The Future of Waste: AI Solutions for a Cleaner Planet
How AI is Revolutionizing Waste Management Systems Worldwide.

Waste is a growing global concern, as urbanization, consumerism, and population growth are putting tremendous pressure on waste management infrastructures. Waste management disposal has historically been poorly managed, wastefully collected, and expensive. Now, AI is helping to reinvent the waste sector by providing smarter, faster, and more sustainable solutions. From automation and predictive analytics to smarter recycling processes, AI is changing how we manage waste, ensuring a cleaner and more efficient planet.
AI in Waste Management and Recycling Market Size was valued at $3.5B in 2023 and is predicted to reach $15.9B by 2031 at a 20.8% CAGR during 2024-2031.
In this article, we explore what waste management is and the seven ways in which AI is (already) proving value in it.
What is Waste Management, and what are the 5R Concepts of it?
Wikipedia describes Waste Management as a collection of processes and actions required to manage waste from its inception to its final disposal. This includes the collection, transportation, treatment, and disposal of waste, as well as the monitoring and regulation of the waste management process and waste-related laws, technologies, and economic mechanisms.
The 5Rs of waste management form a solid framework for individuals, communities, and organizations, which are: Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, Repurpose, and Recycle.
- Refusing is about saying no to items that can contribute to the waste stream. This step is crucial as it can significantly decrease the amount of waste generated. (e.g., opting not to take a plastic bag from a grocery store);
- Reducing is about minimizing the waste we generate by opting for products that have less packaging or are more durable. (e.g., buying products in bulk to reduce packaging waste);
- Reusing items is a straightforward step toward managing dry waste. It extends the life of items and prevents them from ending up in landfills prematurely. (e.g., using glass containers to store leftovers instead of single-use plastic bags);
- Repurposing, or finding new uses for old items, not only saves money but also diverts waste from landfills. (e.g., using an old t-shirt as a cleaning rag);
- Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new products. This can significantly reduce the need for virgin resources. (e.g., recycling paper to produce cardboard).
Why are the 5Rs Important?
The 5Rs represent a roadmap to a more sustainable lifestyle. They encourage us to think more carefully about the resources we use, the waste we generate, and the impact we leave on the environment. Following the 5Rs can help reduce pollution, conserve natural resources, and create a healthier planet for future generations.
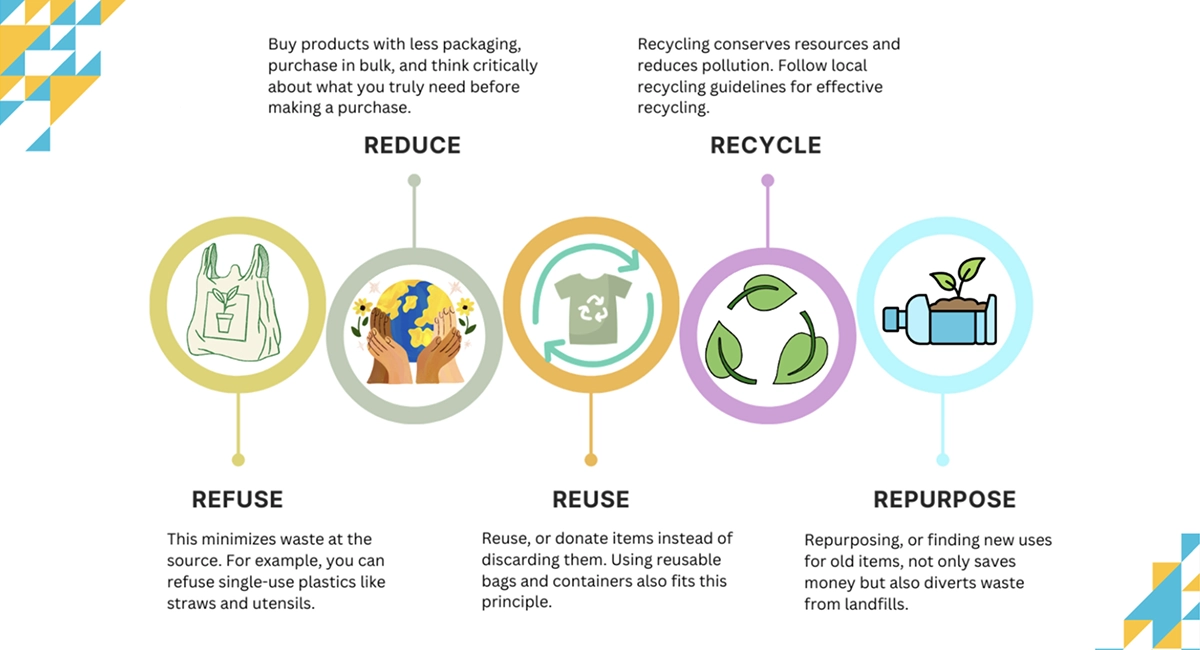
5R Concepts in Waste Management
Key Areas of AI Impact on Waste Management
Based on publicly available information from sources such as Crunchbase, Pitchbook, and other open datasets, we have compiled a list of companies and startups actively developing AI-powered technologies for waste management. These organizations are shaping the future of sustainability by delivering cutting-edge solutions across key segments such as waste sorting, smart collection, predictive analytics, and landfill optimization. Together, they represent the forefront of innovation in the 2025 Waste Management Technology Landscape.

AI in waste Management Innovation Landscape
Let's look at each category one by one.
Automated Waste Sorting
AI-enabled sorting systems are transforming the way recycling centers function. Rather than relying on the work of humans, AI-powered sorting systems use advanced computer vision, robotics, and machine learning technologies to accurately identify and separate recyclables from mixed waste streams with efficacy and efficiency. AI systems can sort, clean recyclables, and ensure far more accuracy than humans, which should help ensure recyclables are not contaminated and should help improve recycling rates and ultimately keep more waste out of landfills. In addition, advanced sorting technologies such as hyperspectral imaging and neural networks enable machines to identify and separate types of plastics, metals, glass, and organic waste in milliseconds.
Glacier (formerly EndWaste) creates compact, AI-based robotic solutions for automated waste sorting in recycling plants. Their technology combines conveyor robotics with computer vision using thousands of real-world images to detect and separate recyclable materials (plastics, metals, paper). The truth is that while their technology will increase accuracy over time, it is intended to reduce overall cost, sustaining small and decentralized material recovery facilities (MRFs) and keeping recycling as an economic option for municipalities.
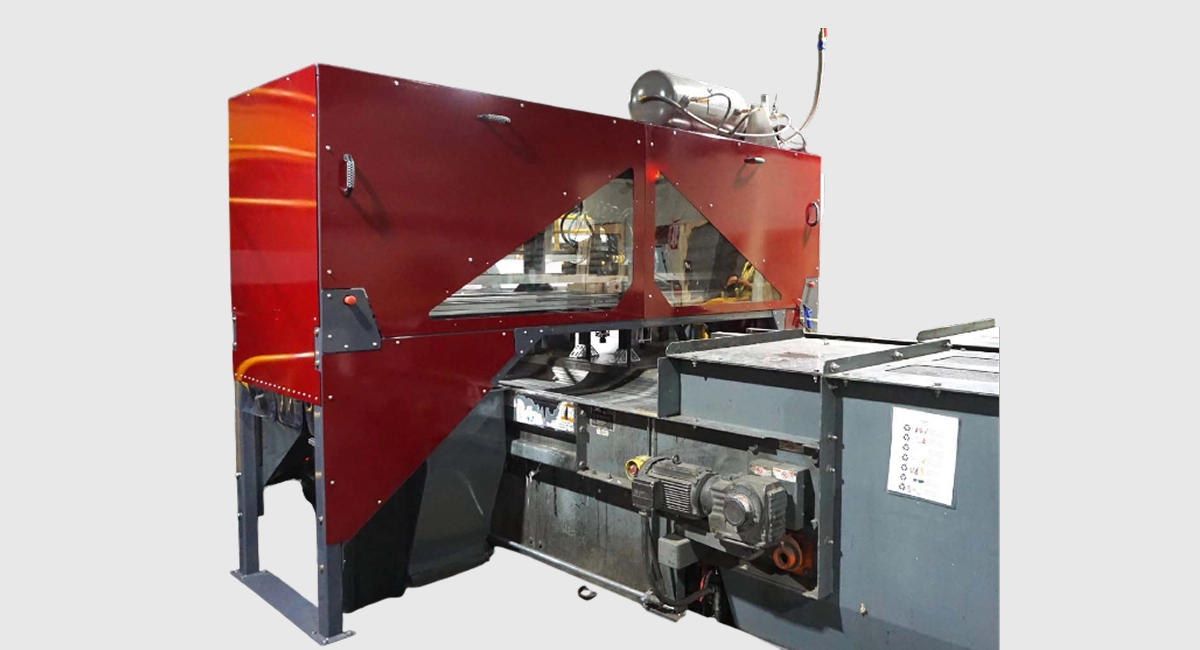

Glacier Robot Installed on a conveyor
Jaipur Robotics creates AI-powered automation systems for waste-to-energy (WtE) and recycling plants, aimed at better sorting and handling of complex waste streams. Their core solution makes use of computer vision, machine learning, and intelligent crane guidance to perform a real-time waste analysis to find hazardous, oversized, or low-calorific materials that will have a negative effect on plant operations. Jaipur Robotics can optimize waste feedstock quality and automate sorting to improve operational safety, efficiency, and energy output for high-processing plants treating waste.
