From Science Fiction to Reality: The Evolution of Humanoid Robots
Bridging the Gap Between AI and Humanity.

For decades, the concept of humanoid robots remained fanciful and a staple of science fiction. The characters of C-3PO in Star Wars and Data in Star Trek created vivid imaginations about robots that could think and learn like human entities and communicate like humans. However, it has become a reality today with rapid advances in Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, and Machine Learning. Human robotic agents, imbued with cognitive capabilities, emotional intelligence, and adaptive learning, are no longer a figment of fiction but are in the process of shaping industries and everyday life.
The global humanoid robot market size was valued at $2.43B in 2023 and was projected to grow from $3.28B in 2024 to $66B by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 45.5% during the forecast period.
This article describes the evolution of robots, current applications, future trends, and their potential to bridge the gap between AI and humanity.
The Origins of Humanoid Robots
Humanoid robots – machines crafted to resemble human appearance, movement, and interaction – have fascinated scientists, engineers, and storytellers for years. These robots are designed to function in environments centered around humans, utilizing artificial intelligence, sensors, and mechanical skills to carry out tasks typically performed by people.
The concept of robotic agents has its roots in early automatic mechanical devices built for repetitive jobs. Further development in robotics in the mid-20th century led to industrial applications, where simple machines transformed manufacturing processes by taking up monotonous and hazardous tasks. These robots, however, were unintelligent and had to execute tasks programmed into them.
According to legend, AI started in the 1950s. With the introduction of machine intelligence, as proposed by Alan Turing among others, came innovations in computing and logic. In the late 20th century, robotics started developing AI-based methods and could learn to view things, analyze them, and perform accordingly.
What we want is a machine that can learn from experience,” and the “possibility of letting the machine alter its own instructions provides the mechanism for this.
The Integration of AI and Robotics
The merging of AI and robotics has been a real milestone in the evolution of anthropomorphic robots. AI-enabled machines process data, learn from experience and interact with the world independently. Natural language processing and computer vision let the robots understand human speech and recognize visual cues.
This integration was realized by breakthroughs like Honda's ASIMO, one of the first humanoid robots capable of walking and communicating, and IBM's Watson, used to make human-like robots cognitive and empathetic. These milestones set a base for developing robots that work as intelligent partners.
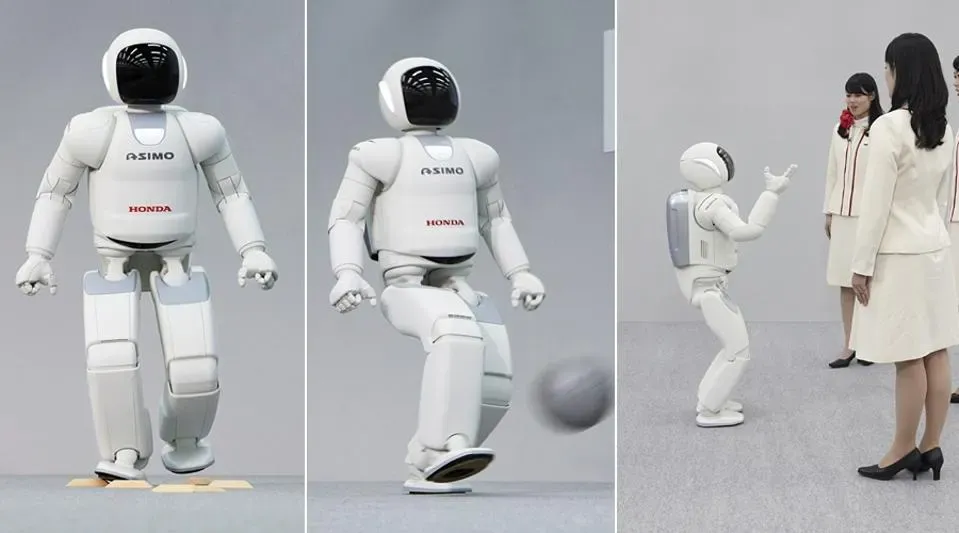

Honda’s ASIMO humanoid robot
Humanoid Robots in the Modern World
Human-like robots have moved from the experimental prototype of a few people's imagination to a standard tool, transforming industries and redefining the relationship between humans and technology. The presence of these sophisticated machines has become vibrant in everyday life through application in healthcare, education, logistics, and many other sectors where they have turned into dynamic partners in innovation.
Recent CES 2025 proved that robotics has come on in leaps and bounds in recent months. From robots shaking hands and doing dishes to huge agricultural robots, the event went big on anthropomorphic robots. These examples show how personal and industrial tasks can be automated with human-like precision, reducing labor strain and increasing productivity. Special attention caught Unitree's G1 humanoid robot with its lifelike abilities, delivering smooth handshakes and performing awe-inspiring backflips. Beyond its physical movements, the G1 is engineered to act as a bridge between humans and machines, paving the way for robots to integrate seamlessly into everyday tasks.

Unitree G1 Humanoid Robot
A significant advancement toward more autonomous and adaptable robots comes from Figure, a US startup focused on AI-powered humanoid robots. The company has successfully created Helix, a generalist Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model developed in-house for greater independence and control over robotic intelligence. Following this milestone, Figure AI has chosen to end its partnership with OpenAI and plans to showcase its new capabilities within 30 days.
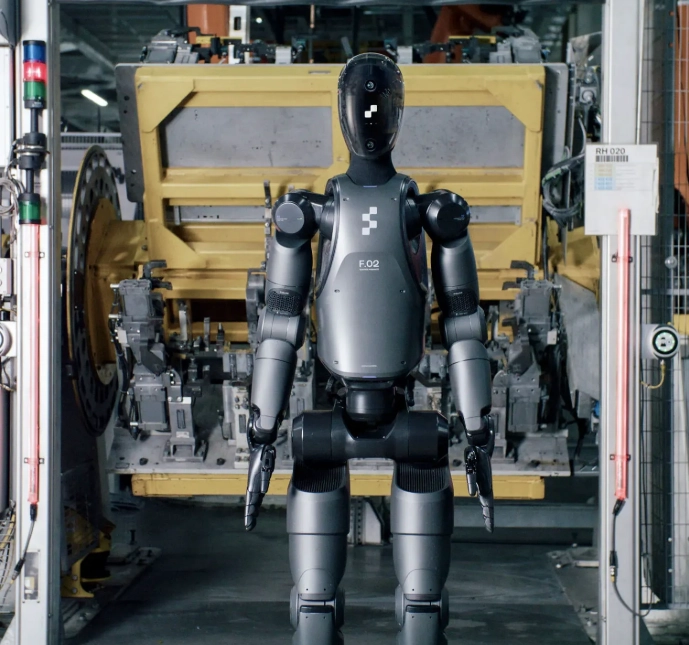
The Figure 02
Powered by the latest in AI, robotics, and emotional intelligence, humanoid robots are developing at an unprecedented pace for a future in which machines can blend seamlessly into the human world. Let’s have a glimpse of industries that utilize anthropomorphic robots.
