algorithm) to pair singles up on zoom dates. |
| Aimatchmaker | Taiwan / 2015 | $138K | Taiwan Startup Stadium | AiMatchMaker is a tech and AI-empowered matchmaker for ethnic Chinese. |
| AIMM | USA / 2015 | — | — | AIMM is the first fully conversational AI-based app. Using the latest facial recognition and a fully conversational design, AIMM asks you a series of questions to determine your best match. |
| Badoo | UK / 2006 | $30M A | FinSight Ventures | Badoo is a dating-focused social network allowing users to chat, make friends, and share interests. The app recently introduced the feature of finding a celebrity lookalike in the app’s database. Users can upload a picture of someone and the app will find lookalikes among Badoo's more than 400 million users worldwide. |
| Betterhalf.AI | USA / 2016 | $1.2M Seed | Angels, FirstPenguin Capital | Betterhalf.ai claims to have the world's largest AI-powered partner prediction engine based on the past data of millions of married couples. Through compatibility scores based on multiple relationship dimensions and users’ interactions with the product, Betterhalf.ai streamlines their search. Today, Betterhalf.AI is on a path to build the largest AI-based relationship engine that can suggest matches taking into account both extensive couples’ relationship data and the users’ comprehensive personality profiles. |
| Blued | China / 2012 | $131.6M D | CDH Investments, Ventech China, Shunwei Capital | Blued is a developer of a mobile-based gay social app designed to connect with the network of guys. The company has deployed AI technology to monitor user-uploaded content and filter out anything related to politics, pornography, or other sensitive topics. Blued runs AI on users' conversations to detect rule breakers. Blued’s users will have the option to pass a photo verification test. It will compare a user’s posed photo taken in real-time to their existing profile photos using human-assisted AI technology. |
| Bumble | USA / 2014 | — | Greycroft, Accel, Bessemer Venture Partners | Bumble challenges female users to make the first move. The app recently launched Private Detector, a safety feature that uses AI to detect the sending of unsolicited pictures, giving users the choice to either open and view this content, or avoid it. It’s proven to be 98% accurate making a dating app that’s safe for women. |
| Chappy | UK / 2016 | Seed | Bumble | Chappy is an online dating app dedicated to gay men.
Dating apps including Bumble, Badoo, Chappy, and Lumen have recently launched Private Detector, a safety feature that uses AI to detect the sending of unsolicited pics, giving users the choice to either open and view this content, or avoid it altogether. |
| ClickDate | USA / 2017 | — | — | ClickDate offers smart matching technology to speed up the process of meeting someone new. It takes less than five minutes to create a ClickDate profile, and the learning algorithm identifies compatibility based on each new click and match. |
| Clover | Canada / 2014 | $11.3M | Jackson Investment Group, Social Starts | Clover is an on-demand dating app that automatically finds people who want to meet you with “algorithmic matching”. Clover’s unique chatroom called “Mixers” reminds the users of the 90’s chatroom. |
| Coffee Meets Bagel | USA / 2011 | $23.2M B | Atami Capital, Quest Venture Partners, Azure Capital Partners1 | Coffee Meets Bagel is an online dating site that connects individuals with a 'friend-of-a-friend' match every day. The company's matching algorithm runs on a deep neural network and uses a "blended" method. Nine models rate the matches, and the system goes through all and comes back with a converged score. Men receive up to 21 matches — or "bagels" — a day to decide on while women receive 4. |
| Desire | UK / 2015 | — | SeedRocket | Desire is an application platform that features AI-based love games for both long-term relationships and new couples. The app analyzes users’ thinking styles, decision-making processes, and behaviour to create intelligent game dynamics tailored to the partners’ desires to both rekindle cooling relationships and boost satisfaction for new couples. |
| DNA Romance | Canada / 2014 | — | Discovery Parks | DNA Romance is an online platform with a more sci-fi character that uses AI to match users with potential partners based on their genes. DNA Romance uses the science of genomics to revolutionize online dating by forecasting "chemistry" between single individuals online. DNA Romance is the first platform to matchmake people based on all three elements of human attraction: appearance, personality & "chemistry". |
| eHarmony | USA / 2000 | $113M B | Fayez Sarofim & Co., Tuputele Ventures, Sequoia Capital | eHarmony's matchmaking service now goes beyond the traditional compatibility into what it calls 'affinity', a process of generating behavioural data using machine learning (ML) models to ultimately offer more personalized recommendations to its users. eHarmony has used AI that analyses people’s chat and sends suggestions about how to make the next move. |
| Feeld | UK / 2014 | $551K Angel | Haatch | Feeld uses machine learning and advanced AI to meet like-minded people and explore sexuality, away from social pressure appealing to individuals and partners looking to join or have threesomes. The matches are done based on user preferences, location, and likes. |
