AI-Driven Agents for HR and Recruitment
How Agentic AI Shapes Talent Management and Employee Engagement.

In today’s fast-paced business world, Human Resources teams increasingly use AI agents to improve employee experiences, expedite processes, and drive decision-making. From hiring to staff development and beyond, these intelligent solutions completely change how businesses handle talent.
According to a PwC study, 75% of HR executives say AI has improved recruitment efficiency, with AI cutting the time to hire by 30-50%. While 53% of execs see AI agents as being core to business operations in the next two years, only 29% of IT practitioners see that coming to pass, according to a new survey from uptime monitoring vendor PagerDuty.
In HR, AI is emerging as more than just a catchphrase; it is a valuable tool transforming routine processes. Let's explore the impacts of AI voice and text agents, their challenges, and the future opportunities for HR technology.
AI Agents, their types, and how they work
AI Agents are sophisticated computer program systems that can interact with users in words, either spoken or written, performing tasks and providing information on their own. They can operate through technologies such as Natural Language Processing (NLP), Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), and Text-to-Speech (TTS) to facilitate fluent, human-to-human conversations.
The adoption rate of AI agents within businesses is poised to increase significantly in 2025. Deloitte asserts that 25% of businesses utilizing generative AI will deploy AI agents in 2025. This is set to increase even more to 50% by 2027.
AI agents are categorized based on their simplicity and decision-making authority:
- Simple Reflex Agents react based on the current percept; nothing else from the percept history is relevant. They use condition-action (if-then) rules and can manage simple tasks in fully observable domains. An example would be a thermostat that generates heat whenever the temperature drops below a predetermined value. It acts as a simple reflex agent.
- Model-Based Reflex Agents possess an internal state derived from the percepts' history, and they can handle partially observable worlds. They use the internal model during decision-making to perform more complex behavior than simple reflex agents.
- Goal-Based Agents act to achieve definite goals. They plan in terms of actions and consequences, choosing actions that move them closer to their goals. Such agents are required where mere reaction will not suffice and there is a need for careful planning.
- Utility-Based Agents account for many potential actions and select the action that optimizes their utility function, which captures their preferences. They can, thereby, deal with trade-offs and uncertainty and pursue the best available outcome.
- Learning Agents have the capability of developing performance through experience after some duration. They consist of elements such as a learning component, a performance component, a critic, and a problem generator through which they learn how to handle unfamiliar situations and refine decision-making capabilities.
In multi-agent systems, multiple AI agents interact within a shared environment. These agents can collaborate or compete, and the system's overall behavior emerges from these interactions. Such systems are used in complex applications like traffic management, where multiple autonomous vehicles must coordinate their actions.
The functioning of AI agents involves several core processes:
- Input Recognition: AI agents capture input in the form of text, speech, or data from internal human resource systems, such as performance reports, feedback from employees, or resumes.
Voice Agents: Utilize ASR to convert speech into text. This involves accepting audio input, suppressing background noise, and transcribing voice with precision.
Text Agents: Operate on textual input directly, analyzing the text and user intent.
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Once the input has been translated to text, NLP algorithms process the meaning, context, and intent of the words. This includes extracting meaning from syntax, semantics, and human aspects of language.
-
Decision-Making: Based on the translated input, the agent determines the appropriate response or action. This may involve inquiring about databases, fetching external services, or performing calculations to yield a relevant reply.
-
Response Generation: The agent generates a consistent natural language reply. For voice agents, the text is resynthesized to speech by TTS technology for oral interaction with the user.
-
Learning and Adaptation: The agents learn constantly through interaction via machine learning techniques, improving their understanding and replying progressively. The adaptability in this learning makes the agents increasingly skilled at handling disparate requests and possessing more advanced interactions.
These agents are used across various applications, including virtual assistants such as Alexa and Siri, to support chatbots for customers and auto-reservation tools, providing practical and scalable alternatives to engage users. Apple recently attempted to enhance its virtual personal assistant to deliver intelligence that’s tailored to the user and their on-device information. However, the company's failure to deliver these features on time has led to criticism, legal challenges, and questions about its innovation strategy.