Healthcare
Human-like robots are giving a new face to healthcare by contributing to improved patient care, smoothing out services, and responding to labor shortages. They strive for that human look to blend into medical service provision with their functional and emotional support.
Robots like Diligent Robotics’ Moxi perform tasks for medical professionals, such as fetching supplies, delivering medication, and transporting lab samples. By automating these tasks, Moxi frees healthcare workers to focus on direct patient care, reducing burnout and improving overall hospital efficiency.
There are also supporting robots in rehabilitation and elderly care, such as Pepper and GR-1. Pepper entertains the patients by recognizing and responding to human emotions, keeping isolated people accompanied. GR-1 is deployed in healthcare facilities to respond to the rising demand for medical services amid labor shortages and the aging population. Also, for older adults and individuals with disabilities, humanoid robots like Abi and Beomni act as social companions, engaging users in conversations, reminding them to take medications, and stimulating health-enhancing activities such as exercising or even going out with people. In identifying and emulating emotions, the devices show their true potential in assisting the isolated.

Fourier Intelligence GR-1
Education
Human-simulating robots benefit education by setting an immersive and personalized learning environment that makes them spellbound. They are increasingly being integrated into classrooms as an interactive tool for teaching complex subjects and creating essential skills. In addition to their almost similar appearance, they mimic human interaction to make learning engaging and much more related.
Humanoid robots can teach how to code, solve problems, and conceptually understand STEM ideas that cannot be taught by traditional methods. They can show how these subjects apply in real life, which creates curiosity and motivates hands-on learning.
Anthropomorphic robots like Proven Robotics’ NAO remain non-judgmental and allow children with learning disabilities or those who struggle to communicate the opportunity to practice their social and cognitive skills in a safe environment. The robots, by adjusting to the speed and requirements of students, make education more inclusive and accessible.
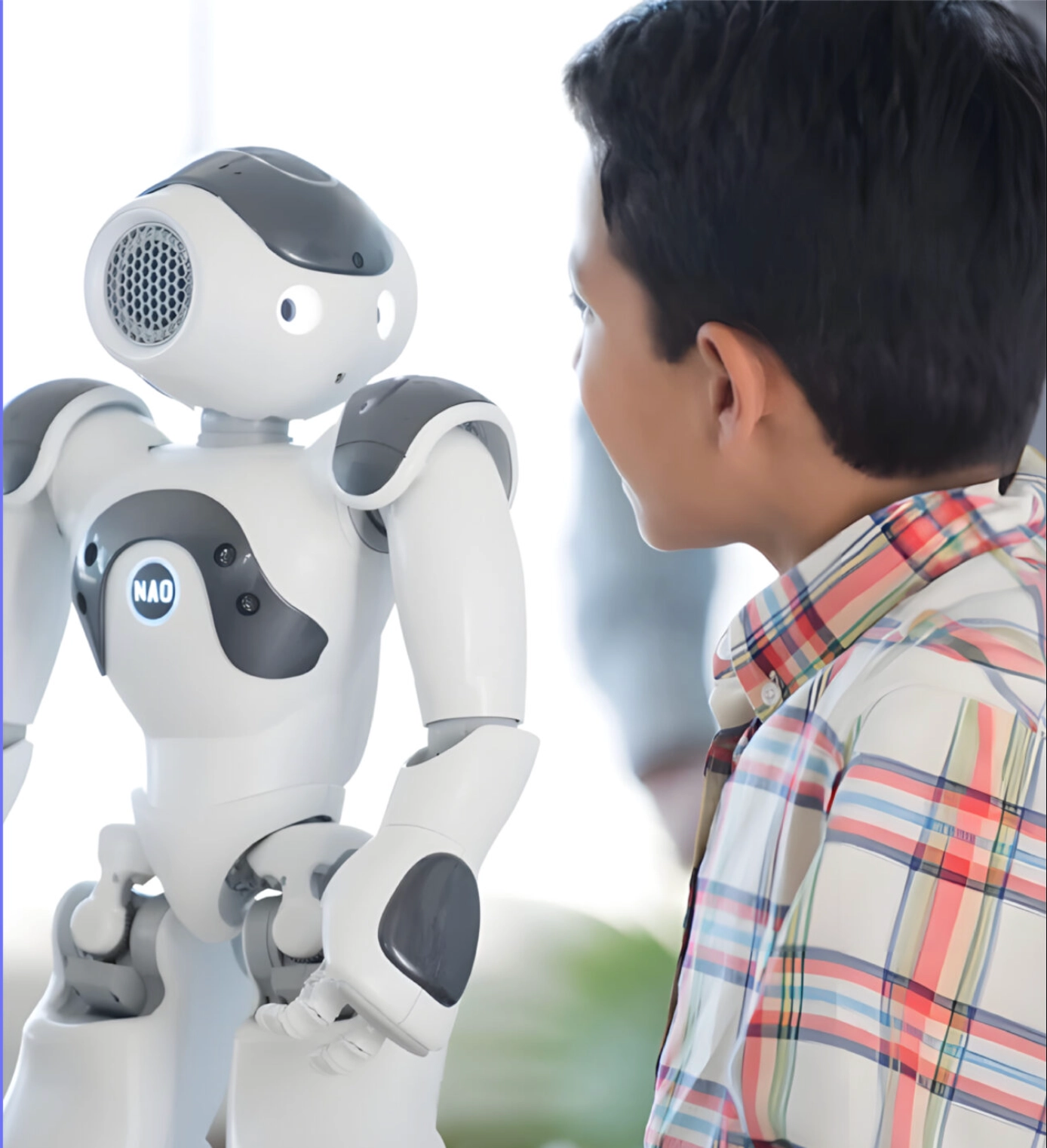
Proven Robotics’ NAO
Humanoid robots additionally teach social and emotional intelligence, allowing students to develop interpersonal skills, and grooming students for a technologically enriched world.
