Automated Guided Vehicles: The Machines That Move Modern Workflows [UPDATED November 2025]
From Vehicle Types to Future Trends. Leading AGV Manufacturers
![Automated Guided Vehicles: The Machines That Move Modern Workflows [UPDATED November 2025]](https://drl.fra1.digitaloceanspaces.com/drl-prod/images/origin/Promo_72_2e65c38013.webp?fit=x1200,x800,x400,x256/width=2400)
In today's world of automation of manufacturing, warehousing, and logistics, Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) have become the pillars of robotization. With the rise of Industry 5.0, AGVs are playing a major role in shaping the future of intralogistics by ensuring the efficient flow of materials through production lines, warehouses, and distribution centers, and keeping the costs down.
This article covers the different types of AGVs, their guidance systems, major applications in industries, and future trends that will continue to fuel innovation in the sector.
Industry 5.0 revolution is all about bringing back the human touch to highly mechanized industries. The focus is on the collaboration of humans with advanced technologies, such as collaborative robots and virtual twins. Humans and robots will work together harmoniously, leveraging each other's strengths to produce spectacular outcomes. This human-oriented approach will make the enterprise more sustainable and resilient, surpassing the dreams of previous revolutions.
Types of Automated Guided Vehicles
1. Cart or Underride AGV
Cart or Underride AGVs transport carts or trolleys by gliding under them, picking them up, or pushing them along a set path. These AGVs are particularly useful in environments where small to medium-sized products must be transported, typically over short distances. Due to its low-profile design, the cart AGV can pass through small spaces and interact with multiple carts at once.
-
Use Case: Frequently used in assembly lines or for material transport between warehouses, where light-weight products or containers are moved between workstations.
-
Capacity: Transport loads ranging from several hundred kilograms to a few tons, depending on the model and the specific configuration of the cart or trolley being carried.
-
Navigation: Primarily uses magnetic tape or laser guidance to move along its route.
-
Example: Moving small containers or carts of parts in a manufacturing facility.
2. Pallet Truck AGV
A Pallet Truck AGV is designed specifically for the transport of palletized goods. It possesses forks that easily glide underneath a pallet to lift and carry it across the ground, much like an ordinary forklift, but automated. Such AGVs are commonly used in environments where ordinary palletized material must be wheeled out of storage areas to other sections of a warehouse or production line.
-
Use Case: Typically in warehouses, distribution centers, and retail operations for moving goods on pallets effectively.
-
Capacity: Transfers standard pallet loads, with capacities depending on the model.
-
Navigation: Usually follows programmed paths through laser navigation, magnetic tape, or optical sensors.
-
Example: Shuttle of pallets of raw materials or finished goods between warehouse locations.
3. Forklift AGV
The Forklift AGV is an automatic version of the conventional forklift truck in its ability to lift, carry, and stack palletized or heavy loads. These AGVs are best utilized in spaces requiring vertical lifting, such as in multi-story warehouses or storage yards. Forklift AGVs can automatically adjust their forks to lift and drop pallets at varying levels.
-
Use Case: Commonly used in high-rack storage systems, distribution centers, and multi-story warehouses where lifting in the vertical direction and precision lifting are needed.
-
Capacity: Capable of lifting heavy payloads, usually of several tons.
-
Navigation: Relying on advanced laser navigation, vision guidance, or SLAM for navigation, pinpointing, and positioning.
-
Example: Automatically transferring pallets between storage stacks in a multi-story warehouse.

Types of AGVs
4. Unit Load or Platform AGV
Unit Load or Platform AGV is applied to transport large, standardized payloads around a warehouse or factory. These vehicles tend to be open, flat platforms that handle several loads, e.g., pallets, containers, or large equipment. Unit Load AGVs tend to be applied where there is a need for flexibility and versatility, as they can be employed to transport goods or workpieces of different nature without additional attachments.
-
Use Case: Used on production lines, assembly stations, or warehouses for shifting heavy and bulk loads that exceed the capacity of usual pallet trucks or forklifts.
-
Capacity: Based on the model, these AGVs can carry heavy loads, typically between a few hundred kilograms to a few tons.
-
Navigation: Like others, Unit Load AGVs use various guidance features, including magnetic tape, laser guidance, or optical sensors to navigate efficiently and safely.
-
Application: Moving bulky assemblies or pieces from one station on the production line to another.
5. Towing Vehicles (Tugger AGVs)
Towing Vehicles, alternatively referred to as Tugger AGVs, are mechanized vehicles with the ability to tow some unpowered carts or trailers behind them. These trucks are particularly appropriate for transporting products across large distances within buildings, such as factories, warehouses, or distribution centers. The towing truck is the motive vehicle, with the commodities being transported by the trailers or carts it pulls behind it.
-
Use Case: Primarily used in manufacturing environments for material transfer between different workstations or for long-distance transportation within a warehouse. They help ease the transfer of products without needing individual handling or additional manual labor.
-
Capacity: Towing vehicles can typically carry multiple tons of material at a time, depending on the number of carts being towed.
-
Navigation: These AGVs often use magnetic tape, laser guidance, or SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) systems for navigation. They follow a precise path, ensuring reliable and efficient transport.
-
Example: Delivering components to assembly stations or moving bulk materials between different areas of a warehouse.
6. Heavy Burden Carriers
Heavy Burden Carriers are tough, self-guided platforms that carry hefty and oversized loads. These carriers are typically used in aerospace, shipyard, and heavy manufacturing industries, where products weigh dozens of tons. Compared to lighter AGVs, which transport lighter goods, heavy burden carriers are designed to be strong and rigid to haul oversized machinery, equipment, or raw materials.
-
Use Case: AGVs like these are normally applied in heavy industry, construction yards, or manufacturing assembly lines for the transfer of heavy parts or assemblies, for example, engine blocks, metal plates, or heavy machinery parts. They become unavoidable in areas where such heavy loads would be inconvenient or even risky to carry manually.
-
Capacity: Heavy Burden Carriers can carry anywhere from several tons up to hundreds of tons based on the model and industrial application.
-
Navigation: For precision and safety, such AGVs frequently employ laser guidance, high-accuracy navigation, or SLAM to navigate down narrow aisles and around obstacles.
-
Application: Moving heavy equipment components in a factory or steel beams on a construction site.
Evolution of AGV Guidance Methods: From Tracks to Autonomous Intelligence
AGVs have evolved through four generations of guidance technologies, each offering increasing levels of autonomy and flexibility.
-
First Generation: Early AGVs relied on electromagnetic guidance or magnetic guidance, where vehicles followed pre-installed metal strips or magnetic tapes embedded in the floor. These methods were simple and reliable but limited to fixed paths.
-
Second Generation: The introduction of image recognition brought greater precision. AGVs began using cameras to read QR codes or AR markers on the floor or ceiling, enabling more flexible and accurate navigation.
-
Third Generation: With laser-based guidance, AGVs used laser beams and wall-mounted reflectors to determine their positions. This allowed more autonomous movement, though it still required significant infrastructure setup.
-
Fourth Generation: The latest systems use SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping), including Visual and LiDAR SLAM. These AGVs navigate complex environments using onboard sensors without external guides, making them highly adaptable and infrastructure-free.
This progression marks a shift from rigid, infrastructure-dependent systems to intelligent, autonomous machines capable of dynamic pathfinding in diverse environments.