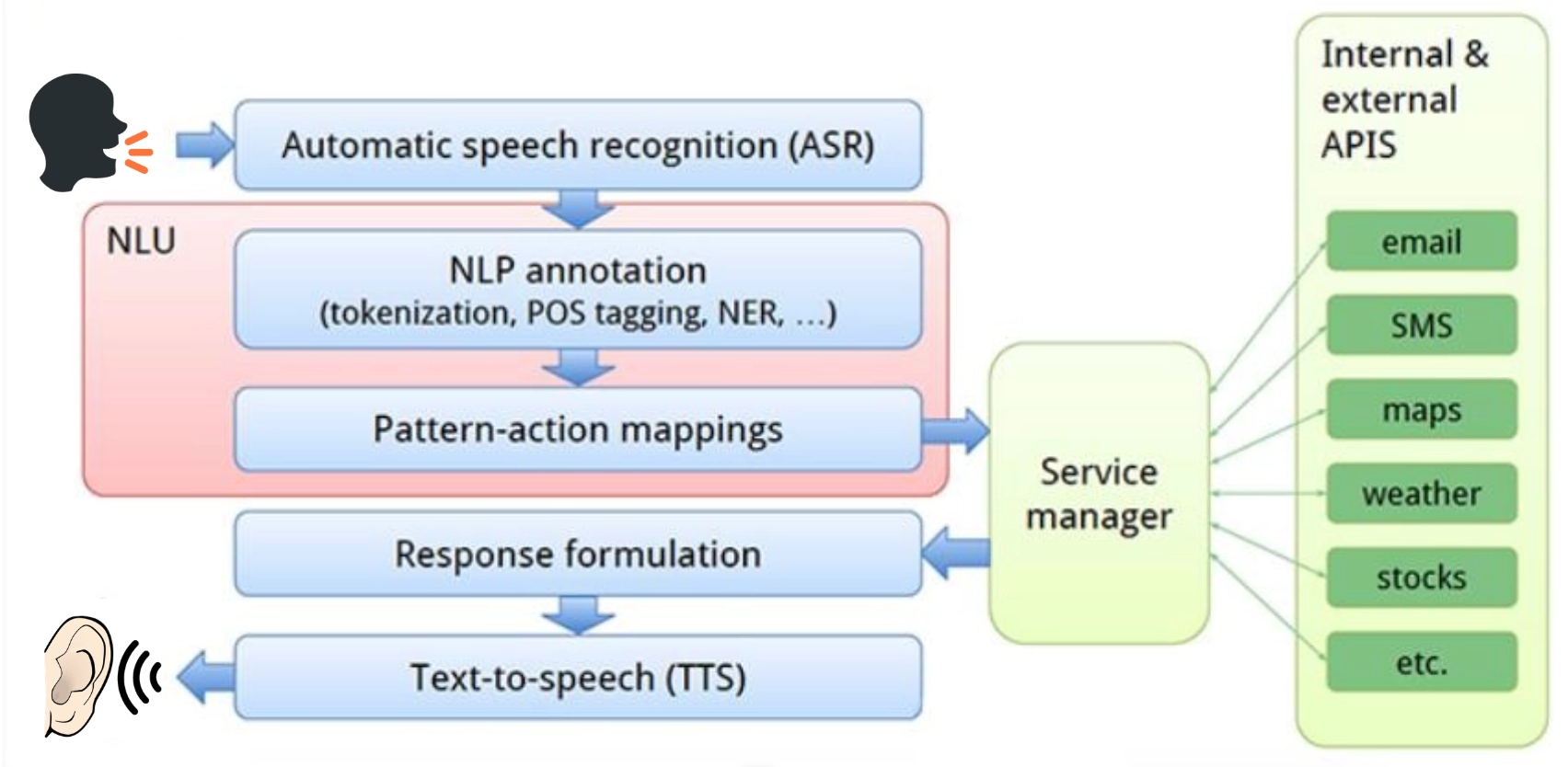
How Siri works
Based on public information gathered from Crunchbase, Pitchbook, and other open sources, we have compiled a list of venture-backed startups that leverage AI to transform parts of HR and Recruitment function. Check out the innovative companies that constitute today's Innovation Landscape in AI in HR and Recruitment.