Logistics & Manufacturing
In logistics and manufacturing, humanoid robots are revolutionizing supply chains and operational workflows. For example, Apollo by Apptronik is a robot designed for warehouse automation; it efficiently and precisely handles and moves heavy packages. Punyo takes a different approach to lifting objects compared to other humanoids. Instead of using just its hands, Punyo leverages its arms and chest to handle hefty loads more naturally. On top of this, android robots are being fitted into last-mile delivery systems. Robots like Digit, from Agility Robotics, integrate mobility with human-like dexterity and can reach customers' doorsteps even through complex urban routes. 1X claims to be the company that sends the first AI-powered humanoid robot into the workforce. The company's robot EVE comes with extremely strong grippers for hands, cameras that support panoramic vision, and two wheels for mobility. A voice command feature is added, which lets users ask EVE to perform multiple tasks in sequence. Most importantly, EVE uses AI to learn new tasks and improve with experience.
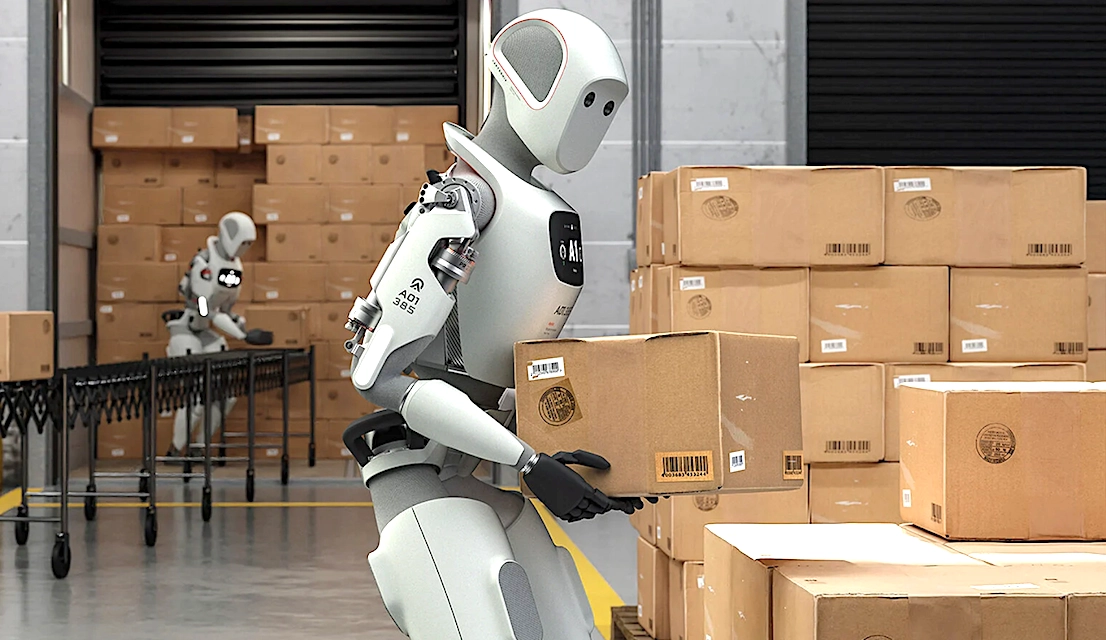

Apollo’s Apptronik
These robots are improving efficiency, besides solving labor shortages in the logistics industry. With anthropomorphic robots automating repetitive and dangerous tasks, businesses are guaranteed faster delivery times, increased accuracy, and cost savings.
Entertainment
Humanoid robots are making their mark in the entertainment sector, where they execute intricate routines and entertain audiences. Capable of complex gestures, mimicking emotions, and even responding to guest interactions, robots are becoming integral components in modern storytelling and immersive attractions.
THESPIAN, a human-like performer, can deliver scripted lines, respond to actors, and show emotion through gestures and facial expressions. The directors and producers experiment with these robots for unique performances that merge AI with human creativity.
In sports, there are also plenty of human-like assistants. Toyota development team made an AI basketball robot CUE, which has achieved its second Guinness World Records title for the "farthest basketball shot by a humanoid robot" from a distance of 24.55 meters.
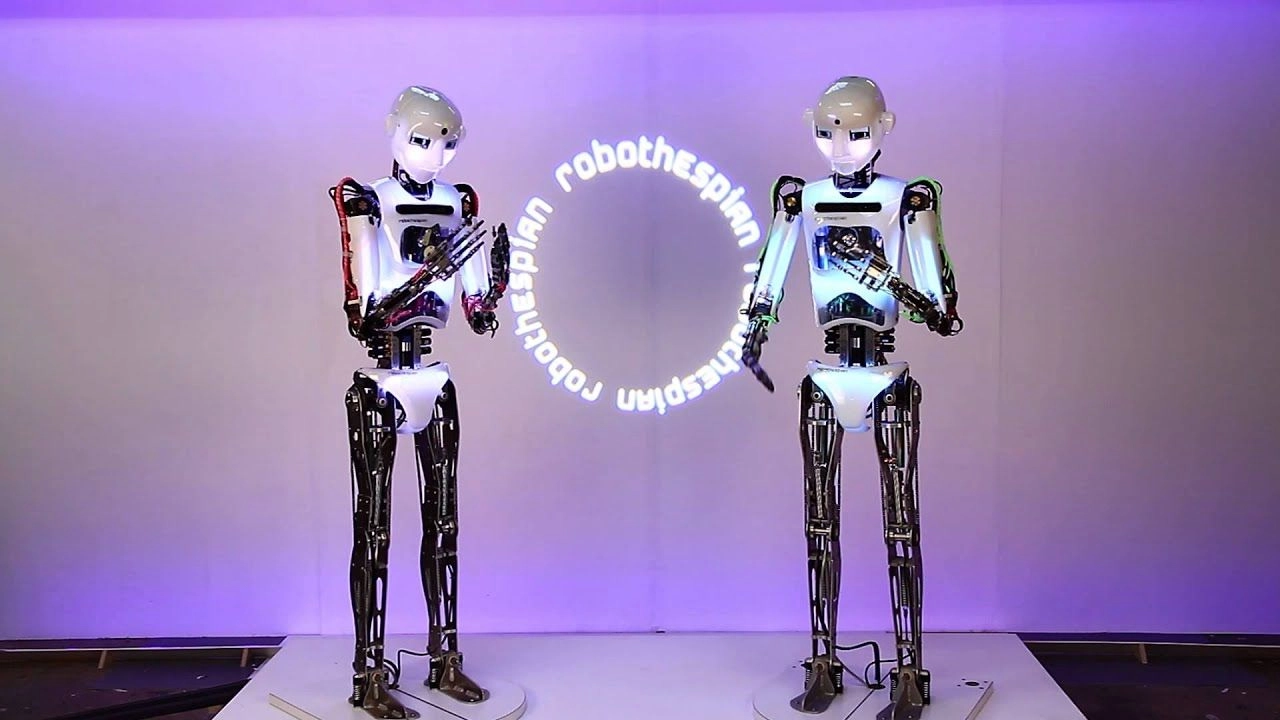

RoboThespian by Engineered Arts
Hospitality
The hospitality industry is increasingly adopting humanoid robots to improve guest experiences and streamline operations. In hotels, robots such as concierge developed by Abu Dhabi-based technology company Kintsugi, assist guests with information on local attractions, recommendations of restaurants, and answers to basic questions in multiple languages. Similarly, android robots in airports and cruise ships welcome travelers, guide them to their destinations, and offer entertainment during wait times.