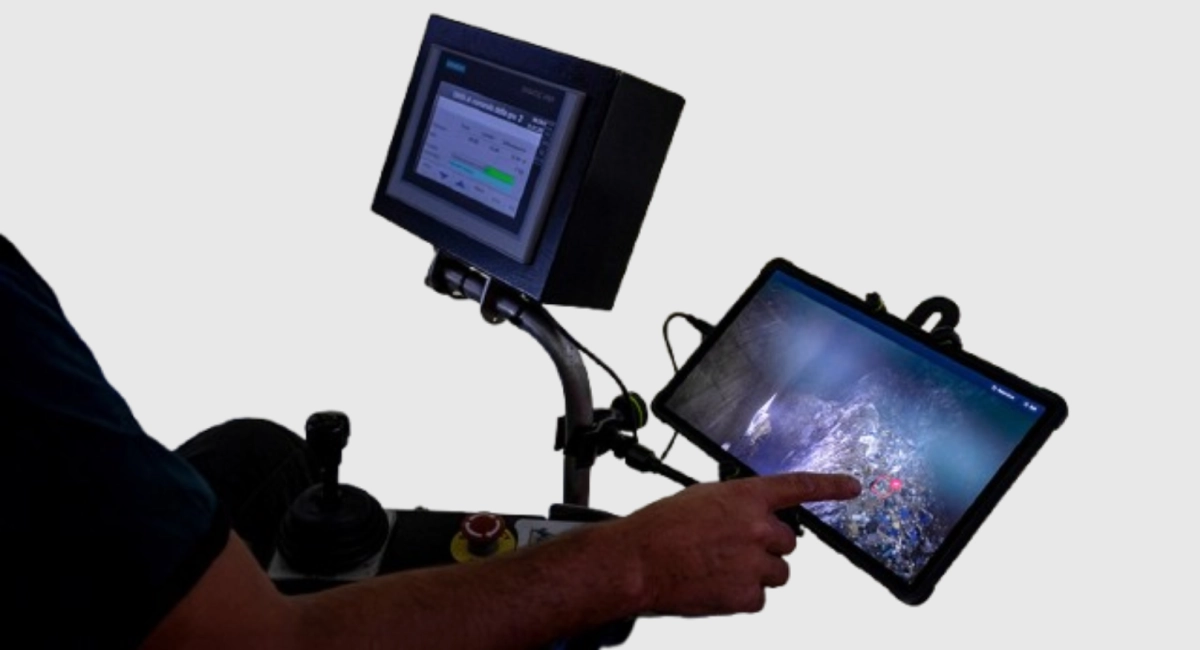

Jaipur Robotics’ AI detects plastic-heavy zones and critical bags in real time - before they reach the hopper
AMP uses advanced AI and computer vision to automate and optimize the processing of recycling and municipal solid waste. The company provides municipalities and waste companies with AI-powered sortation services and automation at scale and operates these systems to achieve best-in-class cost for performance, increase diversion, and meaningfully extend the life of landfills.
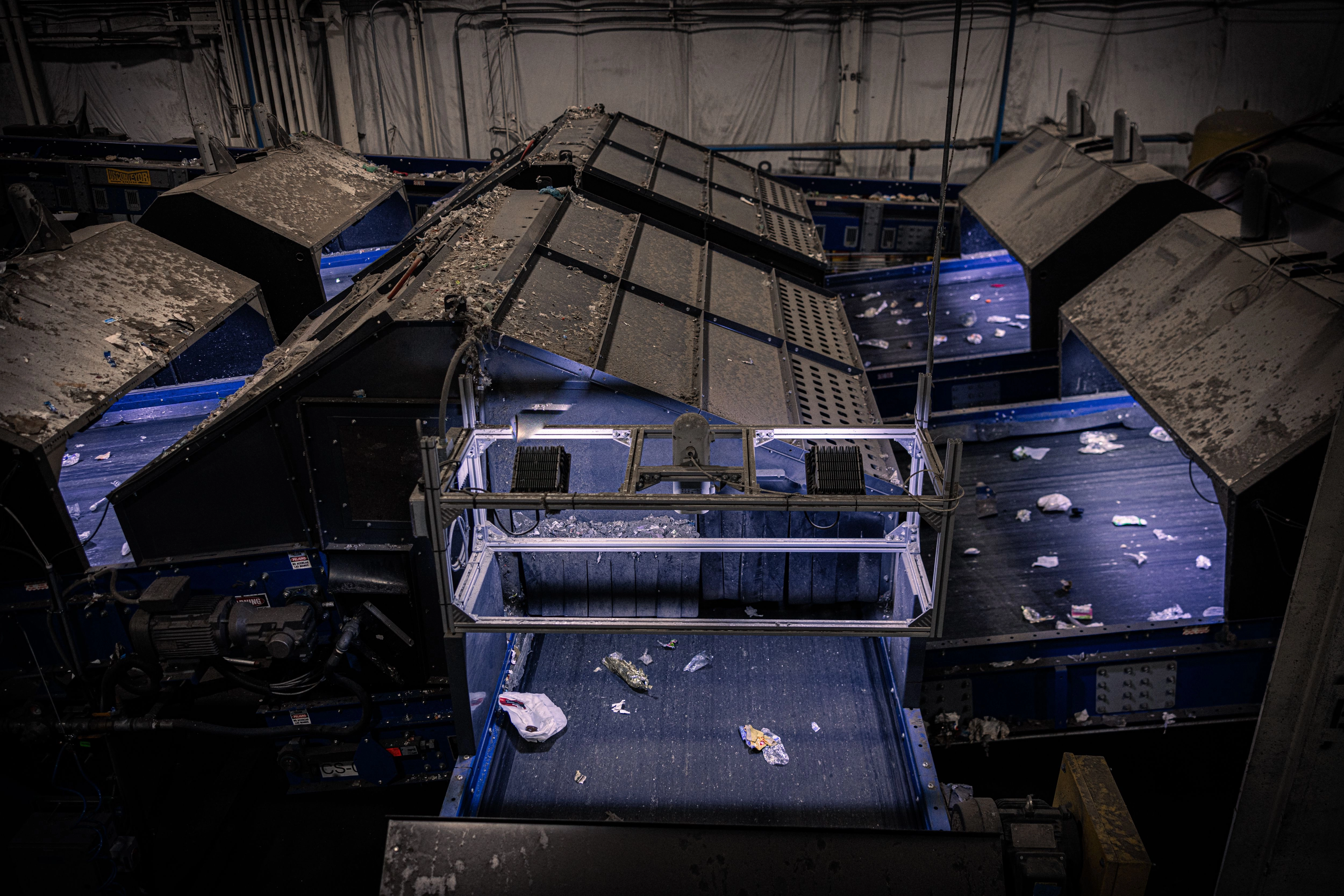

AMP ONE™ sorting system
Waste Robotics develops AI-powered robotic systems for optimized sorting in recycling facilities. Their technology integrates deep learning, computer vision, and robotic picking arms to detect, classify, and separate complex waste materials, helping recyclers reduce manual labor and increase processing efficiency.
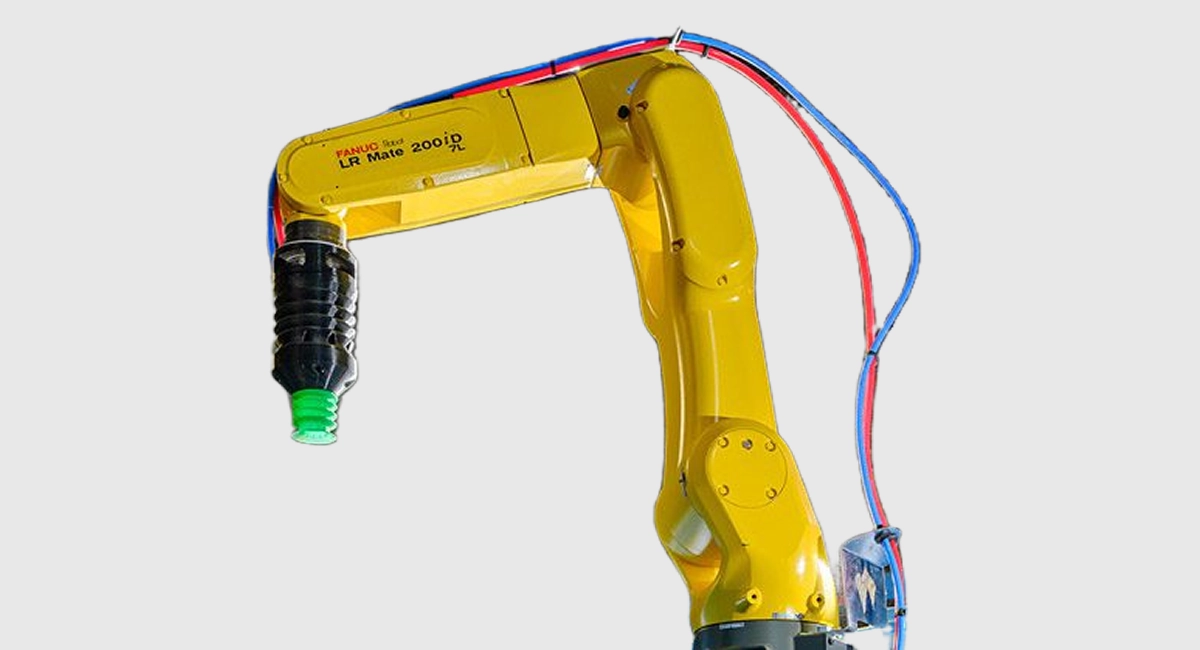

Waste Robotics VentuR Cup for sorting
Smart Collection Systems
For centuries, waste collection has been based on predetermined schedules that do not consider when, how, or where people produce waste. As a result, trash collection wastes fuel by stopping at half-empty bins or missing overstuffed bins. This is changing! AI and IoT sensors are revolutionizing the waste collection industry. Smart collection systems use data analysis and real-time data derived from bin-level fill data, traffic conditions, and waste generation to develop optimized collection routes and schedules. Factoring in elements beyond pre-scheduled trash collections can lower fuel consumption, cut emissions, and reduce operational costs, while improving service quality. Cities around the world are implementing these intelligent systems for more sustainable, responsive urban waste management practices.
Waste Solutions uses smart sensor technology to monitor waste bins and containers in real-time to know when they are full. Their sensors use wireless communications and can link to a whole range of analytics platforms, or simply notify the waste contractor when pickup should be scheduled. In this way, Waste Solutions helps its customers rip off the furnace, resulting in reduced unnecessary rubbish pick-ups and reduced carbon emissions. With publicly-owned bins, Waste Solutions even provides the full data reporting capabilities so that local government or corporations can plan operations optimally in a data-driven manner.