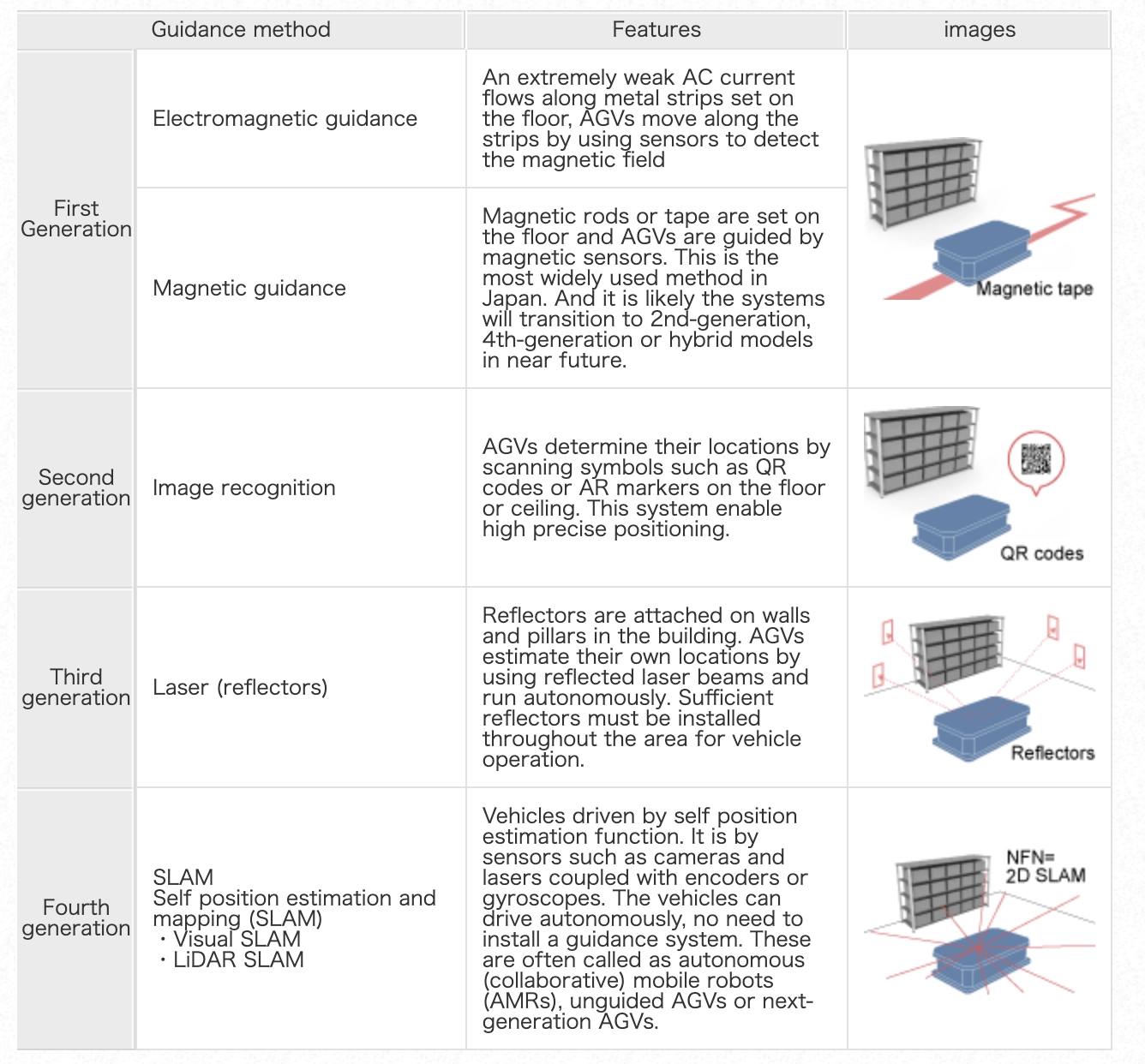
Types of guidance methods for AGVs
Market Landscape at a Glance
Based on public information gathered from Crunchbase, Pitchbook, and other open sources, we have compiled a list of venture-backed startups and large companies that are developing innovative AGVs and related technologies. Explore the companies that are shaping today’s Innovation Landscape in Automated Guided Vehicles, redefining automation, logistics, and material handling across industries.
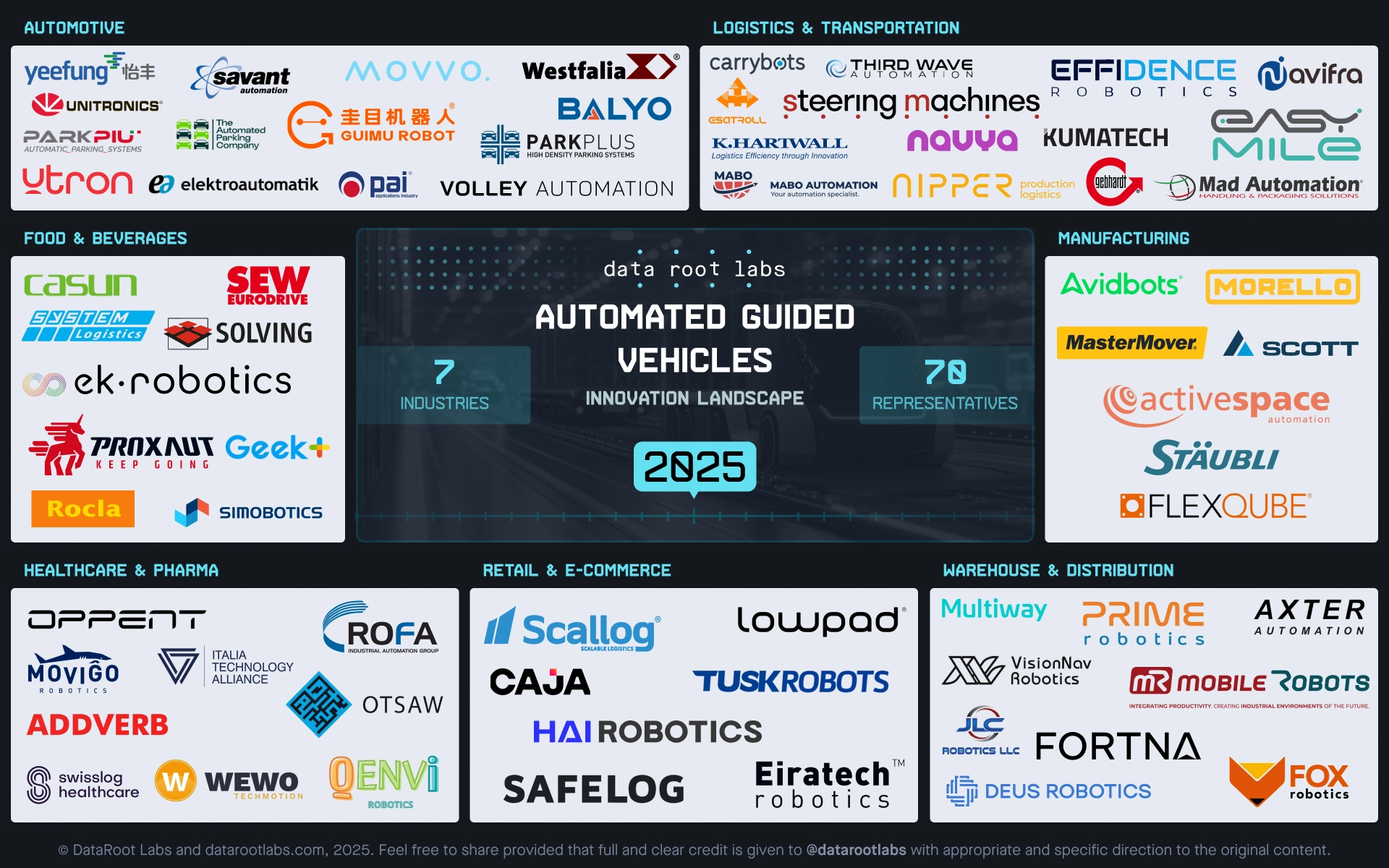
AGV Innovation Landscape
Disclaimer: This landscape is based on publicly available data, company websites, and press materials. Categories are intended to represent major activity areas rather than exclusive focus. We welcome corrections or updates from featured companies..