Restaurants are also making use of humanoid robots that take orders and serve food and drinks; some even converse with customers in friendly, colloquial speech. Robotic bartenders such as KIME, developed by Macco Robotics, bring a futuristic drinking experience with efficient wait time.
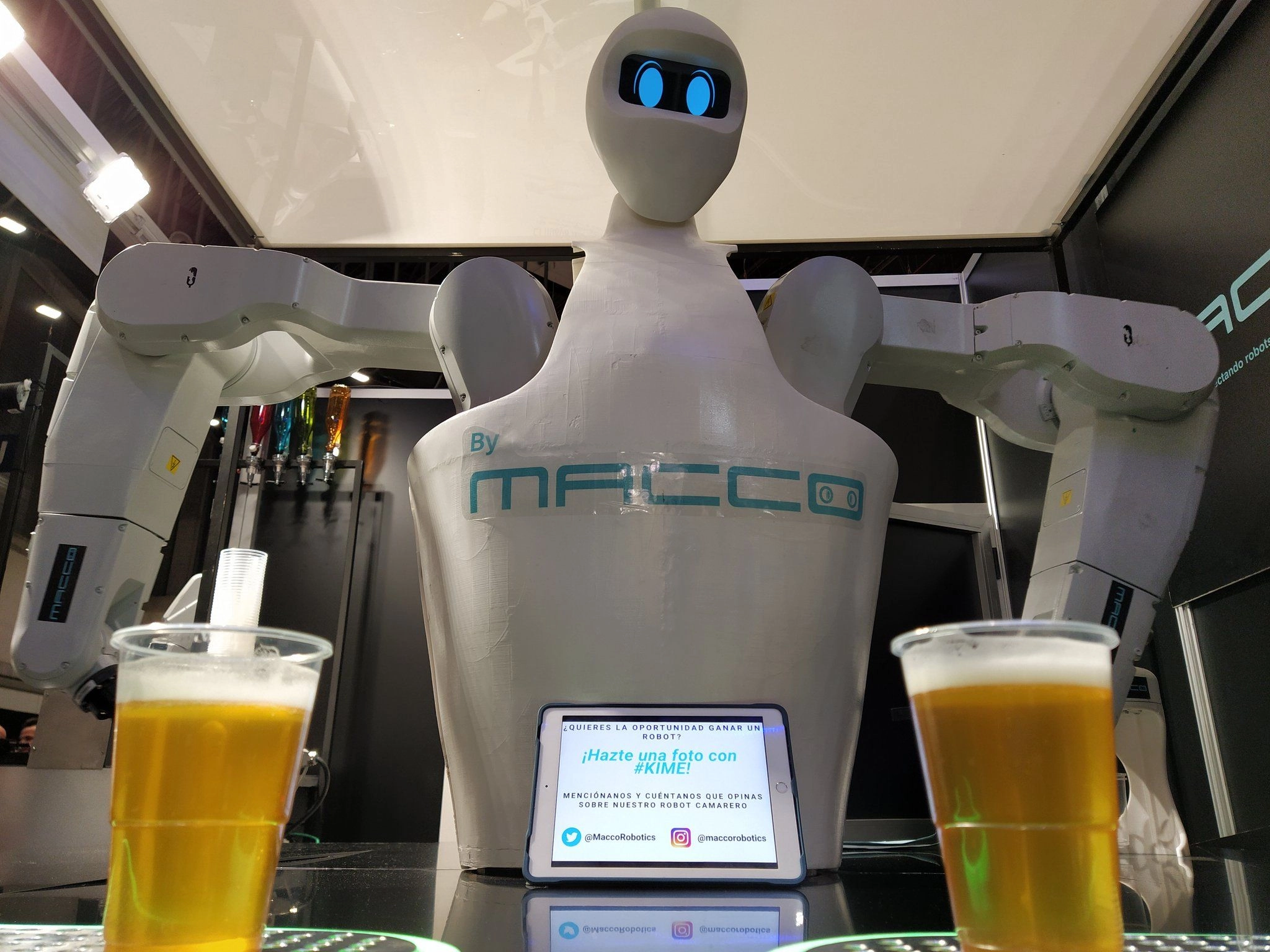

KIME by Macco Robotics
Construction
Humanoid robots are slowly beginning to make their presence felt in the construction industry, hinting at solutions to labor shortages, workplace safety, and efficiency challenges. Robotic human replicas, with their human-like form and advanced dexterity, can navigate complex construction sites, perform physically demanding tasks, and collaborate with humans.