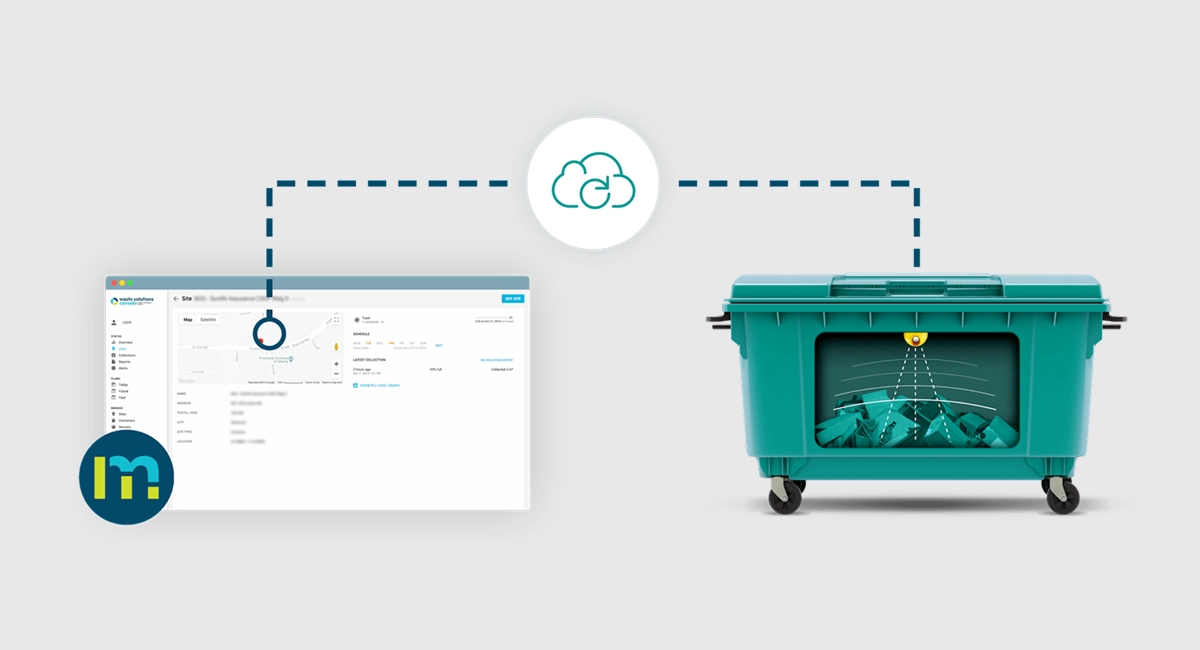
Waste Solution sensors can turn any container into a smart device, revolutionizing the way that we manage waste
RoadRunner & Waste Metering™ technology enables customers to understand their waste generation habits at a container level at multiple sites. It does this with an AI solution that can determine the volume, type, and timing of wastes and recycling streams. This allows businesses to ensure their collection schedules and diversion rates are operating at optimal levels. The platform also offers machine learning capabilities that drive smarter logistics and sustainability reporting.
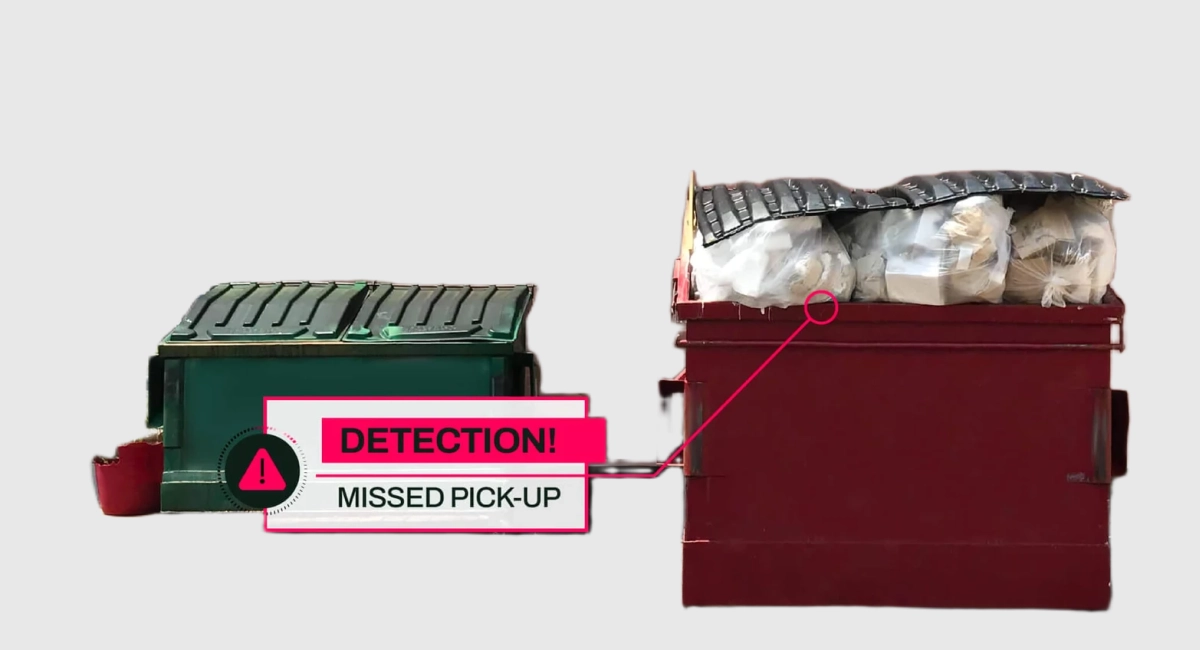
Waste Metering™ technology proactively flags when a hauler misses a scheduled pick-up
Angsa Robotics develops autonomous outdoor robots with AI and computer vision that allow them to find and collect litter from grass, gravel, and, quite simply, unstructured landscapes. Their mobile robots use deep learning built from an AI model to differentiate small or partially hidden waste items, making them ideally suited for use in parks, campuses, or event venues. The system significantly decreases labor intensity while also improving precision in the management of waste within public spaces.
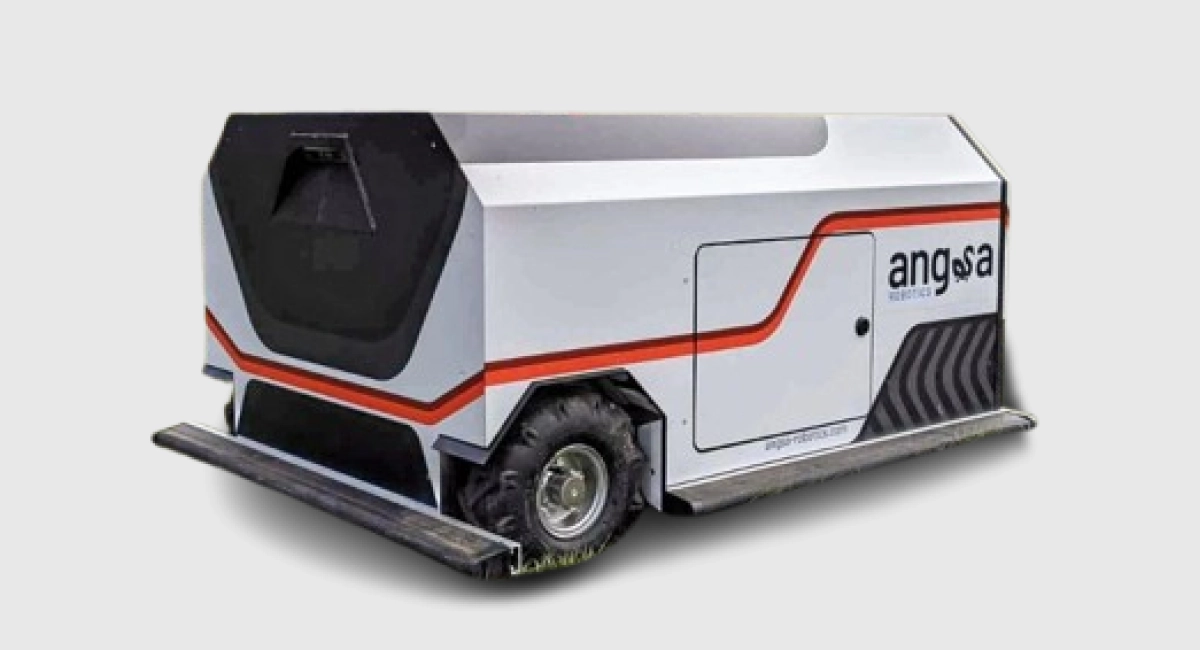

The autonomous robot by Angsa Robotics specializes in collecting small pieces of trash
Predictive Analytics
With AI-driven predictive analytics, municipalities and waste management firms can project waste generation trends with an astonishing degree of accuracy. AI is able to cross-examine historical data against weather and seasonal patterns, demographic changes, and local special events to predict changes in waste volume. As a result, planning purposes can be improved, there can be a reduction in unpleasant operational surprises, and infrastructure upgrades can be designed with a lead in front of a demand spike. Predictive models turn what are largely reactive models into proactive waste management models.
WasteHero offers a full platform for waste management powered by AI that uses predictive analytics to optimize collection schedules and fleet routing. WasteHero predicts the waste generated by evaluating historical data, weather forecasts, smart sensors, and public holidays to promote the most efficient way of working for municipalities and private haulers.