Applications of AGVs
AGVs are used across various industries to improve efficiency, safety, and productivity. Some of the key applications include:
Automotive
In the automotive industry, AGVs facilitate the just-in-time (JIT) supply of parts such as engines, transmissions, and body components to assembly lines. They deliver materials with high accuracy and timing, which is critical in synchronized manufacturing. AGVs also transport heavy parts through welding, painting, and final assembly stations, improving safety and reducing manual handling.
Another growing application in this sector is the use of automated parking AGVs. The equipment parks and retrieves cars automatically in busy parking facilities or logistics hubs, maximizing space utilization and minimizing the level of human labor involved. Parking AGVs are particularly useful in automobile logistics centers, car dealerships, and city center parking complexes, offering a smart solution for space deficits and traffic congestion problems.
Italian parking systems constructor Parkpiù has patented the PRKT+, a car lift trolley with unique technical features and performance to simplify, speed up, and automate system operations as much as possible. The trolley is equipped with Wi-Fi control technology and consists entirely of small cables to transmit the power and provide the signal to communicate all the information needed to operate it. The trolley also has a single cable for power and is capable of fitting into any car at an extremely low height. The trolley's load capacity for the European market is 2,8K kg. For the Chinese market, Parkpiù has developed a customized trolley with a car lifting speed of 1 m/s. Parkpiù also produced a version for the Middle Eastern market. For the latter, the system was designed to carry a load of 3K kg, taking into account the renowned bulky weight of Arab cars.

Parkpiù Patented PRKT+
Designed by Yeefung, GETA is the next-generation AGV parking system. GETA AGV, with laser navigation technology, can achieve a desired positioning accuracy of ±5mm and maintain its speed up to 1.5m/s. With an average retrieval time of less than 120 seconds, GETA is one of the most advanced automated parking systems currently in circulation.
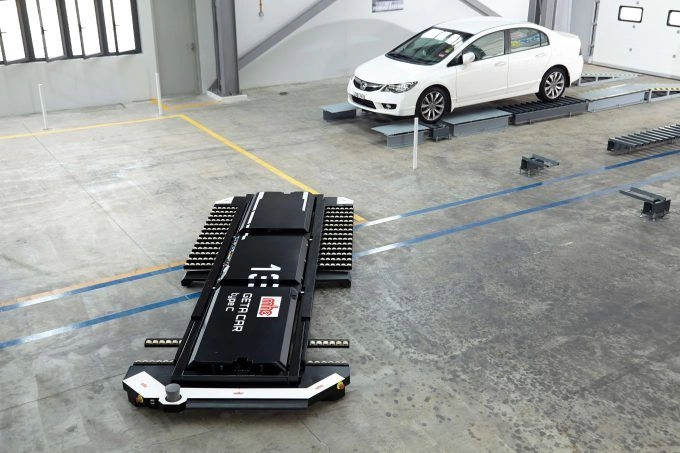

GETA - AGV Parking System by Yeefung
Warehouse & Logistics
In the dynamic warehousing scenario, AGVs are integral to automated storage and retrieval (ASRS) systems. They can transport goods from storage locations to shipping docks or between warehouse sections, reducing manual labor and speeding up operations.
The VisionNav designed VNL20 autonomous pallet stacker to automate warehouse logistics, particularly in transit and distribution centers. It supports high lifting (up to 5m) and handles loads up to 800 kg, making it ideal for multi-level racking systems. Integrated with VisionNav’s Robot Control System, the VNL20 enables automated inbound and outbound operations, standardized pallet handling, and efficient empty pallet management — significantly improving warehouse efficiency, safety, and space utilization.
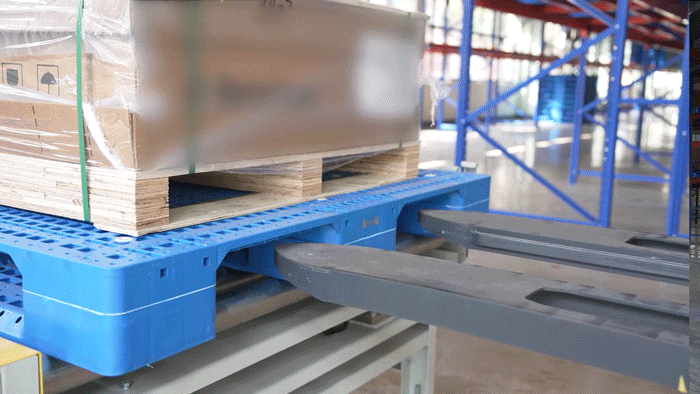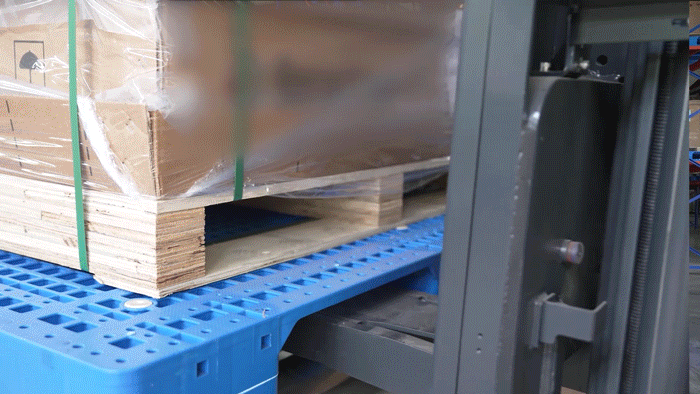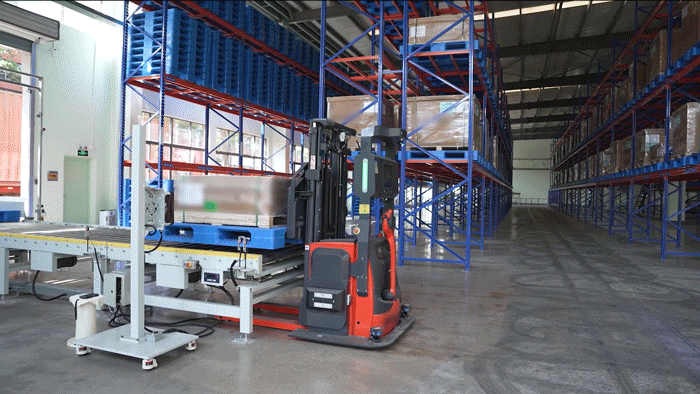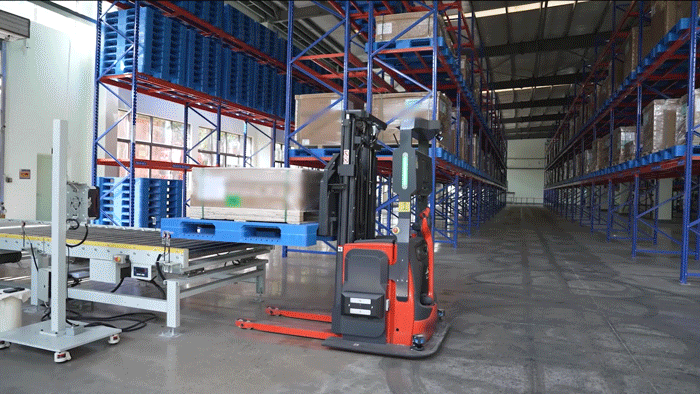
VisionNav pallet truck AGV
Deus Robotics specializes in warehouse and fulfillment automation using advanced robotics and AI technologies. They provide AGVs for pallet, rack, and bin transport, and the Deus S30 sorting robot, which sorts parcels with high efficiency and speed. Their AI-based fleet management system provides real-time coordination, obstacle avoidance, and heterogeneous robot fleet integration. They also offer a scalable Robots-as-a-Service (RaaS) model through which companies can scale their operations cost-effectively based on demand.