HRP-5P from Japan's AIST, for instance, can pick up drywall panels and power tools with high accuracy. This robot measures, cuts, and installs panels, automating repeated hazardous construction work. Its agility and humanoid shape make it more suitable for reaching structures in scaffolding and places considered difficult to reach through infrastructure projects.
Furthermore, the capability of robots like Atlas, which Boston Dynamics has developed, is currently being explored for inspection and material handling at construction sites. Its advanced mobility and balance capabilities can take it over rough terrain and climb stairs with objects in its hands, making it a good candidate for dynamic and unpredictable construction environments.
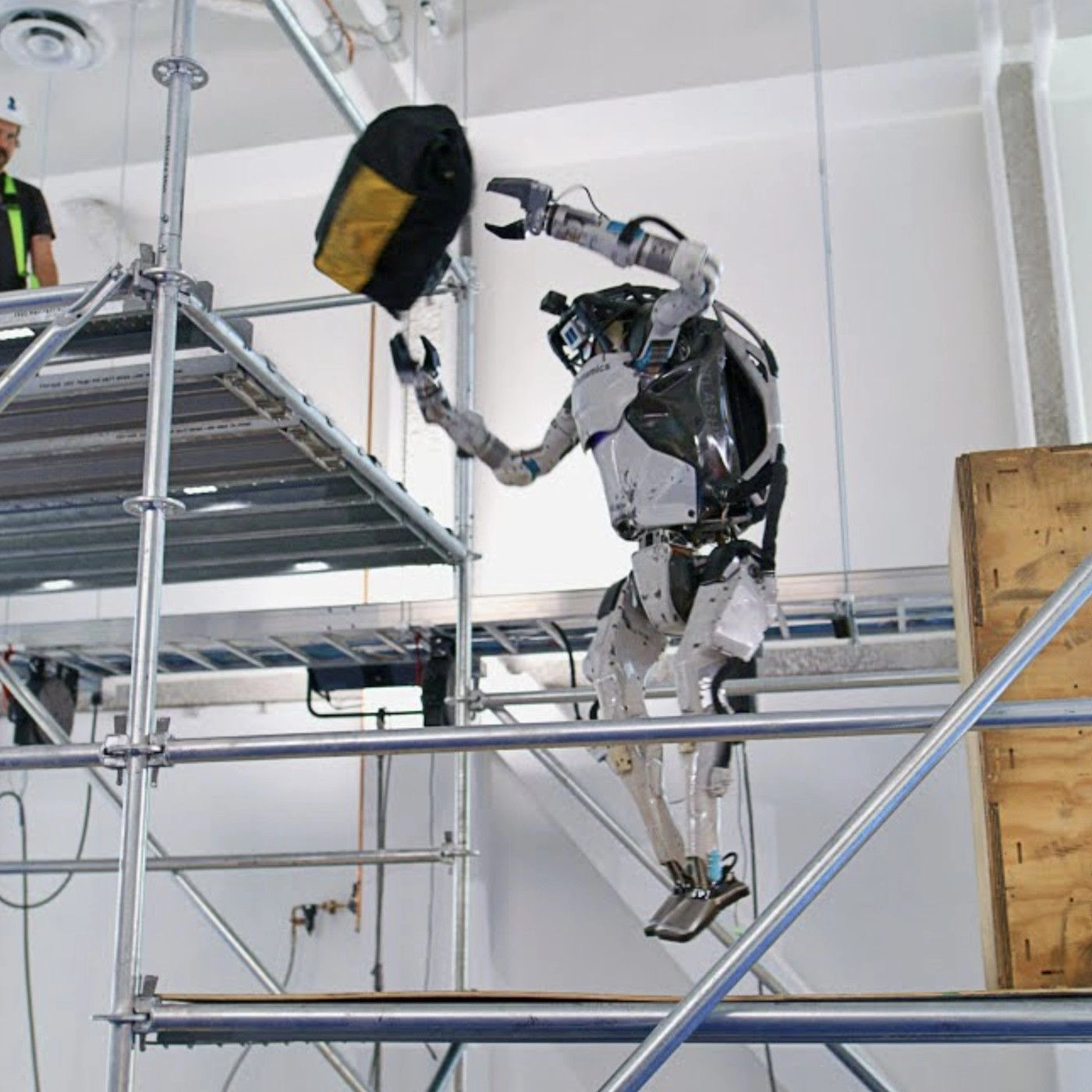

Boston Dynamics' Atlas can now toss tool bags around a construction site
Agriculture & Food Production
With Humamoids' close dexterity to humans, mobility, and adaptability, they can conduct tasks from planting through harvesting and monitoring & executing farm management to managing food production processes. Altopack Group, creator of food packaging systems, has included Robotic human replicas in its lines sold all over the world through Cyborg Line. Halodi Robotics (which is 1X now) developed the hardware, while Cyborg Line taught robots how to interact with machines.
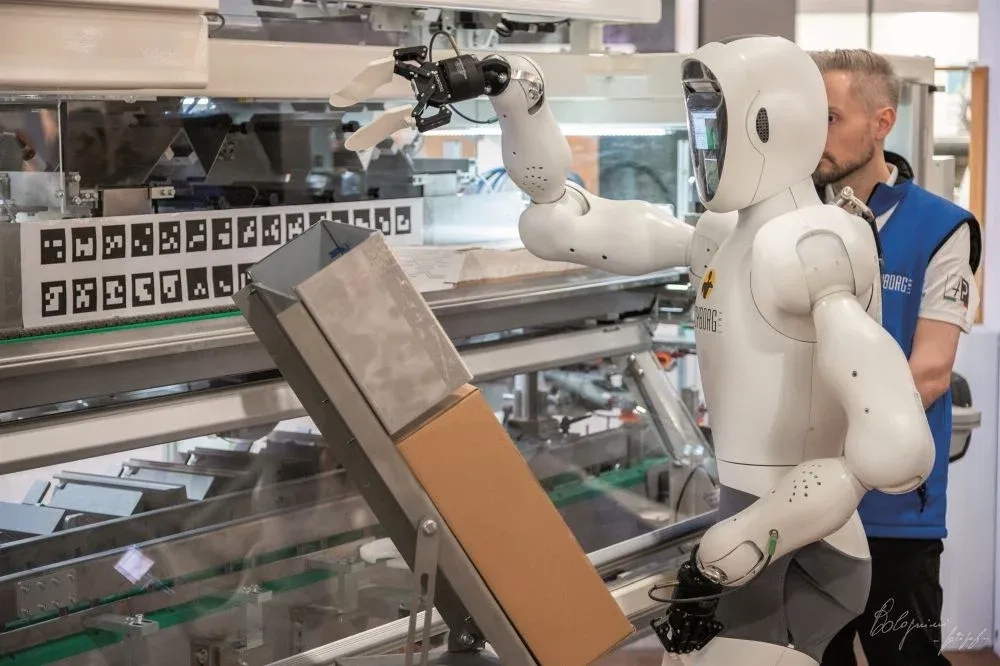

Altopack Robotic humanoid for the food packing industry
High Risk Environments
Humanoid robots are playing an increasingly vital role in high-risk environments, where human safety is a critical target interest. Equipped with advanced AI, sensory perception, and dexterous capabilities, these robots are deployed in hazardous settings such as disaster response, nuclear decommissioning, and space exploration. Their human-like form allows them to navigate environments designed for people, operate standard tools, and perform critical tasks with precision while minimizing human exposure to danger.