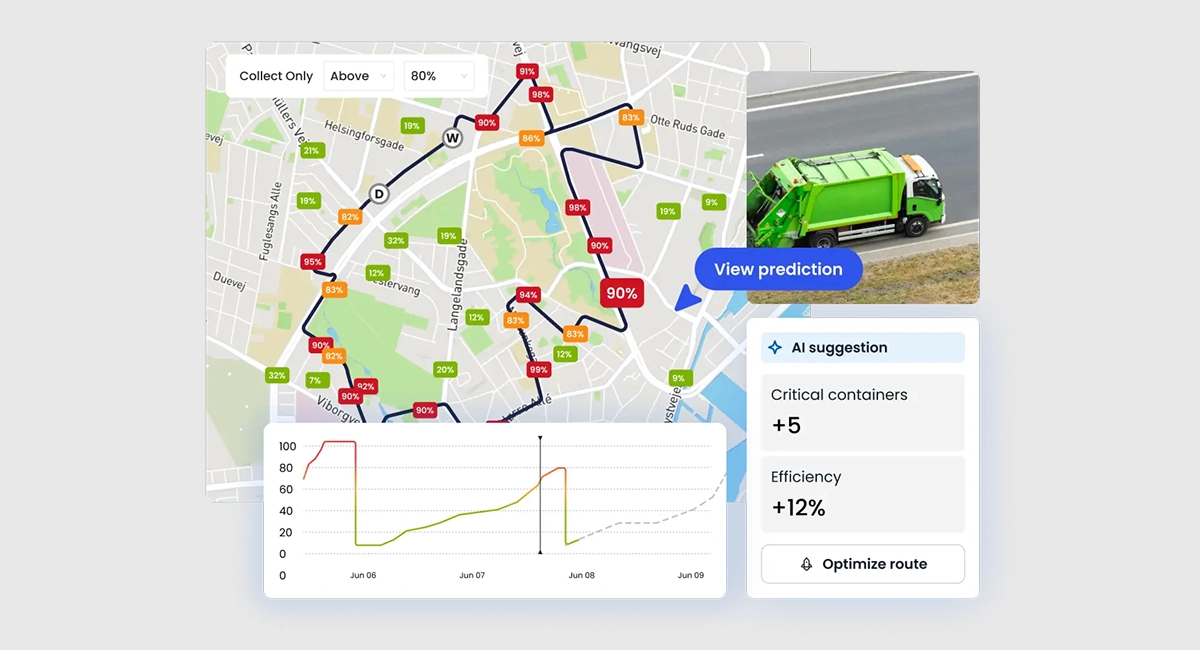
Smart Waste Management with RouteAI™ by WasteHero
WasteDigital utilizes AI to provide real-time monitoring and forecasting in municipal and industrial waste collection. Their platform combines actual container sensor data and analysis of historical usage to help municipalities and private haulers understand fill levels, forecast performance, and implement dynamic collection plans, reducing unnecessary mileage and vehicle levels.
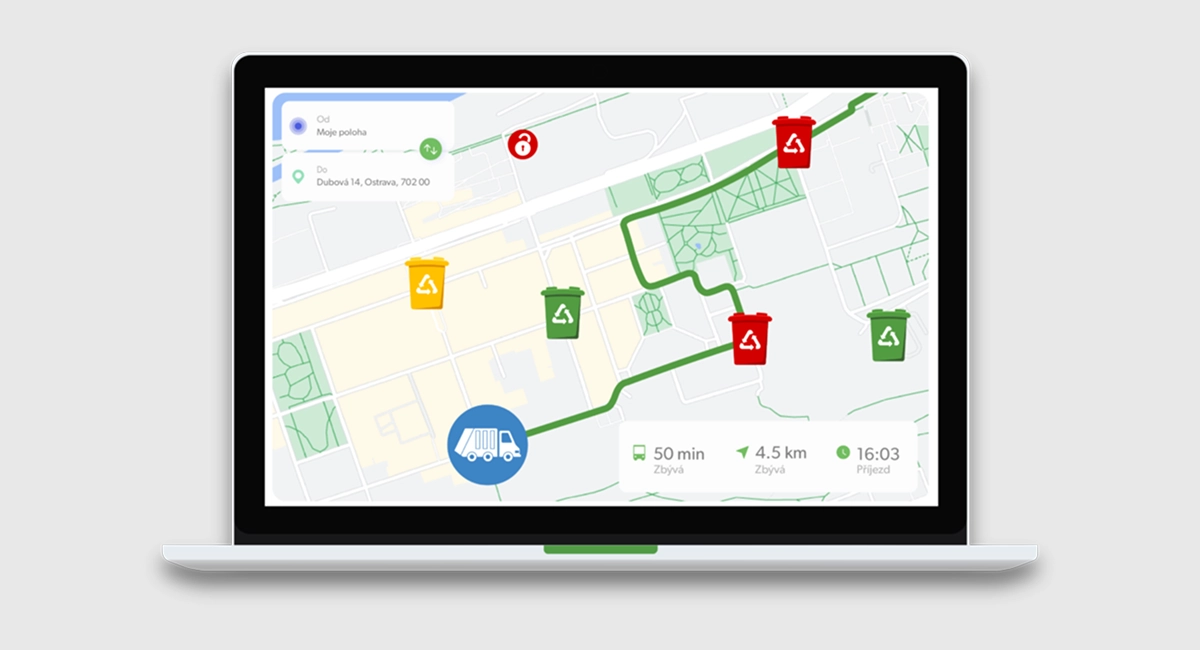
Smart Planning with WasteDigital
RTS (Recycle Track Systems) is a provider of waste and recycling management services intended to maintain environmental transparency and performance standards. At the center is Pello – their AI-powered sensor technology that uses machine learning and real-time data to monitor container levels, improve service reliability, and reduce contamination. With Pello, RTS predicts service needs, identifies inefficiencies, and recommends process improvements, turning waste data into actionable strategies.
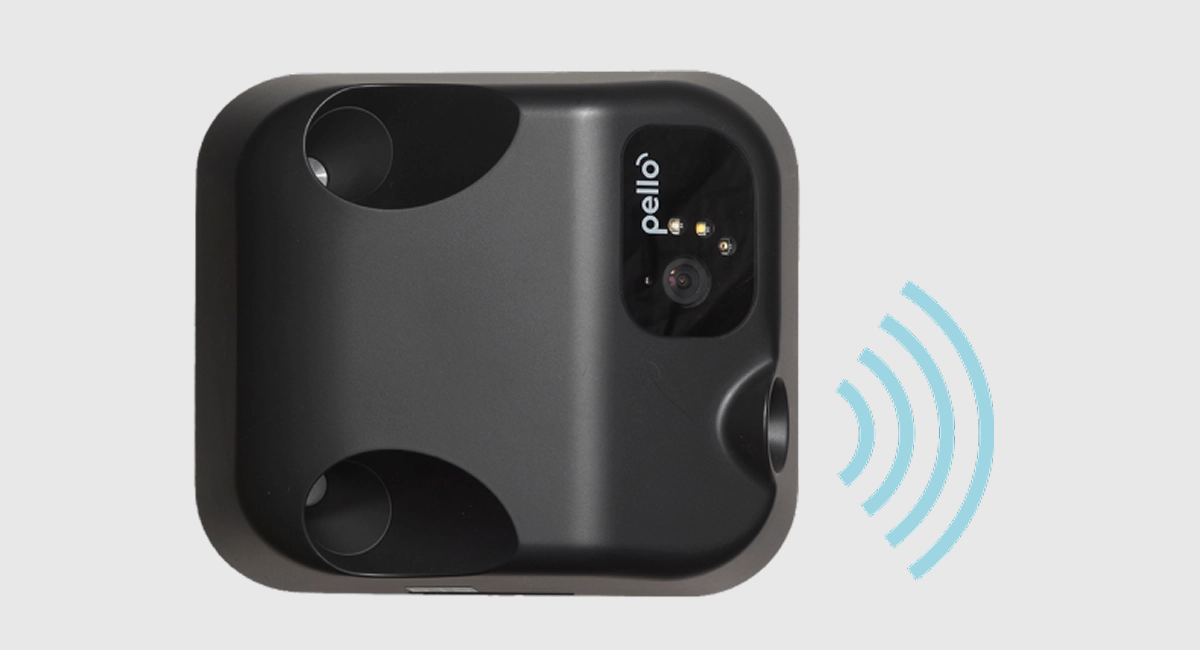

Pello – a Smart Sensor by RTS
Optimized Recycling Processes
Recycling centers have challenges associated with multi-layered and contaminated waste streams. AI improves a recycling facility's processes through automation and precision. Machine learning models use depth information to set the ideal conveyor speed, control the robotic arm for material extraction, and perform image recognition to enhance quality assurance inspections. AI can identify valuable recyclables that would others be impossible and create sorting automation to maximize speed and minimize waste, thus improving the profitability and sustainability of the recycling operations.
Superbin combines AI, robotics, and image recognition to streamline recycling for consumers and facilities. Their "Nephron" smart reverse vending machine uses machine learning to identify, sort, and track recyclable materials, incentivizing recycling behavior while enabling cleaner, more efficient material recovery.
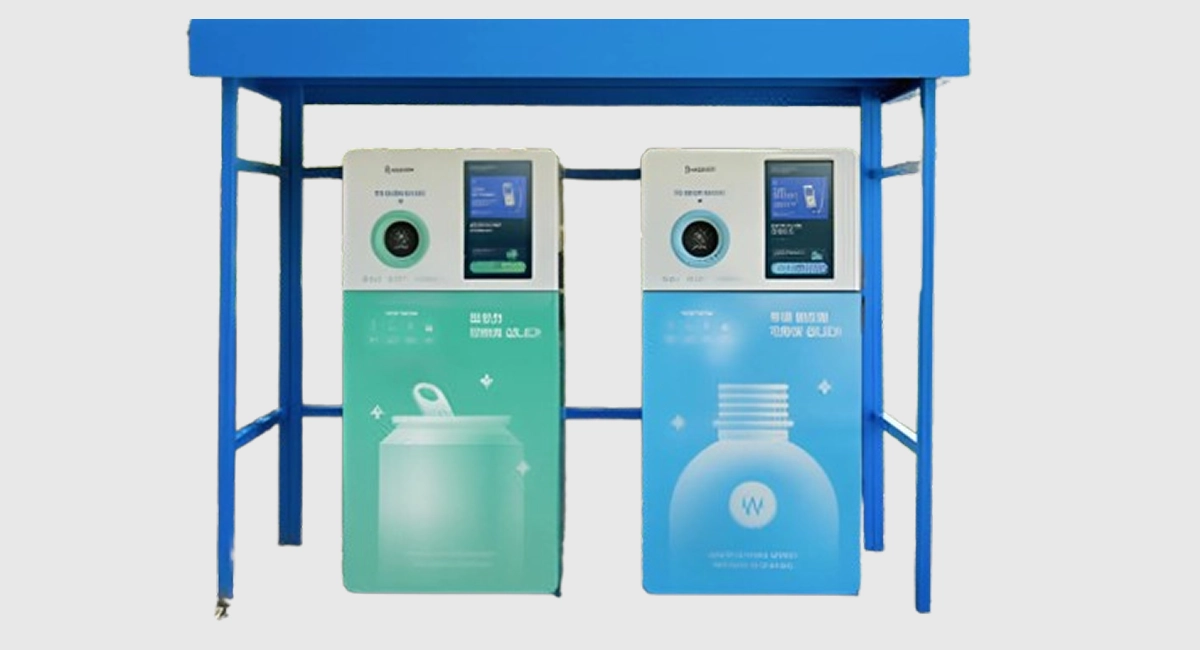

Superbin AI recycling robot Nephron
Sorted creates AI-powered software to help recycling businesses optimize their operations using real-time data-driven insights, workflow automation, and quality control. The sorting platform utilizes machine learning to analyze the information we collect related to the sorting process and enhances material recovery rates, as well as recycling performance, while speeding up compliance with recycling standards.