| Fuse | Germany 2017 | — | — | On FUSE people discover more than just good looks. Listen to someone’s voice, picture their world, and get to know their essentials – even before they match. Fuse is currently entering its final beta testing phase, which will prepare the app for its official launch. |
| GoGaga | India / 2017 | $40K | FbStart | GoGaga is a trustworthy relationship app for women that connects users to friends of their friends, asking the mutual friend to introduce. The app has developed an AI-driven matchmaking system that relies on user profile information to find commonalities in work, education, interests, and lifestyle. |
| Grindr | USA / 2008 | $93M | Kunlun | Grindr is the world's largest social networking app for gay, bi, trans, and queer people. Grindr is using AI for automated decision making - for example, to detect and remove spammers, detect and remove non-compliant images. |
| Happn | France 2013 | $22M | Idinvest Partners, Raine Ventures, Tectonic Capital | Happn is a location-based mobile dating application that enables its users to build connections based on real-time interactions. Happn uses artificial intelligence to rank profiles and fuses AI to create perfect matches. |
| Hawaya | Egypt 2017 | — | — | Hawaya is the first Egyptian application for safe and conservative matchmaking through choosing the best scientific methods and assessments that have been made by relationship experts and Psychiatrists. Using AI and human intervention, Hawaya prioritizes nurturing a secure and moderated environment. Hawaya works through an artificial intelligence engine, based on account data, personal questions, and user-specific assessments, combining all of that data and determining compatibility with all other application users. Their AI engine learns preferences and improves the suggestions. Hawaya also focuses on the privacy and security of its members. |
| Hily | USA 2017 | — | — | Hily makes it easy to find singles for flirting and fun in your city, state, and country. Hily uses AI to analyze profiles and the swipes, using factors such as lifestyle, background, and interests to match people instead of using just geolocation or appearance. Hily works by employing matchmaking algorithms that are based on machine learning instead of the geographical location of a user. Hily ignores attractiveness levels and goes for better matches, identifying users with the same interests and a higher probability of matching, taking data from the depth of dialogue, mutual likes, photos sent, etc. The more person uses the application, the higher are the quality of his/her matches. |
| Hinge | USA / 2011 | $20.6M A | Shasta Ventures, CAA Ventures, Middleland Capital | Hinge is the dating app for people who want to get off dating apps. Hinge uses machine learning and the Gale-Shapley algorithm to send daily recommendations for people who it thinks would be interested in you as you are in them. The system acts based on user behavior by deploying AI and machine learning techniques to continuously optimize its algorithms that show users the highest-potential profiles. |
| Hornet | USA / 2011 | $8.5M A | Ventech China, 500 Startups | Hornet is the world’s gay social network with over 30 million diverse users, providing a community home base that is available anytime, anywhere. The world's premier gay social network is using an AI verification process to clamp down on catfishing. The app will examine user-activity to establish if the person is trustworthy and genuine. |
| IBJ | Japan / 2006 | — | Globis Capital Partners | IBJ supports marriage according to customer's lifestyle to solve the problem of the falling birthrate. The company adopted “Sota,” a small-sized desktop robot, which can communicate by gestures. It will be linked with the app for the marriage-hunting party service and engage in routine tasks, such as the reception, guidance, and explanation of matchmaking parties. In the future, AI is expected to conduct a broad range of tasks, including the arrangement of meetings and the explanation of contracts. |
| iris | USA / 2019 | To watch | — | Iris uses artificial intelligence to build an internal map, fine-tuned over time, of what each user finds attractive - AttractionDNA - at a biological level in order to make better matches. Additionally, Iris seeks to de-gamify dating with the machine learning process, in the long run, streamlines the experience by reducing worthless interactions. |
| Loveflutter | UK / 2013 | To watch | — | Loveflutter plans to use AI to analyze chats between its users to determine their compatibility and suggest when they should meet. Loveflutter already suggests places to go on a first date that are equidistant from both people's homes using information from Foursquare, an app that helps smartphone users find nearby restaurants, bars, and clubs. |
| Lovoo | Germany / 2011 | — | German Accelerator, Edition VC | Lovoo is a dating app & the fastest growing network to meet new people in the area. It developed an intelligent, continuously improving Anti-Spam program. The program automatically and semi-automatically recognizes spam, scam, and fake profiles and fights them with the power of machine learning. Aggressive spam profiles are normally identified and taken out of the picture within a few seconds by Lovoo. |