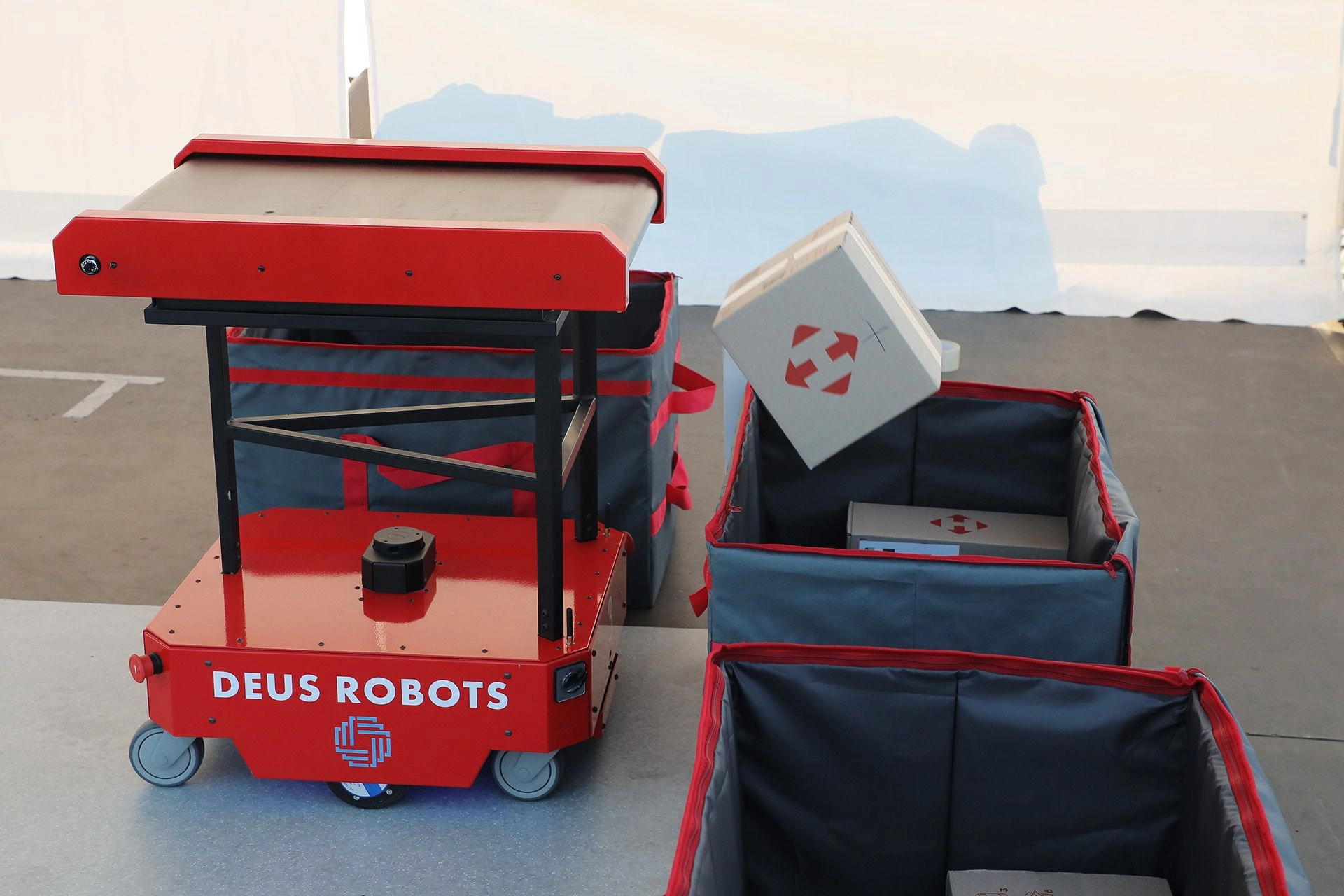

Deus S30 Sorting Robot
Healthcare
AGVs are used in hospitals for multipurpose supply transportation of linens, medications, and meals. AGVs promote cleanliness and order and reduce exposure of humans to potentially infectious items.
Oppent’s AGVs are purpose-built for healthcare logistics, delivering smart, efficient, and hygienic transport solutions for hospitals and medical centers. The ECART AGV is designed for moving meals, linens, waste, and medical supplies, with the agility to navigate narrow corridors and inclines. EROLLER works with roller conveyor systems to automate material transfers in areas with fixed infrastructure. For larger loads, EPALLET handles palletized goods, streamlining warehouse automation and large-scale supply movement. The compact and precise ECOBOT is ideal for transporting smaller items like lab samples or medication kits. ECABINET offers secure, climate-controlled transport for sterile or sensitive materials, featuring modular drawers and shelves for flexible storage. The customizable ONE platform addresses unique logistics challenges across healthcare facilities. Together, these solutions enhance operational efficiency, reduce manual workload, and improve service reliability in medical settings.