T-HR3, developed by Toyota and remotely controlled by human operators, can perform delicate tasks in hazardous areas, such as nuclear facilities and disaster-stricken zones. The sophisticated hand movements combined with force-feedback capabilities in T-HR3 enable it to handle sensitive materials with precision while maintaining operators at a safe distance.
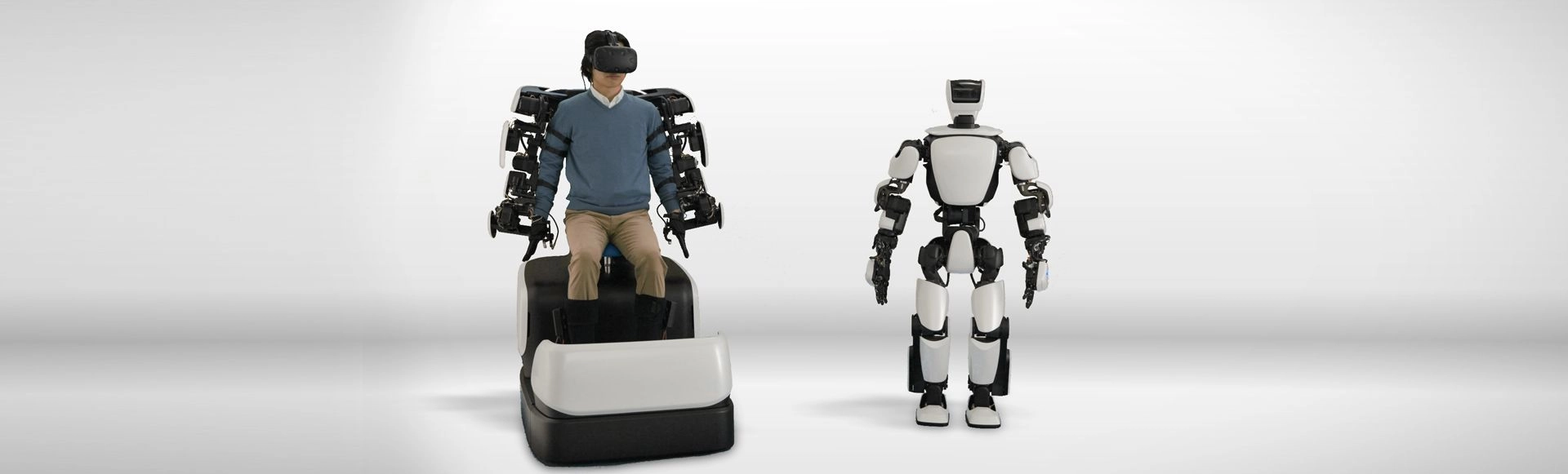

T-HR3, developed by Toyota, controlled by human operators
In disaster response, robots like Atlas are deployed to assist in search-and-rescue missions. The base model of Atlas was designed to execute, for the challenge thrown by DARPA, lifesaving tasks in dangerous conditions: flipping switches, shutting off valves, opening doors, and running power equipment-enabling design components like lightweight hydraulics and 3D-printed appendages. Atlas would demonstrate extraordinary agility and balance to easily travel over debris-saturated terrain to reach people, deliver life-sustaining essentials in earthquake or fire, and perform emergency, lifesaving procedures.
Androids are also making strides in space exploration, assisting astronauts in performing maintenance tasks on spacecraft and space stations. Valkyrie, NASA's development, is designed to function in extreme environments, helping with repairs, system checks, and assembly tasks in extraterrestrial missions. Another NASA creation Robonaut2, developed in collaboration with General Motors, has been adapted to work in radiation-exposed environments. It can handle radioactive materials, inspect equipment, and perform maintenance tasks in confined and hazardous spaces, significantly reducing radiation exposure to human workers. Building on this foundation, Apptronik, in partnership with NASA, is working on humanoid robots designed for space and Earth applications. They are teaming up with Google DeepMind to improve AI capabilities for general-purpose robots. Furthermore, a recent collaboration with NVIDIA advances AI-driven automation, allowing Apptronik’s systems to function with greater precision and adaptability.

Robonaut 2 (a) and Valkyrie (b) developed by NASA
As humanoid robots advance, their role in high-risk environments will expand, providing safer and more efficient solutions in industries where human lives would otherwise be at risk. These robots are proving to be inevitable assets in tackling the most challenging and dangerous situations humans face.
Emotional Intelligence in Robotic Agents
Humanoid robots are becoming capable of detecting and responding to human emotions, providing new ways for interaction and support. Such robots can detect simple emotions through facial expressions, voice tones, and body language, adjusting their interactions to provide a sense of empathy. Used in health and companionship applications, these robots provide reassurance and emotional support through conversation. Through NLP and adaptive learning, such robots become attuned to detect emotional states better with every engagement, producing the illusion of personalization and warmth.
Researchers from Hohai University and Changzhou University developed a two-stage method that enables robots to create more natural, complex facial expressions, enhancing human-robot interactions. A robot equipped with several degrees of freedom in facial expressions learns to create the expressions. The method enabled humanoid robots to perform some facial expressions upon command.