| Lumen | UK / 2018 | 4.8M Seed | Angel | The app offers its users a judgment-free environment for senior dating. Lumen combats scamming with AI software, and a "selfie" registration system that makes users take a photograph of themselves when they register and compares it to the profile photos they then upload to ensure they are genuine. Dating apps including Bumble, Badoo, Chappy, and Lumen have recently launched Private Detector, a safety feature that uses AI to detect the sending of unsolicited pics, giving users the choice to either open and view this content, or avoid it altogether. It’s proven to be 98% accurate making a dating app that’s safe for women and leads to less harassment. |
| Match | USA / 1995 | — | Canaan Partners, Recapex | Match Group is on a mission to spark meaningful connections for every single person worldwide. Founded 25-years ago, Match pioneered the concept of online dating and continues to foster innovation in the online dating industry daily. Match has accumulated a rich trove of personal data, which AI can analyze to predict how we choose partners. Match has an AI-enabled chatbot named “Lara” who guides people through the process of romance, offering suggestions based on up to 50 personal factors. |
| MatchMde | Singapore / 2018 | To watch | — | Matchmde is the next-generation online dating platform with an AI dating coach to help users connect by starting conversations and facilitating dates. It takes the sign-up process a step further by asking personality-based questions including a person’s love language, how they describe themselves, and how they view the world. |
| Meetic | France / 2001 | — | Idinvest Partners | Meetic is a French online dating service that uses AI for content moderation. Meetic has been working with Besedo to try and learn more about how artificial intelligence can help to keep its high-quality standards. |
| Mei (Crushh) | USA / 2016 | — | — | The Crushh and Mei Messaging App use AI to analyze texting relationships. The Mei app has been called “the anti-dating app” because it uses a wealth of data to go a step beyond dating and strengthen text relationships. The Crushh features within the Mei app analyze texting habits and deliver actionable insights to users around the world. |
| Muzmatch | UK / 2014 | $8.9M A | Luxor Capital Group, Starling Ventures, Y Combinator | Muzmatch is a faith-based dating app that introduced the obscenity filter (haram detector). Muzmatch used sophisticated machine learning, coupled with member feedback, and built an algorithm that could detect inappropriate content. |
| OkCupid | USA / 2003 | $6M A | Great Oaks Venture Capital | OkCupid is an online dating website that uses quizzes and multiple-choice questions to find a match for the user. OKCupid uses machine learning both to “connect people” and as a “community improvement tool”. When OkCupid users are not using their most effective photos, the app alerts its members. OkCupid claims to be the only dating app that works on an algorithm that does match-making based on thousands of questions. The data-driven sophisticated algorithm makes the most relevant matchmaking for users based on deeper things, like beliefs and interests, instead of just a photo and other parameters such as the location. Okcupid has a massive real-time data pipe built around Kafka that feeds its machine learning platform constantly. The company also uses data science to protect users from fake profiles or unwanted messages and to analyze the photos that are uploaded to the platform. |
| Once | Switzerland / 2014 | $9.2M Seed | Partech, SV Stars Venture Capital, Investiere | Once is a leading app for quality dating in Western Europe. It leverages AI algorithms to provide just one match per day to each user. Each pair has 24 hours of each other’s attention and can continue chatting if they “like” each other. The AI looks at the account’s info, dating preferences, and previous history in order to find the best possible match. Users can also rate each particular profile to let the AI better understand their taste. |
| Paktor | Singapore / 2013 | $52M | K2 Global, YJ Capital, PT Media Nusantara Citra | Paktor is a dating leader in Southeast Asia. Their AI sieves out potential matches for users by detecting what they prefer via swiping behavior. They use machine learning to check whether an image that is uploaded is of a real person or to detect nudity. |
| Plum | USA / 2018 | 200K Pre-Seed | — | Plum solves the three most common problems in the online/app dating space: profile misrepresentation, sexual harassment, & ghosting. The app, which is currently in its beta version, aims to incentivize men to behave appropriately by implementing a rating system based on three criteria: communication, follow-through, and profile authenticity. |
| S'More | USA / 2019 | $3.2M Seed | Benson Oak Ventures, SDVentures, Mark Pincus, Dating Group, Loud Capital, Boston Harbor Angels, others | S’More links people intellectually rather than superficially. Their AI confirms that your uploaded photos are: 1. Real and of you; 2. Are current; 3. Are not overly altered. The app also introduced a behavioral score to control for bad behavior and abusive content. Their algorithms learn your behavior and make match recommendations in part based on your behavior on the app and on what your profile details about yourself.