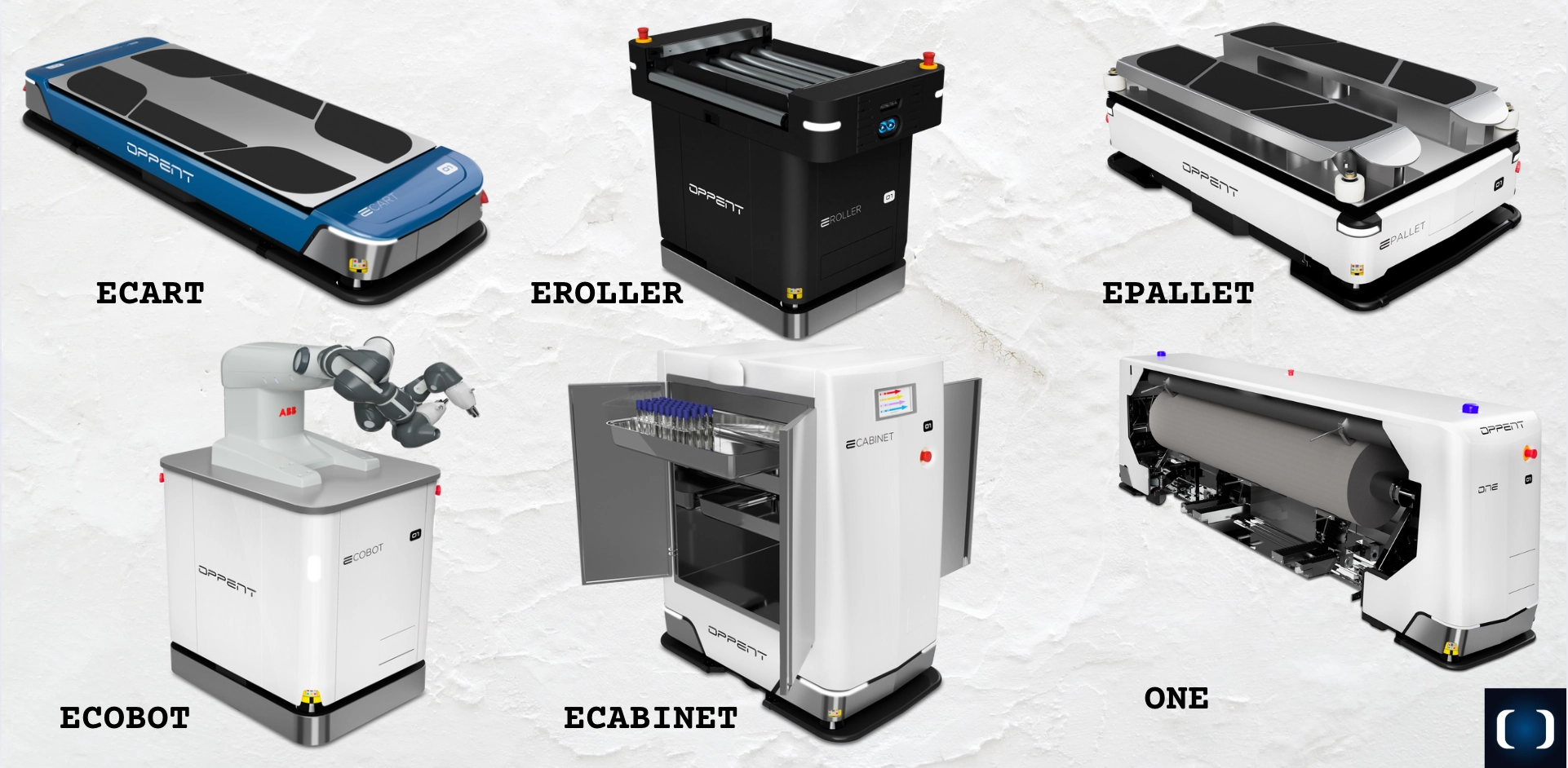

OPENNT Automated Guided Vehicles
Swisslog Healthcare specializes in intralogistics solutions that enhance operational efficiency and patient care. Their AGVs are specifically designed for hospital environments, facilitating the transport of various goods such as meals, linens, medical supplies, and waste.
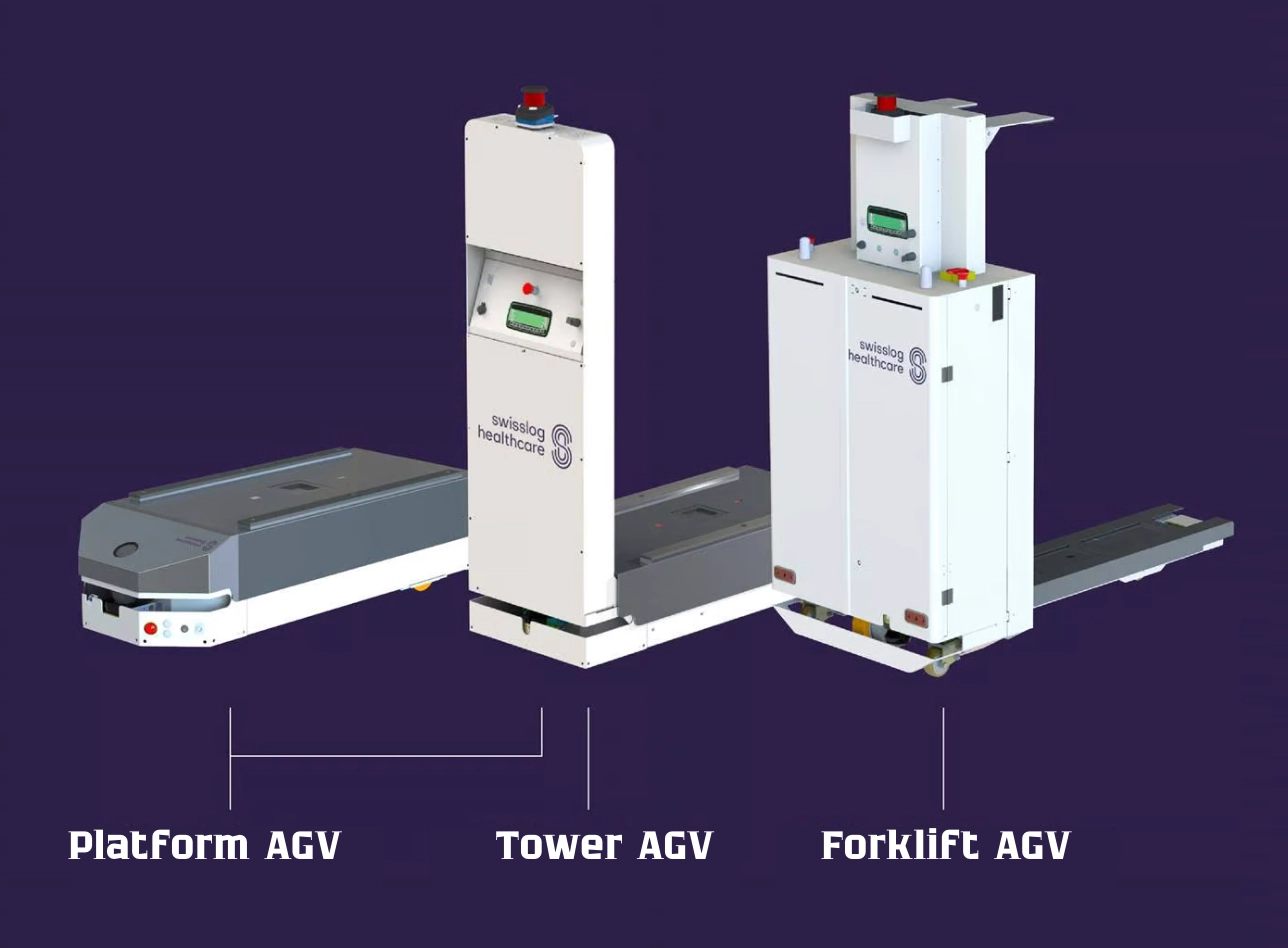
Swisslog Healthcare AGVs
These AGVs utilize advanced laser-guided navigation systems, allowing natural movement without ground infrastructure. They seamlessly integrate with hospital facilities, using corridors and elevators to reach different departments while coexisting safely with staff and patients. The company offers three types of AGVs to accommodate different transport needs:
- Platform AGVs: Designed for containers with a baseplate, suitable for transporting items like meals and linens.
- Tower AGVs: Featuring high visibility for safe interactions within the hospital environment, ideal for various logistical tasks.
- Forklift AGVs: Intended for containers without a baseplate, capable of handling bulkier items, and integrating with existing hospital infrastructure.
Manufacturing
AGVs play an important role in the just-in-time supply of materials so that components arrive on assembly lines as needed. This prevents wastage, conserves time, and increases factory productivity.