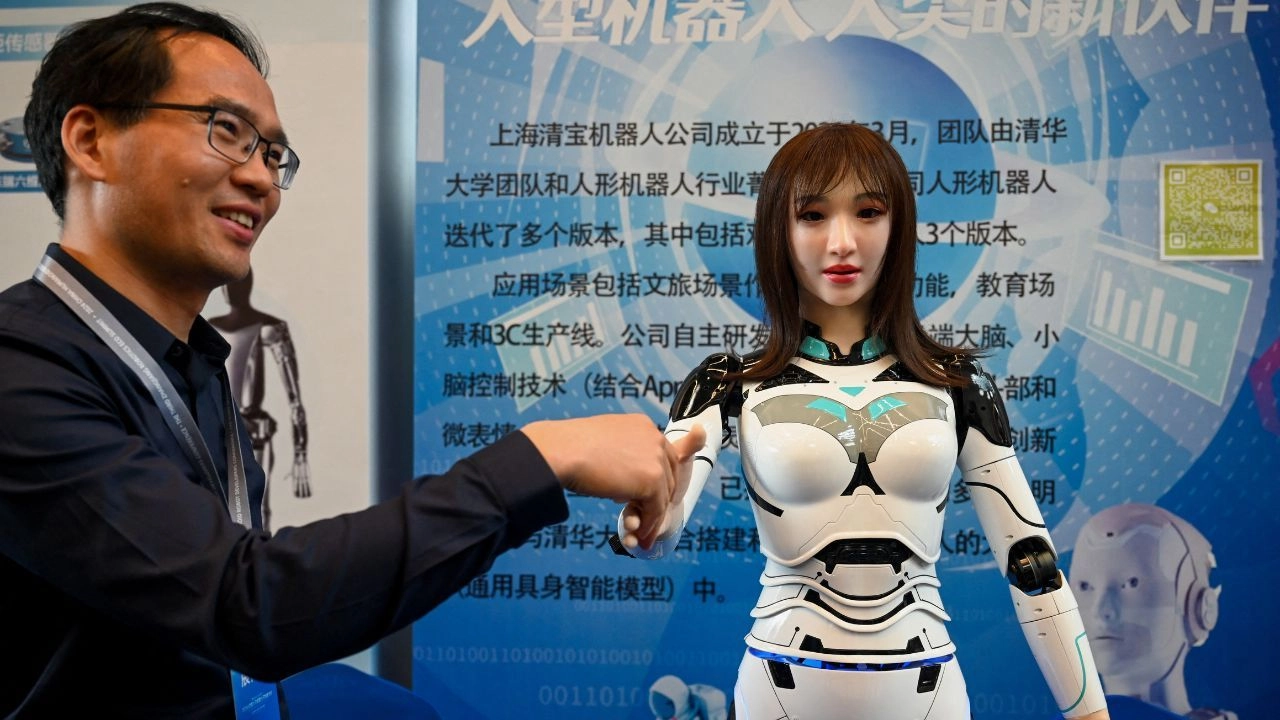

China researcher’s robot with human facial expressions
Even with these advances, however, there are emotional bounds. Humanoid robots do not feel emotions — they simulate empathy through data patterns. This might lead to misinterpretations, especially with more nuanced social indicators like sarcasm or cultural knowledge. In addition, while robots are extremely skilled at surface-emotional communication, they fall short of building deep, lasting emotional bonds or understanding lasting emotional needs. As they become increasingly emotionally engaging, ethical dilemmas may arise, such as the risks of emotional reliance or overly stretched expectations. Paying attention to working around these obstacles will be a chief way that humanoid robots can add to human lives without compromising emotional well-being.
The effectiveness of AI enables further development of emotionally intelligent humanoid robots as they grow to be significant in areas highly reliant on empathy, adaptability, and comprehension. It is the emotional connection that makes these robots transformational. By not being viewed as mere machines, these robots redefine companionship and collaboration by fusing into our everyday lives.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
The integration of humanoid robots into society presents challenges and ethical considerations that extend far beyond initial expectations.
Perhaps the greatest concern is security and privacy. As humanoid robots become deeply embedded in personal and professional spaces, they inevitably handle sensitive data, raising serious questions about how that information is collected, stored, and protected. Without robust safeguards, the risk of unauthorized access to information could undermine public trust and safety.
Intimately related to this is the issue of AI fairness and bias. Robots can mimic creators' biases embedded in algorithms. Correcting these biases ensures humanoid robots treat everyone equally and respectfully.
Technical limitations still hinder the widespread use of humanoid robots. Despite progress, they lack human-like dexterity and mobility. UN AI Adviser Neil Sahota notes that robots struggle with fine motor skills and complex tasks. Real-time perception, decision-making, and control in dynamic environments also demand substantial processing power, often falling short of full autonomy. Energy efficiency remains a challenge, requiring compact, energy-dense power supplies for untethered, long-lasting operation.
The societal implications of humanoid robots are also imperative. Most pressing is the displacement of labor, as automation establishes a foothold in industries that have traditionally relied on human workers. Massive reskilling and the creation of new jobs will be needed to counter the benefits of robotic automation against human life. At the same time, trust and acceptance raise another challenge: not everyone is prepared to cope with humanoid machines, and winning societal trust will require open discussion of their capabilities and limitations.
Overcoming these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach focused on transparency, accountability, and inclusivity. Former Google CEO Eric Schmidt, speaking at Stanford University, emphasized the need for careful AI and robotics design to prevent unintended consequences. Joking that robots are "boring" compared to humans, he highlighted the unique creativity and emotional depth that robots lack.
In short, while the creation of humanoid robots is a tremendous opportunity, it's clear that we're just beginning. With responsible innovation, humanoid robots can be integrated into society enhancing human potential, creating new opportunities, and building a future where technology serves people without undermining our values or well-being.
Future trends
The future of humanoid robots is set to bring more integration, intelligence, and capabilities across various sectors. As technology progresses, several key trends are emerging that will shape the next generation of these machines.