|
| Say Allo | US / 2017 | $1M A | — | Say Allo is the first dating discovery app that uses a continuous learning algorithm and compatibility index co-developed by a developer of Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT). The app uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to help offer singles more compatible matches. |
| SCRUFF | USA / 2010 | — | — | SCRUFF is the top-rated, social app for more than 15 million gay, bi and trans, and queer men worldwide. SCRUFF Match uses machine learning to suggest a stack of guys you are most likely to match with - the more you use SCRUFF Match, the smarter it gets. |
| Shaadi.com | India / 1996 | $8M | InnoVen Capital, Sequoia Capital India | Shaadi.com is an online matrimonial website based in South Asia, enabling users to find suitable partners. Shaadi.com adopted AI and ML. Through object and scene detection, facial analysis, face comparison and facial recognition, the matrimony site is now able to quickly and affordably automate a highly complex process. |
| SKOUT | USA / 2007 | $22M | Andreessen Horowitz | SKOUT is a mobile network and community platform for connecting with new people that leverages ML and human moderation to proactively find, block, and remove the majority of the abusive content. |
| SLIDE | South Korea / 2020 | — | — | ‘SLIDE' is a video-first dating and social discovery app. Through video-based profiles, AI-driven matching tools, and a real-time video “Vibe Check” feature. SLIDE enables users to effectively find, match and ‘test the waters’ with others in a transparent, efficient, and fun way. The first-of-its-kind “SLIDE AI” feature — which allows users to select several profiles to analyze and generate their ideal match, and then customizes matches based on that ideal — is built on Hyperconnect’s world-class artificial intelligence technology. |
| Tantan | China / 2014 | $107M D | JOYY, Genesis Capital, Bertelsmann Asia Investments | Tantan is a Chinese mobile social dating platform designed to find and interact with new people. Tantan is using AI to ensure that the platform has verified photos. Also, the technology will be used to help the company accurately identify new users, increase the accuracy of advertising and contribute to growth in terms of numbers of users and revenues. Additionally, AI prongs users to swipe more and ensure that they see pictures more suitable to their tastes. |
| Tastebuds | UK / 2010 | $600K | Techstars, Springboard, Black Ocean | Tastebuds is an innovative social discovery platform that lets you meet like-minded people who share your love for music. It was founded by two musicians and was launched in June 2010. The site integrates directly with Last.fm to pull in users listening profiles as well as using songkick.com for upcoming events. |