Active Space Automation specializes in the development of AGVs for manufacturing environments. Their portfolio of AGVs includes the ActiveONE 2.0, ActiveONE MINI, Active MOD, Active 3, Active Forklift, and Active Tugger, all designed to carry out a variety of material handling and intra-logistics tasks in high-throughput factory environments and warehouses. The AGVs offer flexibility in transporting various materials, enhancing productivity, and reducing logistic processes. By implementing these solutions, manufacturers can achieve efficient, automated processes aligned with Industry 4.0 strategies.

Active Space Automation AGVs
BLEICHERT offers modular AGV systems for manufacturing environments. Their omnidirectional AGVs accomplish such tasks as material transport, assembly line integration, and intralogistics. Some of its key features include SLAM navigation for precise maneuverability, 360-degree safety scanning, and flexibility for various loading possibilities. These AGVs are customized with conveyor elements, lifting tables, and different navigation systems (inductive, magnetic, or optical guidance) to meet specific manufacturing needs. Designed with flexibility and versatility in mind, BLEICHERT's AGVs are intended to optimize efficiency and productivity in manufacturing processes.

BLEICHERT AGV with precise maneuvering capability
Food & Beverages
AGVs in the food and beverage industry handle raw materials, packaging, and finished products under hygiene and timing requirements. They ensure clean-room conditions and minimize human handling of consumables. From moving bottled beverage pallets to carrying ingredients within a production plant, AGVs increase traceability and compliance and improve throughput.
ek robotics engineers and implements AGV solutions designed for the food and beverage industry. Its AGVs attain high levels of hygiene certification and are reliable enough to operate in demanding environments, such as dairy processing and packaging facilities. Notably, at Arla Foods' dairy plant, one of Europe's largest fresh milk dairies, ek robotics installed over 90 dedicated transport robots. Additionally, a German cheese dairy has utilized ek robotics' AGV solutions for over two decades. In 2024, the facility upgraded its system by adding a third, custom-made transport robot, resulting in increased efficiency and flexibility while maintaining high hygiene standards.

ek robotics AGVs on a Milk Production Plant
CASUN, one of the leading AGV manufacturers in China, offers tailor-made automation solutions to food and beverage enterprises. Their vehicles can operate effectively in clean, dust-free, and temperature-controlled environments, making them highly suitable for food production lines, packaging stations, and cold storage warehouses.
CASUN's AGV product series includes various models, such as forklifts, unit load carriers, lift trucks, and custom solutions, all of which are designed to achieve maximum operational efficiency, reduce labor costs, and ensure hygiene compliance. The AGVs offer flexible, cross-line production and real-time monitoring of products, addressing the industry's need for individualized and complex processes.

CASUN AGVs for Food & Beverage
Retail & E-commerce
AGVs are being widely used in fulfillment centers to mechanize product movement. AGVs sort and distribute goods to packaging stations, increasing order fulfillment speed and accuracy. The greatest benefits of AGVs in these industries are greater safety, efficiency, and cost savings through reduced human labor and the potential for fewer accidents.
Dublin-based Eiratech Robotics targets goods-to-person automation solutions in retail fulfillment. Its flagship vehicle, the Eirabot, operates under the Eirasystem – a modular and extensible platform combining autonomous mobile robots, intelligent shelving, and picking stations. In one high-profile deployment for the Benelux region's largest do-it-yourself retailer, Eiratech deployed over 30 Eirabots and built six dedicated picking stations, serving over 33K storage locations.

Eirabot AGV for Retail Fulfillment
Swisslog boasts a full range of AGVs designed to optimize retail order fulfillment processes. Their vehicles assist in safe and efficient product transportation across warehouses. Swisslog's AGV solutions include different vehicle types, such as forklifts, conveyor deck vehicles, and platform AGVs, all intended to fulfill specific operational needs. Designed with flexibility as the primary objective, such AGVs can be easily integrated into current warehouse structures, such as high-bay storage and loading docks, without significant layout changes. Equipped with sophisticated navigation technologies, including real-time communication through Wi-Fi and safety scanners, these AGVs ensure safe and accurate mobility within the plant. The system is also highly scalable, and businesses can expand or shift operations by adding additional vehicles or altering the configuration as needs evolve.
These AGV systems are also extremely helpful to retailers who want to streamline their logistics activities. They offer greater efficiency, reduced labor expenditure, and increased reliability of material transport.

Swisslog AGVs
In the table below, we list companies together with their funding, investors, and a short description of what they do to provide a clear overview of the current AGV market landscape.
| Company | HQ / year founded | Amount Raised, $ | Investors | What they are doing |
| Active Space Automation | Portugal / 2004 | — | — | Provider of AGVs and robotics designed to deal with harsh environments. It offers software for managing the fleet operations of AGVs. Its products include AGVs for towing objects, hydraulic lifting, Pinhook vehicles, forklift AGVs, etc. |
| Addverb | USA / 2002 | $132M B | Reliance Industries | Addverb offers innovative automation solutions with intelligent robots, powered by modular software. |
| Avidbots | Canada / 2014 | $106.4M D | 500 Global, Felicis, Golden Ventures, others | Developer of fully autonomous cleaning robots, specifically the Neo autonomous floor scrubber, powered by AI for large commercial and public spaces. |
| Axter Automation | France / 1992 | — | — | They build AGVs such as pallet trucks, stackers, tractors and custom carriers, support flexible navigation & routing, and provide a real‑time “AGV Supervisor” system for managing missions and analytics. |
| Balyo | France / 2005 | $11.8M Post-IPO | Bpifrance, Amazon, Seventure Partners, others | Balyo designs, develops and markets material handling robots. The robots are used by industrialists and logisticians to reduce their pallet handling costs by robotizing their equipment and improving the security of the spaces in which it operates.navigate autonomously inside buildings - without the need for any additional infrastructure. |
| Caja | Germany / 2017 | $12.6M B | New Era Capital Partners, Kima Ventures | Developer of an order fulfillment technology intended to facilitate the transition to automated warehouses with systems and flexible robotics. |
| Carrybots | Germany / 2021 | — Accelerator | UP2B Accelerator, Flexlog | Manufacturer of AGVs. The company's automated driverless robotic vehicles provide intralogistics services, aiming to enable companies to get started with transport automation. |
| Casun | China / 2007 | $9.3M — | Northern Light Venture Capital, Dami Ventures, others | Developer of industrial robotic auxiliary system and AGVs designed for material handling and lifting. |
| Deus Robotics | Ukraine / 2019 | $4.6M Non Equity Assistance | Google for Startups, 1991 Ventures, u.ventures, others | Developer of robotics software intended to unify warehouse robots from any brand into one intelligent system and enhance them. |
| EasyMile | France / 2014 | $89M B | Bpifrance, Searchlight Capital Partners, others | EasyMile develops software to automate transportation platforms without the need for dedicated infrastructure. EasyMile’s cutting-edge technology is revolutionising passenger and goods transportation, offering completely new mobility options. |
| Effidence | France / 2009 | — | Sofimac Investment Managers | Developer of autonomous robotic systems designed to optimize workflows involved with logistics, industry, and last-mile delivery markets. |
| Eiratech Robotics | Ireland / 2014 | — | — | Eiratech Robotics is an innovator of a complete goods-to-person robotics automation platform for multiple applications, including e-fulfilment, materials handling, kitting and retail, and developing into a seamless, end-to-end goods-to-consumer digital e-commerce experience. |