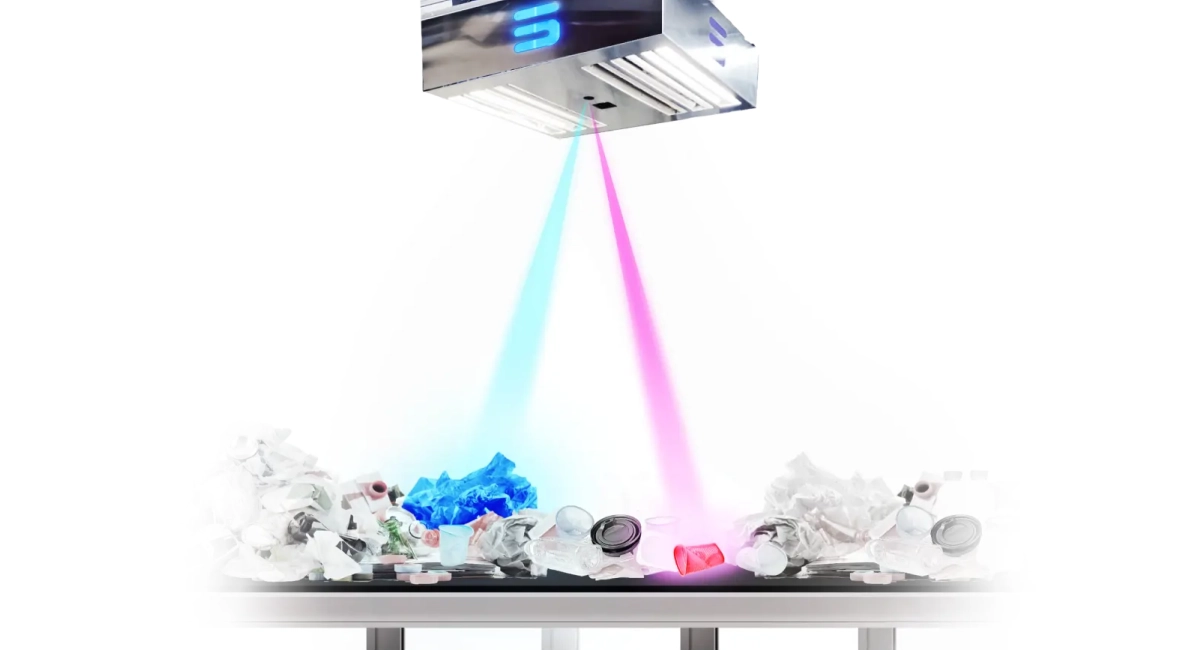

Sorted systems are placed above conveyor belts, utilizing advanced camera technology powered by AI to continuously monitor the materials
EverestLabs incorporates both AI and computer vision into recycling facilities for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Using past and current 24/7 data from robotic sorters and the robotics equipment, their Robotic Operations Center monitors machinery and tools to facilitate and identify contamination and mechanical opportunities early enough to allow facilities to decrease downtime, increase the lifespan of machines and tools, and improve operational effectiveness.
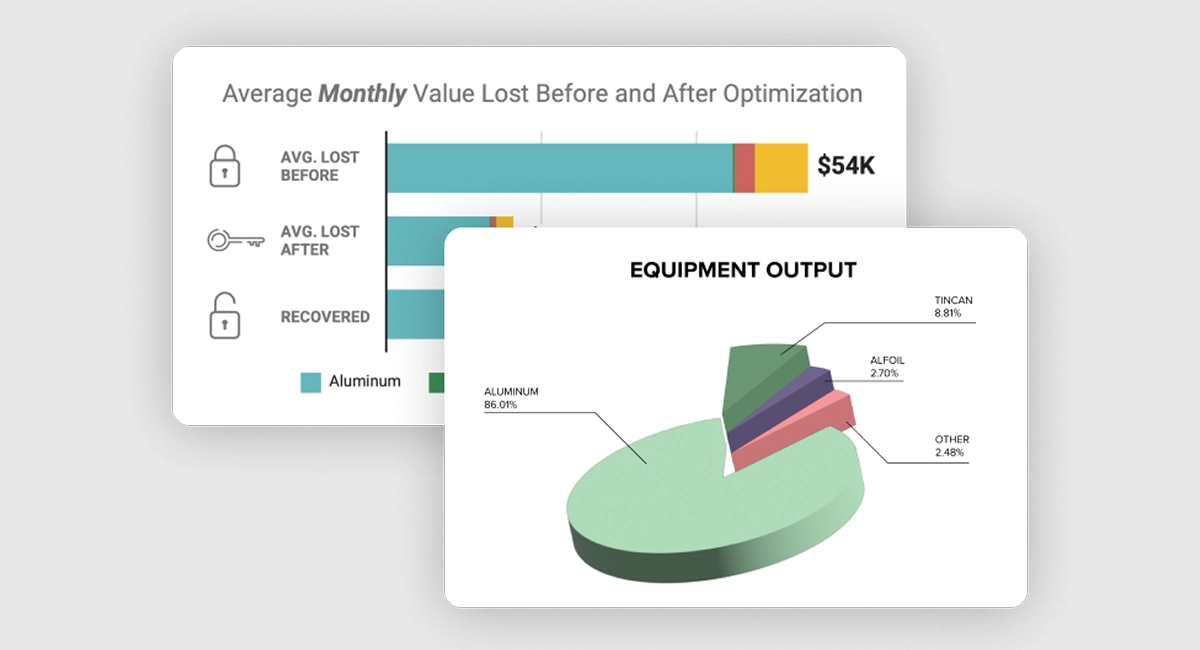
MRF equipment optimization with EverestLabs
Waste Monitoring and Analysis
Intelligent bins with AI-enhanced sensors monitor fill levels and waste type in real-time, sending all findings to a centralized location to track trash levels while improving collection schedules and identifying potential overflow incidents. AI also looks for trends in waste composition, allowing organizations and governments to develop better recycling programs or waste reduction programs that better target the citizens. Full analytics also allows for policies to be more directive regarding the environment, or to develop community awareness campaigns targeting specific waste issues.
Sensorita uses AI-enabled IoT sensors to digitize & monitor waste containers in real-time. Their platform services clients with digitally enabled waste containers or digital twins that capture the day-to-day activities and operational reality of waste containers; this allows waste operators to analyze and track reporting on the use of containers, forecast end-of-life collections and optimize logistics. These operational improvements will allow organizations to reduce emissions, costs, and offer real waste efficiency in service.
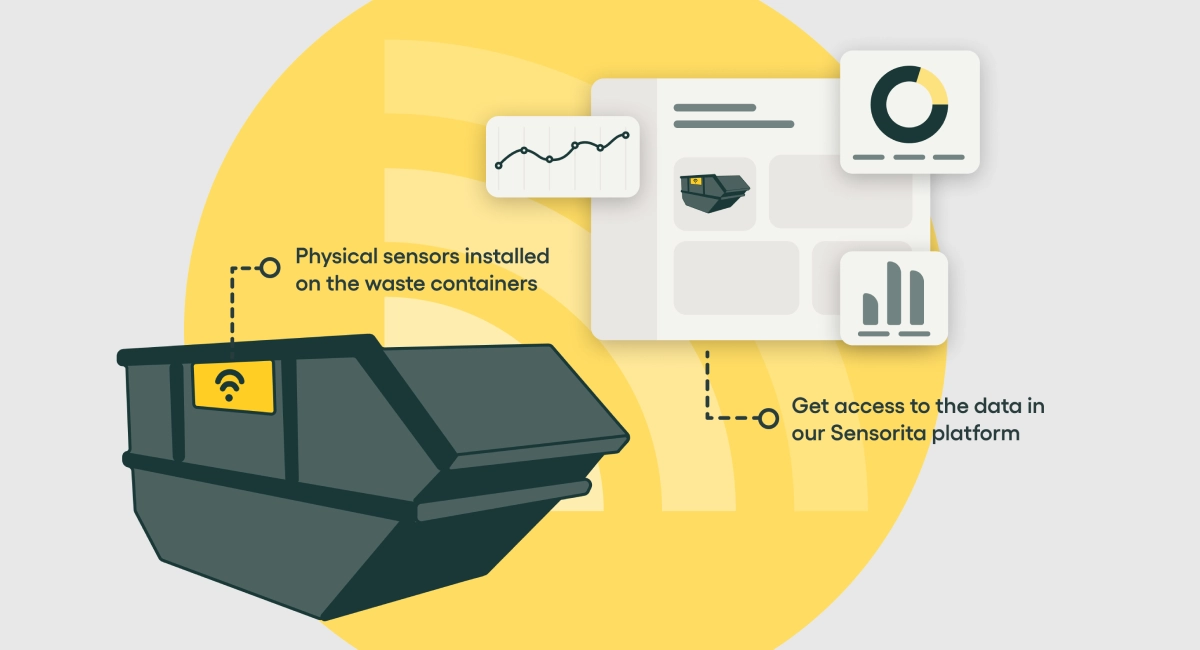
Sensorita has developed a new sensor technology that enables the measurement of fill levels in open waste containers
Greyparrot offers an AI and computer vision-based automated waste composition analysis service at recycling facilities. Their service analyzes waste streams over conveyor belts in real time, providing granular and comprehensive reporting on the types of materials, contamination, and volumes in their quantified development stage within recycling centers. Their service empowers recycling facilities to capture better waste data that will improve recycling targets and regulatory compliance in sourcing better feedstock with increased levels of accuracy, reliability and validity.