| The League | USA / 2014 | $2.3M Seed | Structure Capital, Ridge Ventures, Third Wave Digital | The League is a dating application that enables users to find and socialize with similar individuals. The League has an acceptance algorithm that then scans social networks (LinkedIn and Facebook) to ensure applicants are in the right age group and are career-oriented. Once accepted, users can then browse through a handful of matches that are offered to the user. New batches of matches are supplied to users during “happy hour” every day at 5 pm. The app uses an algorithm to ensure that users aren’t shown current coworkers or people within their primary network to avoid awkward interactions. |
| Tinder | USA / 2012 | $50M | Benchmark, IAC | Tinder anonymously finds people nearby that like each other and connects them if they are both interested. Since the beginning of 2020, Tinder has leveraged AI to battle unwanted content. Additionally, Tinder integrated with a personal safety app Noonlight, which connects users to personal emergency services. Finally, Tinder offers photo verification, which compares real-time to profile photos to verify match's authenticity. |
| TrulyMadly | India / 2013 | $6.8M | Helion Venture Partners, The Chennai Angels, Inflection Point Ventures | TrulyMadly is a new, modern way to find true, mad love. A platform that brings singles together based on common interests and psychological matching. The company’s algorithm checks that you are single and active on social networks, and your score thus increases. TrulyMadly says it uses proprietary software, called the Compatibility Assessment Tool, to match potential partners. It also conducts verification checks and claims to have a stringent approval process for users. |
| Yidui | China / 2015 | $11.4M B | Xiaomi, Sky9 Capital, BlueRun Ventures | Yidui provides an innovative dating experience, where the date is moderated by a third person—a “matchmaker”—who facilitates the conversation. The date is live-streamed and the audience can comment, live chat with the matchmaker, and even compete for the attention of the dating participants with virtual gifts. Big data algorithms allow the Yidui app to accurately discover potential daters that meet the basic requirements of each user from tens of millions of other users and recommends them to each other. |
| Zoosk | USA / 2007 | $61.6M E | Bessemer Venture Partners, Canaan Partners, Crossroads Capital | Zoosk is the #1 dating App, offering a truly personalized dating experience through its Behavioural Matchmaking™ technology.
Zoosk has a unique dating algorithm called SmartPick that sends daily matches using behavioral matchmaking based on your preferences and compatibility. Zoosk’s unique Behavioural Matchmaking™ technology is constantly learning from the actions of over 27 million active members in order to deliver better matches in real-time. |
| Zotality | USA / 2010 | — | — | Zotality employs proprietary AI to merge NASA's planetary data with insights of astrologers (with a postgrad or PhD in predictive karmic astrology - "Jyotish") for compatibility matching and as a preventive protocol to manage relationships and life. |
M&A Activity and Key Players in Online Dating with Artificial Intelligence