One notable development is the emergence of hyper-realistic robots, where advancements in material science and AI will enable humanoid robots to look, move, and behave almost like humans. Improved emotional intelligence will allow these robots to better understand and respond to subtle human emotions, leading to deeper natural interactions. Recently, Clone Robotics, a startup based in the United States and Poland, introduced its latest creation: the Protoclone V1, a full-bodied synthetic human prototype. With over 200 degrees of freedom, 1,000 Myofibers, and 500 sensors, the faceless android has been referred to as anatomically accurate by the company and is "ground zero for the age of androids." With pneumatics already driving it, the prototype will transition to hydraulic systems. The android uses synthetic systems mimicking human skeletal, muscular, vascular, and nervous structures, which makes it different from other humanoid robots.
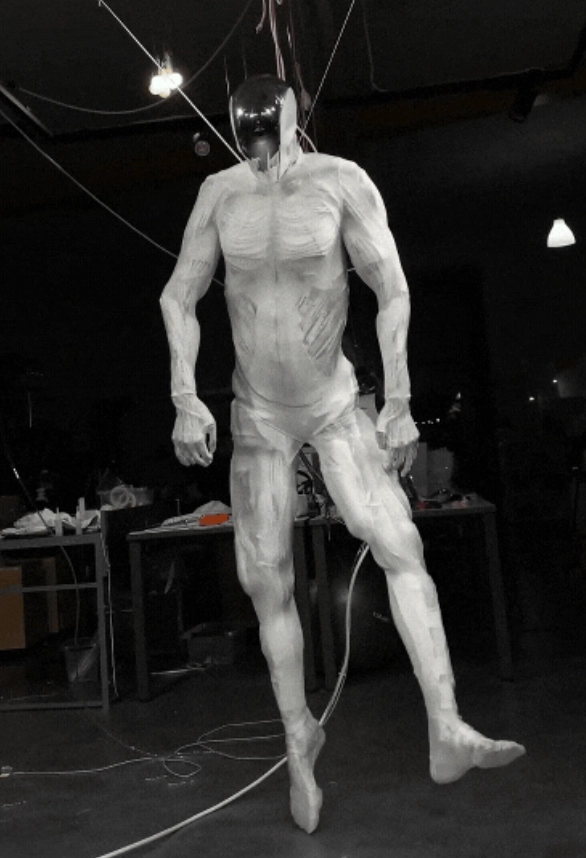

Clone Robotics’ Protoclone V1
Another trend is the growth of collaborative robots (cobots) — robots designed to work safely alongside humans in various workplaces. In addition to their use in service and industrial applications, humanoid robots are being quickly developed for companionship and close contact, with advances in AI creating lifelike robots that offer emotional support, companionship, and romantic engagement. A prime example of this is Melody by Realbotix, which was unveiled at CES 2025. For $175K, Melody can engage in eye-to-eye contact, engage in profound conversations, and remember personal data, offering a personalized companionship experience. Although not intended to be an intimacy doll, she can conduct adult-level conversation.
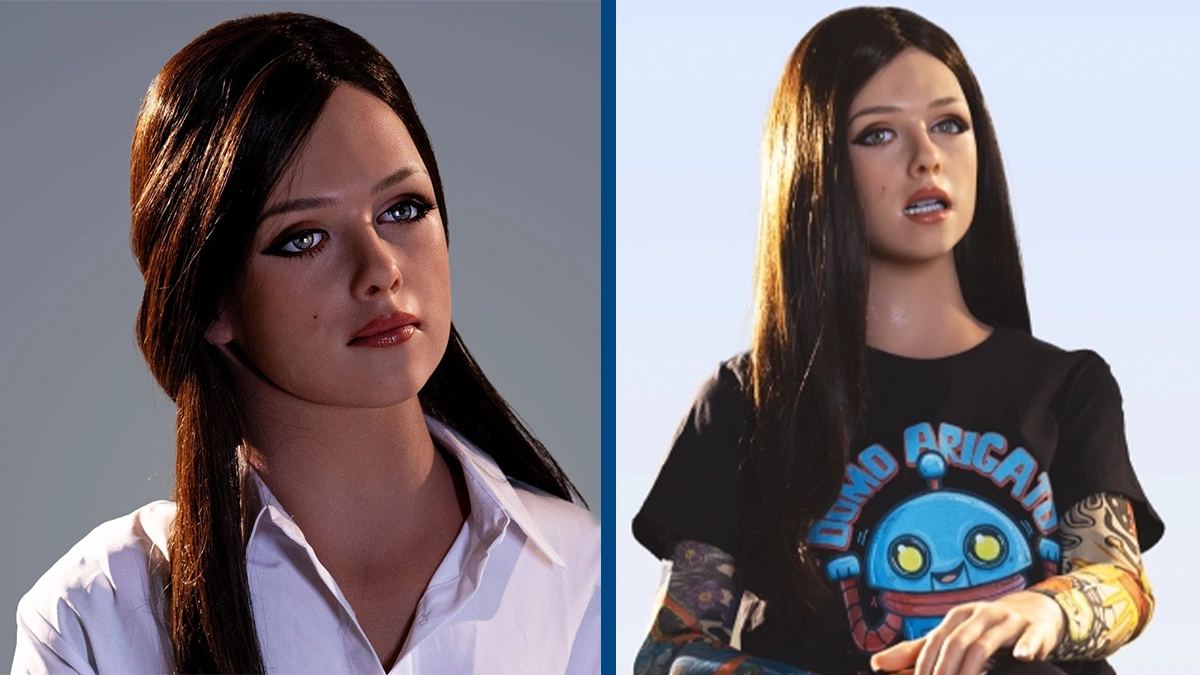

Melody by Realbotix
Conclusion
Once confined to the pages of science fiction, human-like robots of today have come a long way and have been instrumental in changing the face of our society. Gone are the days when such robots existed only in the pages of novels or on movie screens; they are evolving into intelligent, empathetic companions and collaborators that blend seamlessly into industries, homes, and communities. They are improving lives, building comprehension, and advancing in manners that once appeared unrealistic by closing the gap between AI and mankind.
However, the phenomenal rise of humanoid robots is only starting. While innovation is breathtaking, the reality is that humanoid robots are barely present — most humans have not met one on the streets, in a hospital, or an office. Broad-based integration will be a decades-long journey. By prioritizing ethical design, humanoid robots can help build a future where technology serves humanity with intelligence, empathy, and efficiency.