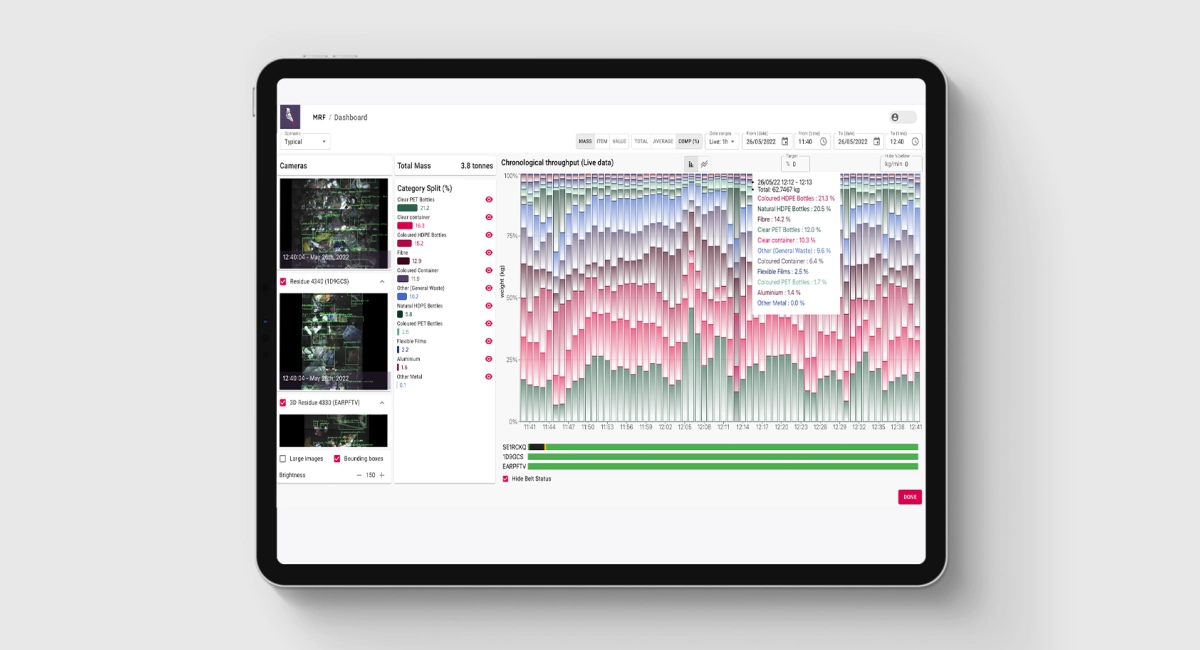
Greyparrot Analyzer dashboard
WWWASTE uses AI and machine learning algorithms to extract and analyze data from waste collection trends to provide tangible insights for more sustainable waste logistics. WWASTE can forecast fill levels of containers, predict service levels, provide improved routing solutions, and enable cities and businesses to reduce operational costs while decreasing emissions and reducing service frequency with excellent service levels.
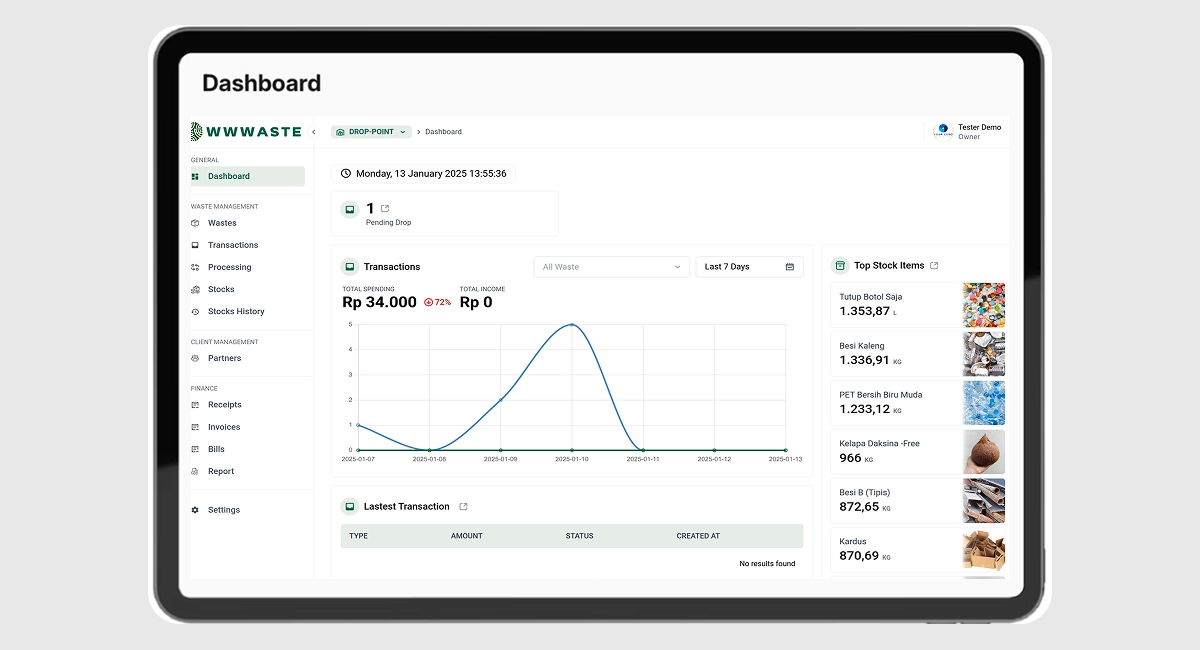
WWWASTE Dashboard
Predictive Maintenance of Recycling Machinery
Operational downtime in recycling facilities is expensive and disruptive. AI analyzes data from machine sensors to predict when a piece of machinery is likely to break down or need maintenance. By picking up subtle indicators of wear and tear, AI systems can instigate preventative repairs that minimize downtime, enhance asset development, and ensure uninterrupted operations for as long as possible. Predictive maintenance can also provide a safer workplace by eradicating unwanted surprises of equipment failure.
Winnow offers AI-powered food waste monitoring software, which lets commercial kitchens and food service operations automatically monitor and analyze food waste. Their monitoring hardware includes computer vision and smart scales to identify what food is wasted, when, and why. This creates actionable insights into wasted food, leading to reduced waste, reduced food cost, and increased operating efficiency in commercial kitchens and food service.
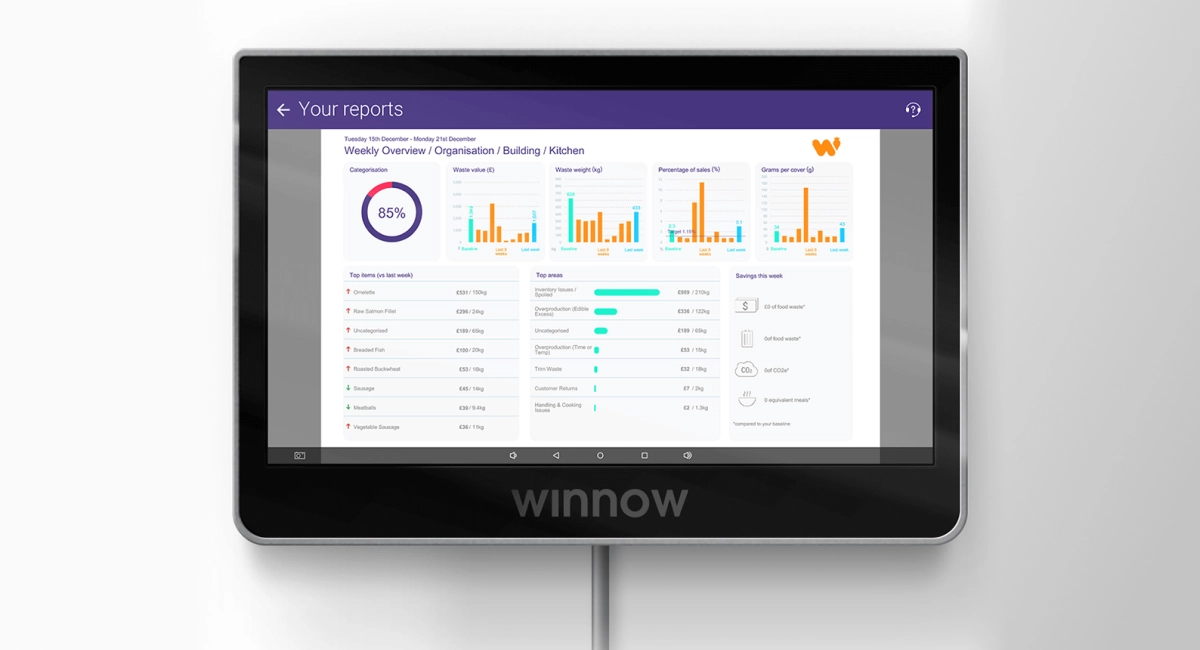
Winnow in kitchen waste reporting
Aiomatic provides a predictive maintenance platform that leverages AI, machine condition data to correlate early wear and breakdown functions based on learned behavior patterns. Embedded in industrial equipment, including recycling equipment, their technology reduces planned unscheduled maintenance with real-time diagnostics and actionable alerts to avoid lost downtime.
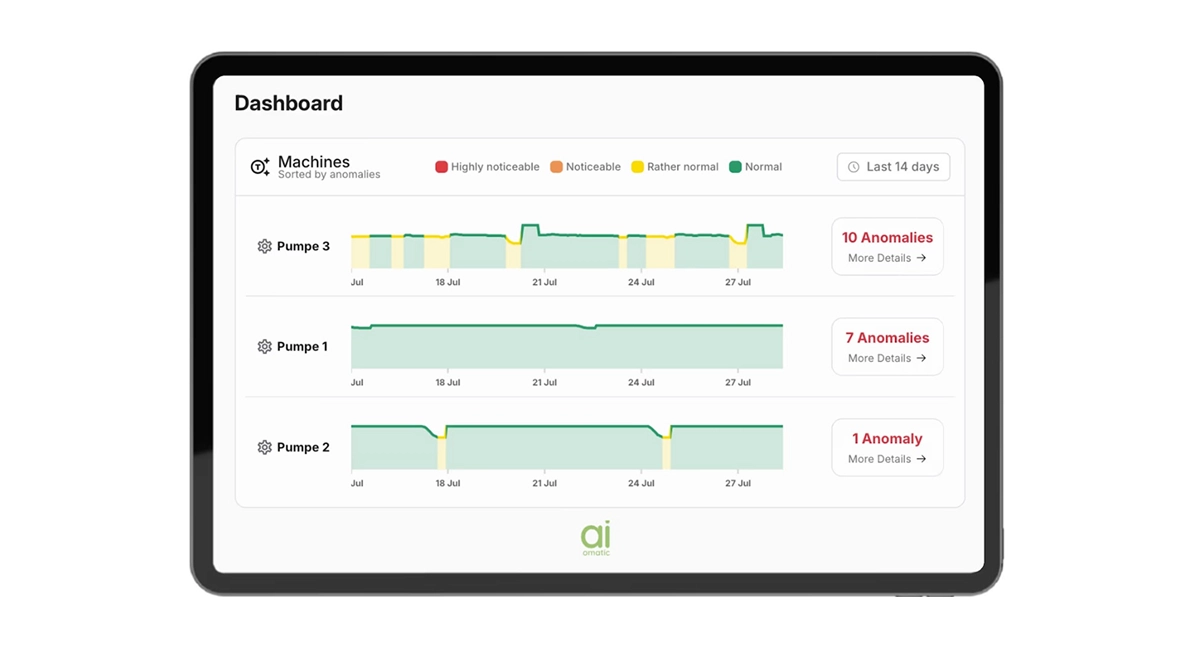
Aiomatic's anomalies prediction dashboard
Groundup.ai provides predictive maintenance with its proprietary IoT sound sensors and AI analytics. They routinely retrieve, capture, and analyze acoustic data emitted from the machinery in recycling and other relevant industries, to detect and identify anomalies, and alert the operator before a failure occurs or the delivery of poor performance. This minimizes unscheduled downtime, optimizes scheduled maintenance, and adds value to reliability and dependability.