The Online Dating industry is fairly consolidated with a few industry groups owning multiple dating services, some acquired and some launched internally. The industry is dominated by Match Group, The Meet Group (now part of NuCom Group), Bumble, and Spark Networks. Take a look at the infographic below to see who owns who in this industry:
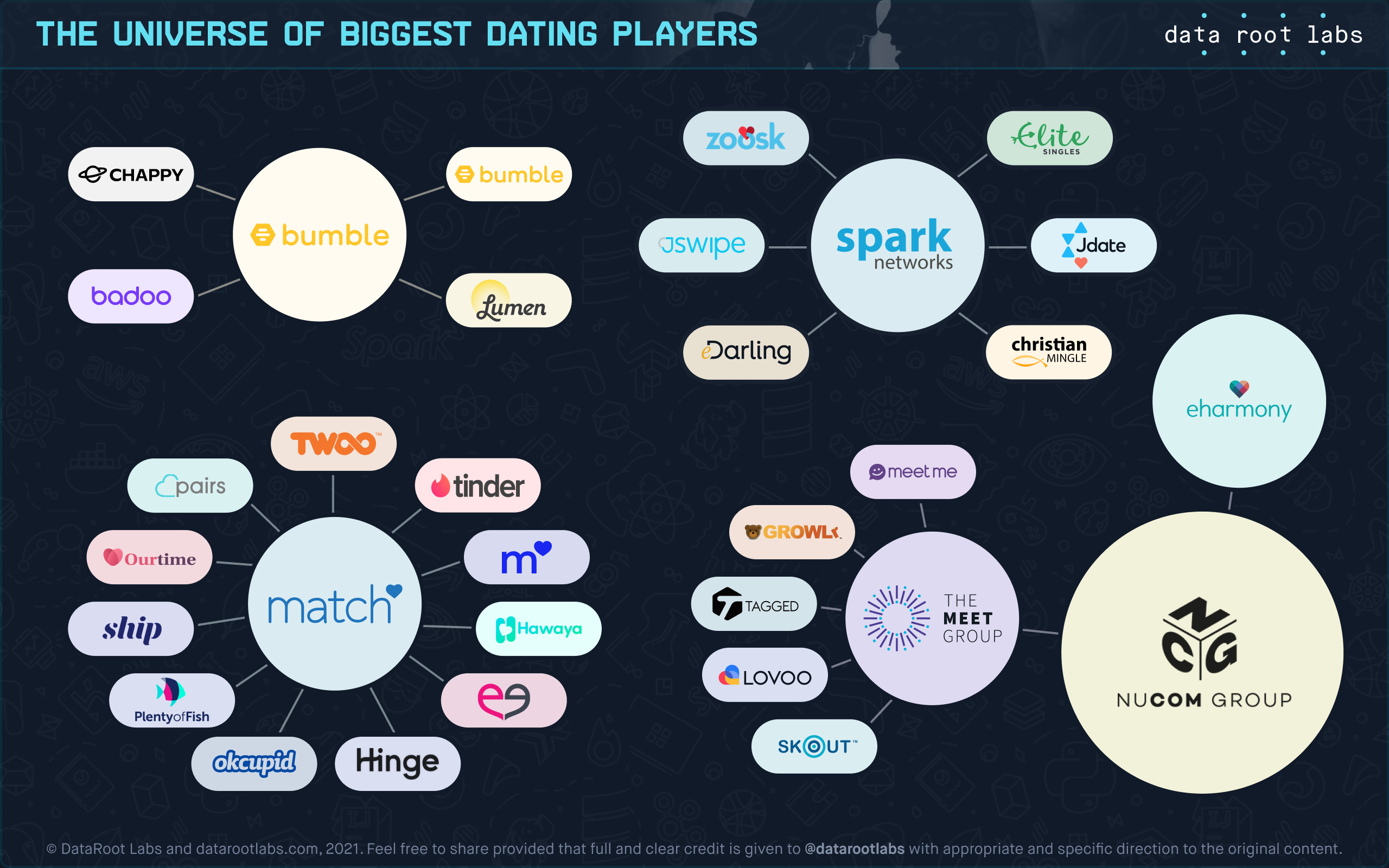
M&A Activity and Key Players in Online Dating with Artificial Intelligence
For the past year, the Online Dating industry has not seen many deals but the ones that happened were significant:
2021 has started with the acquisition of a Swiss slow dating app Once by the Dating Group, one of the largest companies in the dating, for $18M. Once leveraged AI to deliver one match per day.
In September 2020, The Meet Group, Inc., a publicly-traded co-announced closing of acquisition by eHarmony parent company Parship Group estimated at $500M. The Meet Group’s dating apps MeetMe, LOVOO, Tagged, Skout, and GROWLr, now join Parship Group’s brands eHarmony, Parship, and ElitePartner.
Chinese gaming company Beijing Kunlun Tech Co has finally agreed to sell Grindr, a gay dating app, back to the US player. The US has ordered Kunlun to divest Grindr amid concerns regarding the safety of the personal data it handles, such as users’ private messages and HIV status. As a result, Grindr was sold to a little known San Vicente Acquisition for $640M.
Outlook and Remaining Challenges
Most AI-based dating apps already use AI in one or another capacity. Yet, it can and will do more to battle the outstanding challenges of modern dating.
Enjoyable online dating experience still remains a challenge where many users report being overwhelmed by unwanted attention and unsolicited content. Although many machine learning dating apps start taking user's safety more seriously, the lack of it still remains one of the biggest downsides of using online dating sites. Additionally, concerns about user data and privacy feel as poignant as ever and can go up to the national security level as we have witnessed with Grindr's acquisition.
Finally, we are witnessing a rising number of people who substitute real human interaction for technology, a phenomenon called "hikikomori" in Japanese. Will real and virtual robots replace our partners? Completely or partially? I will leave it up to you to decide whether it is a sad and concerning trend or an inevitable part of technological progress with the potential to save millions from our increasingly individualistic and lonely society.
One thing is clear - AI does not substitute "us" in the online dating world as people still remain final decision-makers. Tech does not have to replace real-life soulmate searching. It can, however, aid us in this journey and provide a convenient alternative.
Want to suggest a dating app startup to include in this research? Please, contact me at ys {at} datarootlabs.com
Have an idea? Let's discuss!

Talk to Yuliya. She will make sure that all is covered. Don't waste time on googling - get all answers from relevant expert in under one hour.