| EK Robotics | Germany / 1980 | — | — | EK Robotics is a manufacturing company that offers logistics consulting, automated guided vehicles, and industrial automation services. |
| Elektroautomatik | Sweden / 1965 | — | — | Provider of industrial automation services catering to the manufacturing sector and family businesses. The company offers automation, material handling, packaging, processing, assembly line and machine services to automation, medical and healthcare, food and beverages and logistics sectors. |
| Esatroll | Switzerland / 1995 | — | — | Esatroll specializes in the development and production of automated shuttles, technology, and navigation systems for the industrial sector. |
| FlexQube | Sweden / 2010 | $12.5M Post-IPO Equity | Danske Bank, ALMI Tillväxtlån | FlexQube develops and offers a flexible system of few standardized components that can be used to build industrial material handling applications like pallet carts, racks, kit carts, and fixtures. |
| Fortna | USA / 1946 | — | — | Manufacturer of material handling automation systems catering to electronics, food and beverage, parcel, retail, healthcare, and other industries. The company's products support a variety of material handling processes such as conveying, sortation, singulation, and scanning, and are backed by in-house software, thereby clients to keep pace with digital disruption and growth objectives. |
| Fox Robotics | USA / 2017 | $37M B | Menlo Ventures, SignalFire, Foothill Ventures, others | Manufacturer of self-driving forklifts intended to load and unload trailers in an automated environment. The company's forklifts can increase workplace productivity up to two to three times and can be feasibly integrated into the warehouse system, enabling companies to automate their workplace while reducing environmental impact. |
| Gebhardt | Germany / 1952 | — | — | Manufacturer of automated handling systems intended for material transport and logistics optimization purposes. |
| Geek+ | China / 2015 | $539.4M E | Vertex Ventures, Warburg Pincus, others | Geek+ offers a series of AGV solutions to empower warehouse fulfillment and industrial material transport, enhancing supply chain efficiency while reducing reliance on manual labor. |
| GUIMU Robot | China / 2016 | $5M A | Digital China Investment, Bojiang Capital | The company offers special machines and motion control systems, assembly stations, quality control systems, intralogistics, and palletizing systems, also researches and develops artificial intelligence, and intends to create integrated systems for production, internal logistics, and data management. |
| HAI ROBOTICS | China / 2016 | 285M D | HSG, Walden International, Source Code Capital, others | Manufacturer of robotics and artificial algorithms intended for apparel, retail, grocery, healthcare, electronics and automotive industries. The company's warehousing technologies leverage artificial intelligence and robotic technology to improve warehouse functions, enabling warehouse operators to improve working efficiency and automate storage functions. |
| JLC Robotics | USA / 2022 | — | — | "Industrial automation distributor that specializes in simple, powerful AGV and robot fleet solutions.
They primarily offer the Thouzer AGV, a cost-effective automated guided vehicle, and CaPow Genesis, a perpetual power system that charges robots while they move. |
| K.Hartwall | Finland / 1932 | — | — | K. Hartwall’s A-MATE® line delivers advanced AGV solutions — from the nimble and powerful FreeLift, to the space-efficient Counter, and versatile Lite model. These robots automate logistics with high precision, safety, and adaptability. |
| Kivnon | Spain / 2007 | — | — | Manufacturer of robotic systems intended to support material handling and intralogistics operations for industrial businesses. |
| Kumatech | Netherlands / 2018 | — | — | Offers robust and cost-effective AGV solutions designed to automate internal logistics by transporting pallets, carts, and racks between machines in industrial settings. |
| Lowpad | Netherlands / 2017 | — | — | Lowpad provides autonomous mobile robots for optimizing internal logistics and distribution, capable of transporting various pallet types. |
| Mabo Automation | Belgium / 2010 | — | — | Mabo Automation supports and integrates automation projects and specializes in AGVs. These tailor-made machines fully automate the internal logistics of a production/logistic facility. |
| Mad Automation | Italy / 2007 | — | — | Designs and manufactures Laser AGVs for automated material handling within industrial processes. |
| Master Mover | UK / 1997 | — | — | Specializes in high-performance AGVs designed to transform material handling operations, offering a broad range of electric tugs with advanced navigation and safety capabilities. |
| MLR System | Germany / 1971 | — | — | MLR System manufactures specialized AGV systems for use on in-plant transportation, material flow, and warehousing. |
| Morello | Italy / 1946 | — | — | Morello manufactures a wide range of trucks, AGV self-propelled trailers, industrial trailers, rolltrailers, lifting platforms and tilters operating in many manufacturing sectors. |
| Movigo | Netherlands / 2018 | — | — | The company focuses on developing and implementing Industry 4.0 AGV solutions, specializing in horizontal pallet transport and custom-built AGV robots. |
| Movvo. | Spain / - | — | — | MOVVO Móviles offers smart intralogistics forklifts equipped with sensors and advanced software to optimize material handling within warehouses. |
| mR Mobile Robots | Germany / 2019 | — | — | "Manufacturer‑independent integrator of autonomous mobile robots (AMR/AGV) for intralogistics.
They design, install, and service customized AMR systems (including pallet transport, KLT/parts transport, and cobot‑palletizing), integrating fleet management and connecting robots to ERP/WMS systems. |
| Multiway Robotics | China / 2019 | $56M B | Plum Ventures, Cyber Creation Ventures (CCV), others | Multiway Robotics is a provider of intelligent intralogistics solutions, specializing in autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) and automated forklifts. |
| Navifra | South Korea / 2022 | $4M / Seed | FuturePlay, HL Mando Aftermarket | Navifra offers self-driving logistics robots and integrated robot control system for monitoring multiple robots. |
| NAVYA | France / 2014 | $117.3M Post-IPO Debt | European Investment Bank, 360 Capital, others | Navya designs, manufactures and markets a range of autonomous, driverless and electric vehicles. It offers a range of two autonomous vehicles: the shuttle Autonom and the Autonom Cab robot-taxi. |
| Nipper | Netherlands / 2013 | — | ECFG | Manufactures compact automated vehicles for unmanned internal pallet transport, provider of AI & web-enabled autonomous pallet trucks. |
| Oppent | Italy / 1960 | — | UP2B Accelerator, Flexlog | Oppent develops innovative solutions for the logistics industry, and recently, has developed an AGV called EVOcart. |
| Otsaw | Singapore / 2015 | $22.2M IPO | MassRobotics, Serial System | Otsaw designs, develops, manufactures various advanced AI-enabled AMRs, Ultraviolet-C (UV-C) disinfection systems, hospital intralogistics AGVs and other robotics solutions, which are empowered by its proprietary core robotics software and outdoor autonomy technology. |
| Pai Applications Industry | Spain / 1970 | — | — | PAI Applications Industry designs and manufactures machinery for handling and controlling loads. |
| Parkpiu | Italy / - | — | — | Parkpiù designs, constructs, and maintains automated parking systems. |
| ParkPlus | USA / 1969 | — | — | ParkPlus is a designer, manufacturer, and installer of automated parking systems. |
| Prime Robotics | USA / 2015 | $2M — | — | Developer of industrial automation robots designed to facilitate warehouse management. The company's robots are for clients in all facets of the supply chain and empower companies to accelerate and optimize their value chain ecosystem, providing businesses with a suite of robots that collaborate to fulfill the needs within a warehouse. |
| Proxaut | Italy / 1996 | — | — | The company offers products including AGV loaders and AGV lifters along with supervision and control softwares, thereby allowing to receive any change in status from the vehicles. |
| Qenvi Robotics | France / 2008 | — | — | QENVI Robotics develops autonomous and semi-autonomous mobile robots capable of carrying heavy loads. They combine robotics with AI, embedded systems, and fleet‑management software, offering tailored solutions for inventory handling, transport, and logistics. |