Magnetic-based IoT sensors serve as the foundation of Groundup.ai’s Predictive Maintenance solution
Reducing Landfilling
Landfills will continue to serve an important role in waste management, but they also pose several environmental challenges. AI is now providing additional support to maximize operations in landfills with features that optimize predictive modeling involving gas emissions and methane production, leachate management, and the movement of earth in maintaining structural stability. When landfills are managed under AI systems, we can use methods to anticipate methane production to improve regulated gas capture to generate energy. Additionally, AI helps landfills be more productive with respect to the amount of airspace used and maintains compliance with environmental regulations in its operation, minimizing the ecological footprint of landfills.
Chuck™ harnesses the power of AI and data science to improve wood waste pick up at construction and manufacturing sites, creating a consistent and optimized supply chain for bioenergy plants. Chuck™ offers a value-added digital process to automate the pickup and sorting process, helping to improve landfill diversion rates and also making for a more sustainable landfill process through recovery and tracking of materials.

The Woodchuck.AI™ AI-powered platform for sustainability tracking, reporting, and validation
ZoharTech is a leading tech company specializing in advanced imaging systems with AI analytics to manage and monitor landfill conditions, the landfill's gas emissions, and anything that can become a potential environmental hazard reaching the environment. Their products add value to your operations by providing live actionable information for operational decision-making, improving landfill safety and regulatory stats, and optimizing waste for engineered decomposition.
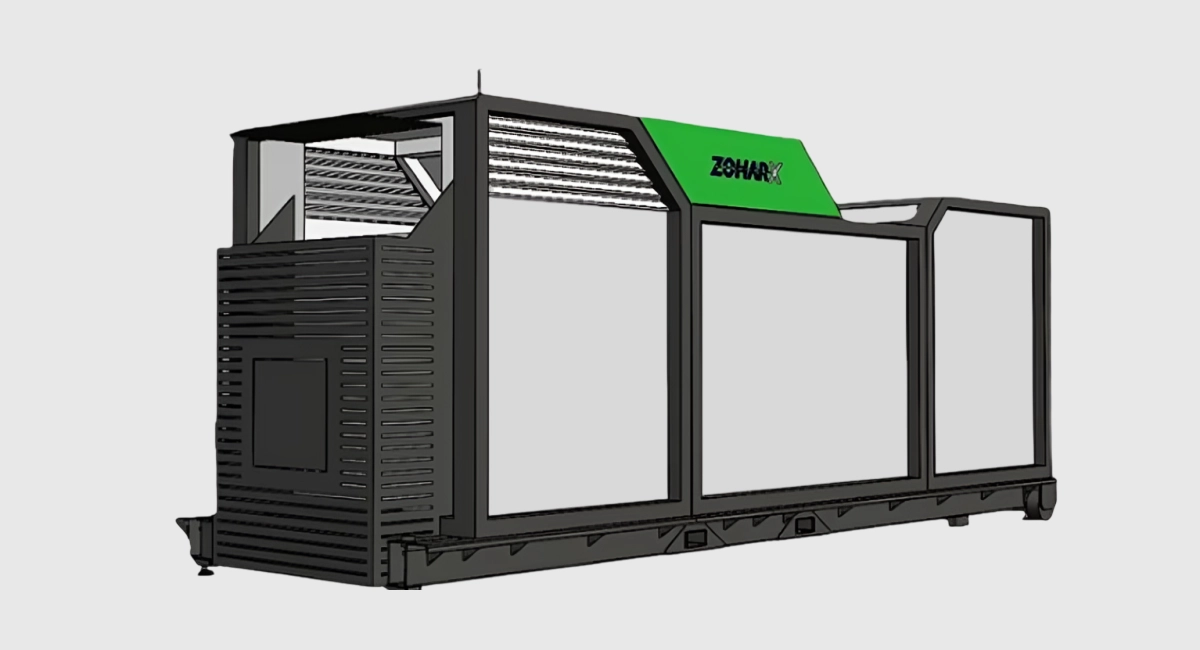

ZoharX - Waste Disposal System by ZoharTech
In the table below, we list companies together with their funding, investors, and a short description of what they do in Waste Management.
| Company | HQ / year founded | Amount Raised, $ | Investors | What they are doing |
| Aetech | South Korea / 2020 | $3.63M A | Tyche Investment, Hana Securities, KB Securities | Develops a waste sorting technology designed to increase the efficiency and accuracy of recyclables selection. |
| Aiomatic | Germany / 2020 | $2.2M Seed | EIT Manufacturing, 4Tree Capital, Haufe Group | Developer of an innovative predictive maintenance software designed to detect and evaluate anomalies without previously defined limited values. |
| AMP | USA / 2015 | $270M D | Congruent Ventures, XN, Sequoia Capital, Blue Earth | AMP designs, builds, and operates advanced, cost-competitive facilities to process single-stream recycling and municipal solid waste using AI. |
| Angsa Robotics | Germany / 2014 | $2.8M Seed | Husqvarna Ventures, TUM Venture Labs | Develops an autonomous trash-picking robot that uses an artificial neural network trained on a large dataset of human-labeled images to detect small and partially occluded waste objects on grass and gravel. |
| Bin-e | Poland / 2009 | $2.7M — | EIT InnoEnergy, LT Capital, Altamira, others | Manufacturer of a smart waste bin intended to optimize waste management for buildings and public spaces. |
| Chuck | USA / 2023 | $3.8M — | The Right Place, Mason Fink, NorthStar Clean Energy, others | Chuck’s platform leverages cutting-edge AI to identify, sort, and process wood waste, diverting it from landfills and converting it into high-quality biomass |
| CleanHub | Germany / 2020 | $11.9M — | 468 Capital, Lakestar, Integra Partners, others | An AI-powered track-and-trace platform automates the monitoring of collected plastic waste through mobile app inputs, including QR-coded registrations and photos of waste bags. |
| CleanRobotics | USA / 2015 | $11M Grant | SOSV, Innovation Works, Monozukuri Ventures, others | Develops waste management bins designed to utilize cloud-connected robotics systems and AI to sort commercial waste, along with cameras and sensors that scan items. |
| Danu Robotics | UK / 2020 | $600K Seed | SOSV, Scottish Enterprise, Sustainable Ventures, others | AI-controlled robotic waste management systems designed for the recycling management industry. |
| DataBeyond | China / 2018 | $44.3M Grant | HSG, Matrix Partners China, Fortune Venture Capital, others | DataBeyond Technology uses AI and big data to manufacture intelligent equipment for solid waste sorting and recycling. |
| E-Buho | Spain / 2015 | — | BIND 4.0 | E-Buho develops industrial predictive maintenance systems designed for monitoring recycling machinery by combining AI-powered IoT sensors with features like machine status visualization, condition severity analysis, and cloud-based data storage. |
| EcoOrbit Solutions | India / 2021 | — Seed | T-Hub | Standardizes waste sorting with AI and robotics, offering a robot that sorts plastics, paper, and cardboards. |
| Ecube Labs | South Korea / 2011 | $31M C | Coolidge Corner Investment, LB Investment, TIPS Program, others | The company's offerings include a comprehensive, smart waste management alternative using cloud-based software and smart bin technology and real-time and historical data to optimize waste collection schedules and routes, enabling organizations to make decisions ahead of time and offer insights into waste bin locations. |
| Etrash | Italy / 2023 | — Pre-Seed | Ecovera Holding, DAINt | Etrash is a smart bin that uses AI technology and ML algorithms to automatically identify the material composition of waste and sort it into the appropriate recycling compartment, streamlining the recycling process through intelligent, automated sorting. |
| EverestLabs | USA / 2018 | $31M A | Sierra Ventures, Translink Capital, Benhamou Global Ventures,others | AI-powered recycling and data analytics platform designed for optimizing recycling processes, leading in predictive maintenance for recycling facilities by leveraging high AI classification accuracy and 24/7 monitoring through its Robotic Operations Center to swiftly detect and eliminate contaminants before they disrupt operations. |
| Glacier | USA / 2019 | $20.5M A | Alumni Ventures, New Enterprise Associates, Elemental Impact, others | Provider of AI-based automated waste sorting robots with a proprietary robotic design that picks and sorts with high precision, sorts 30 plus different materials, and more. |
| Greyparrot | UK / 2019 | $30.8M Corporate Round | Plug and Play, Speedinvest, Closed Loop Partners, others | AI-based solution provider for waste management. It offers solutions such as object recognition enabled smart bins, waste composition monitoring, and software-based robot for automated sorting of wastes. |
| Groundup.AI | Singapore / 2020 | $6.1M A | Wavemaker Partners, Tin Men Capital, Seeds Capital, Hiven | Developer of IoT, sound sensors, and a cognitive maintenance platform doing AI analysis for sound, vibration, and thermal IoT sensors designed to prevent unplanned downtime and reduce wastage. |
| Intuitive AI | Canada / 2017 | — Accelerator | Alchemist Accelerator, Creative Destruction Lab (CDL), others | Developer of an AI-based waste recycling platform designed to minimize global landfills by maximizing the efficiency with which waste is recycled. |
| IPercept | Sweden / 2019 | $8M Seed | Luminar Ventures, RunwayFBU, J12, AI.FUND, Backstage AB | Ipercept Technology provides an industrial IoT and edge analytics platform tailored for predictive maintenance and performance optimization of heavy machinery, making it highly suitable for recycling facilities. |
| Ishitva | India / 2018 | $1M — | Inflection Point Ventures, Grp, Spectrum Impact, others | Manufacturer of automatic sorting machines intended to segregate waste to recover recyclables effectively. |
| Jaipur Robotics | Switzerland / 2024 | $1.1M Pre-Seed | Techstars, Venture Kick, TiVentures | Develops an AI-powered platform designed to automate and optimize operations in Waste-to-Energy plants. The company's platform offers deep learning-based object detection, intelligent waste recognition, calorific value mapping, real-time decision support, and crane tracking. |
| Lemon Tri | France / 2011 | $1.17M — | Amundi, Mirova, Banque des Territoires, MAIF Impact, PhiTrust Impact Investors | Lemon Tri is committed to combating waste incineration and landfilling by offering innovative sorting, recycling and reuse solutions for all “outside the home” spaces: offices, stores, campuses, hotels, airports, company restaurants, etc. |
| MyMatR | USA / 2021 | — Accelerator | NC IDEA, AcceliCITY powered by Leading Cities | Manufacturer of IoT-based smart waste containers intended to sort waste at its source. Uses AI for automatic sorting, waste reduction, and waste stream data analytics. |
| NordSense | Denmark / 2017 | $12.6M — | New Enterprise Associates, Root Ventures, ACME Capital, others | A waste management system designed to improve the waste management industry with smart sensors and data. The company's system can be installed in any container to monitor waste levels with a user-friendly platform that monitors in real-time which waste bins need servicing, enabling clients to address the inefficiency and lack of sustainability in traditional waste management. |
| NuManufacturing | Turkey / 2022 | — Accelerator | Innogate, Winglobal, MONAT Investment | The company develops AI-based predictive maintenance and condition monitoring technologies by combining sensor arrays with algorithms and software. |