| ROCLA | Finland / 1942 | — | — | Rocla AGV Solutions, part of Mitsubishi Logisnext Europe’s AGV operations, develops, manufactures, and markets electric warehouse and counterbalance trucks, automated guided vehicle systems and provides complete services throughout their lifecycle. |
| Safelog | Germany / 1996 | — Pre-Seed | Antler | SAFELOG provides complete and robust intralogistics solutions with a variety of mobile robot offerings and picking systems. |
| Savant | USA / 2005 | — | — | Savant Automation sells, engineers, installs, and services a full line of AGV Systems, including automatic guided carts, unit load carriers, tow units, fork units, and automatic truck loading units. |
| Scallog | France / 2013 | $8.5M — | WILCO, Colruyt Group, others | Developer of robotic products designed to help automate the process of warehouse logistics. |
| Scott | New Zealand / 1913 | — | — | Scott designs and manufactures automated production, robotics, and process machinery. |
| SEW Eurodrive | Germany / 1931 | — | — | Manufacturer of drive technology intended to optimize industrial automation and motion control. Their MOVI‑C® modular automation system integrates drive technology, motion control, control hardware, and software. |
| Simobotics | Bulgaria / 2021 | — | — | Simobotics designs and manufactures innovative autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) for material handling across various industries. Their modular AMHR combines AMR, AGV, APR, and IMR functionalities, offering rapid deployment, flexible applications, AI-based pallet recognition, and fast charging. |
| Solving | Finland / 1977 | — | — | Specializes in the design and manufacture of automated load handling systems. Their products range from simple hand-controlled devices to highly sophisticated automated handling systems using both air bearings and wheels. |
| Stäubli | Switzerland / 1892 | — | — | Manufacturer of electronics and mechanical engineering products intended for textile plants and heavy equipment manufacturing businesses. |
| Steering Machines | Spain / 2019 | — | Brinc, Bind 4.0, Keihanna Global Acceleration Program | Steering Machines facilitates the development of new autonomous mobile robots (AMR/AGV). Their robot MOBY is a patented omnidirectional mobile robotic platform that uses conventional wheels. |
| Swisslog Healthcare | USA / 2018 | — | — | Developer of AGVs designed to help hospitals take control of their on-demand and routine material transport activities. |
| System Logistics | Italy / 1986 | — | — | Developer and supplier of intra-logistics and material handling systems catering to food and beverage, distribution and cold storage industries. |
| Taiprora | Italy / 1993 | — | — | The company offers special machines and motion control systems, assembly stations, quality control systems intralogistics and palletizing systems also researches and development artificial intelligence and intends to create integrated systems for production internal logistics and data management. |
| The Automated Parking Company | USA / 2000 | — | — | The Automated Parking Company designs, builds, and services advanced automated parking systems. Their core mission is to help real estate developers and architects maximize parking capacity in urban projects, while reducing costs, footprint, and environmental impact. |
| Third Wave Automation | USA / 2018 | $97M C | Norwest Venture Partners, Eclipse Ventures, others | Manufacturer of an autonomous forklift technology designed to deliver general, robust, precise, and correct automated movement of material and inventory. |
| Tusk Robots | China / 2020 | — A | ZhenFund, 01vc, Huolala, Engage Capital, Zero One Ventures | Operator of a robotics company intended to empower intelligent logistics in smart factory. The company develops intelligent pallet robots that are widely applied in fields of medicine, electronics, auto parts, tobacco, chemical industry, supermarket, shoes and clothing, and eCommerce, providing enterprises with handling solutions and enabling intelligent logistics and smart manufacturing. |
| Unitronics | Israel / 1989 | $47M Post-IPO | Amber Group | Provides critical AGV control hardware and software like PLCs, HMIs, variable frequency drives (VFDs), servo drives, and I/O modules. |
| Utron | USA / 1989 | — | — | Utron provides automated and semi-automated parking systems for real estate developers, architects, and parking operators. |
| VisionNav Robotics | USA / 2016 | $130M C | Meituan, ByteDance, others | Developer of automated guided industrial vehicles designed for intralogistics and warehousing scenarios. |
| Volley Automation | USA / 2018 | $25.2M A | Thursday Ventures, Rudin Ventures | Developer of parking technology designed to solve parking problems. The company's technology uses robotics and cloud computing to densify new and existing parking assets. |
| Westfalia | USA / 1992 | — | — | Westfalia specializes in the design and installation of warehouse automation systems, specifically high-density, unit-load automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) and automated parking systems. |
| Wewo Techmotion | Netherlands / 2006 | — | — | Specialises in AGVs that are used for moving materials and products in various environments. |
| Yeefung | China / 2003 | $1.52M Angel | Fuhai Yintao | Developer of automated robotic parking systems intended to deliver efficient, reliable and sustainable parking fixes. |
Future Trends in AGV Technology
Here are a few upcoming trends that are shaping the way AGVs will operate:
-
AI and Machine Learning. AGVs are becoming intelligent as they integrate AI and machine learning. The technologies allow them to re-route in real-time, better avoid obstacles, and adapt to shifting environments.
-
5G and IoT Integration. The introduction of 5G and the Internet of Things is enabling real-time communications between AGVs and other equipment in a networked environment for better coordination in places with several vehicles working in parallelly.
-
Hybrid Systems (AGVs + Humans). In the future, we can expect hybrid systems where humans and AGVs collaborate in more complementary manners. Such vehicles will perform repetitive or heavy tasks, and humans will perform more complex or decision-based tasks.
-
Transition from AGVs to AMRs. There is a shift towards Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), which are more adaptable and can navigate dynamic spaces without needing pre-defined paths. As their technology becomes more affordable, AMRs will become more prevalent.
-
Sustainability. The future of AGVs also focuses on sustainability, with more focus on electric vehicles and energy efficiency. As industries shift towards greener options, AGVs will assist in reducing the carbon footprint of manufacturing and logistics operations.
Conclusion
Automated Guided Vehicles have evolved from simple material handling systems to sophisticated, smart machines, revolutionizing industrial processes. From their diverse range and advanced navigation methods to their growing uses across industries, AGVs are spearheading the automation revolution. Looking forward, AGVs will continue to take the lead in innovation, as advancements in AI, IoT, and sustainability unlock the way for even more agile, efficient, and sustainable solutions. The flexibility and constant innovation of AGVs will remain a key to keeping them at the heart of intralogistics in the digital age.
DataRoot Labs’ Role in Autonomy
DataRoot Labs has extensive expertise in autonomy solutions. With our own R&D team in reinforcement learning, we are privileged to be a partner of choice of startups and enterprises in autonomous driving and greater autonomy. Our expertise includes:
- Autonomous Transportation & Mobility
- Autonomous Business & Workflow Automation
- Autonomous Decision-Making Systems
- Self-Learning & Adaptive Models

DataRoot Labs is a trusted partner in autonomous solutions
To find out more about DataRoot Labs' contribution to the development of Automated Guided Vehicles, contact our team. We excel at reinforcement and deep learning, and autonomous solutions.
Have an idea? Let's discuss!

Talk to Yuliya. She will make sure that all is covered. Don't waste time on googling - get all answers from relevant expert in under one hour.

![AI in Logistics: Emerging Startups, Challenges and Use Cases [UPDATED 2024]](https://drl.fra1.digitaloceanspaces.com/drl-prod/images/origin/ai_in_logistics_emerging_startups_2024_71afef795f.webp?fit=x1200,x800,x400,x256/width=2400)