| PIN IoT | UK / 2018 | $1.5M Seed | Startupbootcamp IoT London | Developer of tracking devices and a platform intended to track waste containers and vehicles in real-time. |
| PolyPerception | Belgium / 2021 | $1.18M Corporate | TOMRA Systems, imec.istart, others | Operator of an AI-powered waste sorting and analysis system intended to improve recycling efficiency. |
| Prairie Robotics | Canada / 2017 | $600K Seed | Conexus Credit Union, Cultivator, others | Provider of IoT-based recycling services to solve the problem of eliminating recycling and organic contamination. |
| Recycleye | UK / 2019 | $26M A | Promus Ventures, DCVC, Playfair Capital, Seaya, MMC Ventures | Recycleye provides solutions for automated waste sorting. It uses machine learning and computer vision to detect and analyse waste. |
| Resourcify | Germany / 2018 | $27M A | Speedinvest, HTGF, Revent, Ananda Impact Ventures, others | Developer of waste management platform designed to automate disposal and improve recycling. |
| Reworld Waste | USA / 1939 | — | — | Reworld™ is a sustainable waste management company committed to eliminating landfill dependency through its Zero Waste to Landfill initiative. |
| RoadRunner | USA / 2014 | $174.1M D | Headline, Franklin Templeton, Greycroft, FJ Labs, Fifth Wall | RoadRunner Recycling is a provider of a data-driven waste management platform for commercial waste recycling. |
| RTS | USA / 2015 | $151.7M — | Gaingels, Edison Partners, Volition Capital, others | RTS is redefining waste and recycling through advanced technology, deep industry expertise, and a proven history of operational excellence. At the center is Pello – their AI-powered sensor technology that uses ML and real-time data to monitor container levels, improve service reliability, and reduce contamination. |
| Sensoneo | Slovakia / 2017 | $12.97M A | Credo Ventures, Taiwania Capital, Ysoft Ventures, EIC FUND, others | Sensoneo is a global provider of smart waste management solutions that support the digital transformation of waste management to achieve efficiency, transparency, and sustainability. Sensoneo started with a waste fill-level monitoring solution that consisted of sensors measuring waste level in bins and a smart software system. |
| Sensorita | Norway / 2020 | $3.3M Seed | Brick & Mortar Ventures, Telenor | Sensorita creates digital twins of waste containers with smart sensors, giving real-time insights into fill levels, location, and waste trends. Their co-pilot helps waste management companies optimize planning, logistics, and collection. |
| Sorted | UK / 2022 | $2.07M Seed | Antler, Pi Labs, The Conduit Connect, Archipelago Eco Investors | AI-based platform designed to help waste management companies segregate their recyclable materials. |
| Superbin | South Korea / 2015 | $31.3M B | Korea Investment Partners, Korea Development Bank, others | Develops a waste recycling robot intended to spread the values of recycling, sustainable growth, and a way of living together. |
| Tractian | USA / 2019 | $183.7M C | General Catalyst, Y Combinator, Sapphire Ventures, others | Tractian is a machine intelligence company that provides condition monitoring and asset performance management. |
| UptimeAI | USA / 2019 | $19M — | Venture Catalysts, YourNest Venture Capital, Emergent Ventures, others | Predictive maintenance software, designed to predict and mitigate impending failures in process industries, uses AI-based algorithms to identify irregularities, predict early defects, and analyze the data to understand the correlations between upstream and downstream operations, enabling clients to improve process outcomes. |
| Waste Robotics | Canada / 2016 | $9.8M — | Mirova, Creative Destruction Lab (CDL), Fondaction, V3 Ventures, others | Waste Robotics designs and delivers intelligent recycling robots to replace human pickers in recycling centres. |
| Waste Solutions | Canada / 2006 | — | — | Waste Solutions integrates smart sensor technology into its waste management services to provide clients with precise, real-time monitoring of bin levels and service needs. |
| WasteDigital | Czech Republic / 2021 | — | — | WasteDigital uses predictive analytics and smart data models to optimize municipal and commercial waste collection. Their platform collects real-time data from IoT-enabled smart sensors installed in waste containers and applies predictive algorithms to forecast fill levels, plan efficient collection routes, and prevent overflows. |
| WasteFlow | Switzerland / 2024 | $200K Seed | Venture Kick, Kickfund, Business Angels | The company's platform leverages advanced AI algorithms to optimize recycling operations, predict equipment failures, identify contaminants, and estimate material quality, enabling the recycling industry to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance sustainability. |
| WasteHero | Denmark / 2017 | $7.8M — | Momenta, Anorak Ventures, Circles & Squares | WasteHero uses AI and ML algorithms to optimize waste collection routes and predict bin fill levels. By integrating data from smart sensors, weather patterns, and historical collection trends, their AI models forecast when and where waste bins need to be emptied. |
| WASTELINQ | USA / 2017 | $24.6M C | Ridgepeak Partners, Freestone Sponsors | WasteLinq incorporates AI-driven automation to improve waste profiling, manifest generation, and regulatory compliance. Its platform uses ML to standardize complex waste data, predict regulatory classifications, and flag anomalies for risk reduction. |
| Winnow | UK / 2013 | — | — | Winnow develops an AI-powered food waste management software that helps commercial kitchens track, measure, and reduce food waste. By using a combination of computer vision, scales, and AI analytics, the system automatically identifies and records food being discarded, providing chefs and operators with real-time data and actionable insights. |
| Wwwaste | Singapore / 2022 | — | — | Wwwaste's platform uses predictive analytics to forecast bin fill levels and streamline collection schedules, supporting smarter, greener, and more efficient waste operations. |
| Zest | USA / 2022 | $2.5M Grant | BridgeAI, Innovate UK, ReLondon | Zest provides software that uses AI and ML to help food manufacturers monitor their supply chains, identify and prevent food waste, and intelligently reallocate surplus, generating actionable insights to maximize value recovery and improve the distribution of unavoidable waste. |
| ZoharTech | Israel / 2017 | $1.85M Seed | Climate First, Reality Investment Funds, Doral Energy Tech Ventures | ZoharTech provides decentralized onsite waste disposal systems that treat unsorted residential waste at the source, aiming to reduce landfill use, urban traffic, and greenhouse gas emissions by converting household waste into energy. |
Challenges
While there is great potential for implementing AI in waste management, there are several obstacles to adoption:
- High Upfront Cost: Implementing AI technologies requires substantial upfront spending on equipment, software, and infrastructure.
- Data Limitations: Accurate and reliable data is critical for AI performance. However, many waste management systems lack consistent data collection and standardized processes, making it difficult to gather the necessary inputs for AI models.
- Integration Difficulties: Incorporating AI into existing waste management operations can be complex, as legacy systems and established processes may not be easily adaptable to new technologies.
- Talent Shortage: Successful use of AI requires expertise in data science, machine learning, and related fields. Such specialized skills are often lacking in traditional waste management organizations.
Future Trends
Looking forward, however, AI's waste management practices are expected to evolve and expand in several significant ways. AI will increasingly enable circular economy models by facilitating product and supply chain designs for recycling systems that will consider waste prevention at the outset. The Advanced Materials Recovery Facilities (MRFs) of the future will utilize autonomous AI-driven operating systems to fully realize not only operating efficiencies, but also maximize material recovery efficiencies that will completely change how materials will be sorted and processed. AI will also enable new decentralized systems of waste management, allowing easier connectivity to smaller, local processing systems, thereby decreasing the need for transportation and diminishing the impact on the community's sustainability profile. Finally, AI will progress in conjunction with greater environmental technologies to integrate waste management practices with climate initiatives such as energy generation from waste and carbon capture and recycling, thus further embedding AI in practices that create a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
AI is not only impacting how we deal with waste, but it is also redefining it. Automated, predictive, and optimized AI systems are changing waste from a liability into a resource. If the technology develops as expected, AI-based waste management and technology have the potential to create a cleaner, smarter, and more sustainable world for cities, businesses, and our planet. Taking advantage of these innovations today will ensure a cleaner future tomorrow.