AI driven agents for HR and Recruitment
AI Agents in HR and Recruitment
Smart agents, which support a variety of tasks throughout the employee's lifetime, are among the most promising uses of AI in Human Resources. These technologies have the following effects:
Recruitment and Onboarding
By conducting preliminary candidate screenings, setting up interviews, and responding to frequently asked questions, AI-powered chatbots expedite the hiring process and drastically cut time-to-hire. Voice agents also provide interactive onboarding experiences, helping new hires navigate business policies and documentation to ensure a seamless and interesting beginning to their career with the organization.
The most exciting advancement that AI brings to recruiting is automated screening calls. Wayfaster, an AI-powered recruitment platform, automates candidate screening through human-like voice interviews, enabling companies to conduct interviews 10 times faster and at a fraction of the cost. By integrating with Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS), Wayfaster streamlines the hiring process, allowing recruiters to efficiently identify top talent and fill roles more quickly.
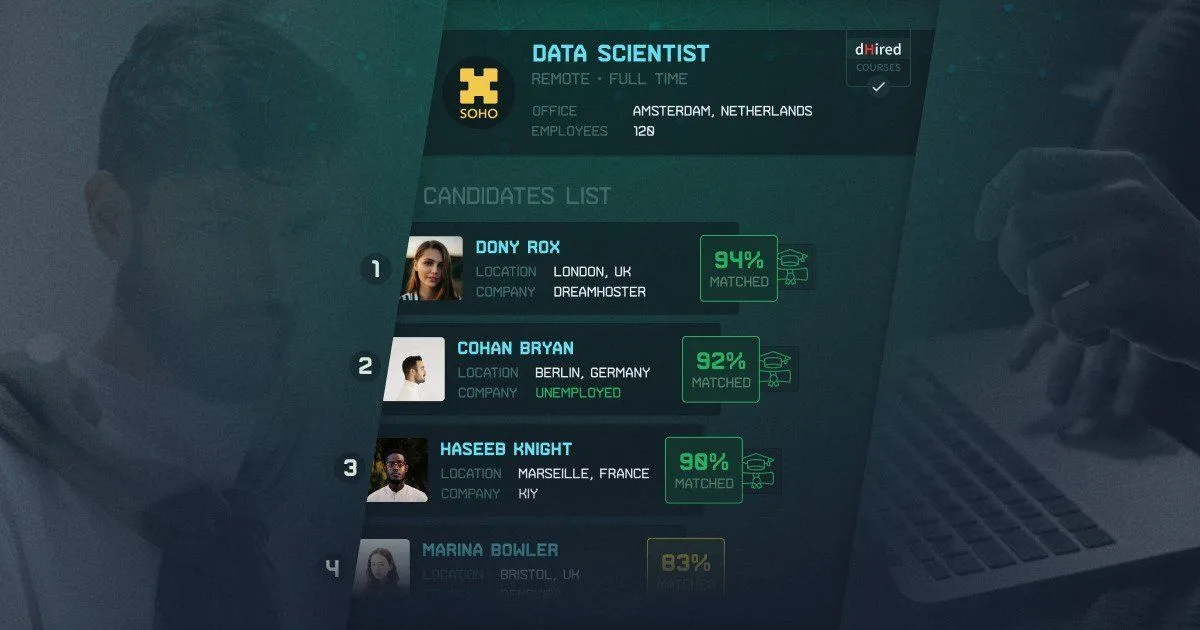
In a variety of interviewers, there is also Sara, Kiku’s AI agent for recruitment, which is designed to automate and enhance the hiring process. Sara helps HR teams by screening resumes, conducting initial candidate interviews, and evaluating applicants based on predefined criteria. It uses AI to analyze candidate data, identify the best-fit candidates, and streamline communication. Kiku focuses on high-volume recruitment for frontline workers in service, fast food, construction, warehousing, and logistics.
Candidate evaluation process by Sara, Kiku’s AI agent
For recruiting and onboarding, AI-powered assistants like Rootle and Gecko come in handy. Rootle automates candidate outreach through voice-based conversations and engages candidates at their preferred times, assessing their interest and suitability for roles, thereby enhancing recruitment efficiency. By automating repetitive pre-screening calls, Rootle enables recruiters to focus on interested candidates, increasing reach and improving hiring quality. Gecko's text-based AI capabilities include automated resume parsing, personalized email campaigns, persistent follow-ups, candidate pre-assessments, sentiment analysis, and comprehensive reporting, which helps engage candidates effectively and enhances hiring efficiency.
Gecko Text-based AI Capabilities
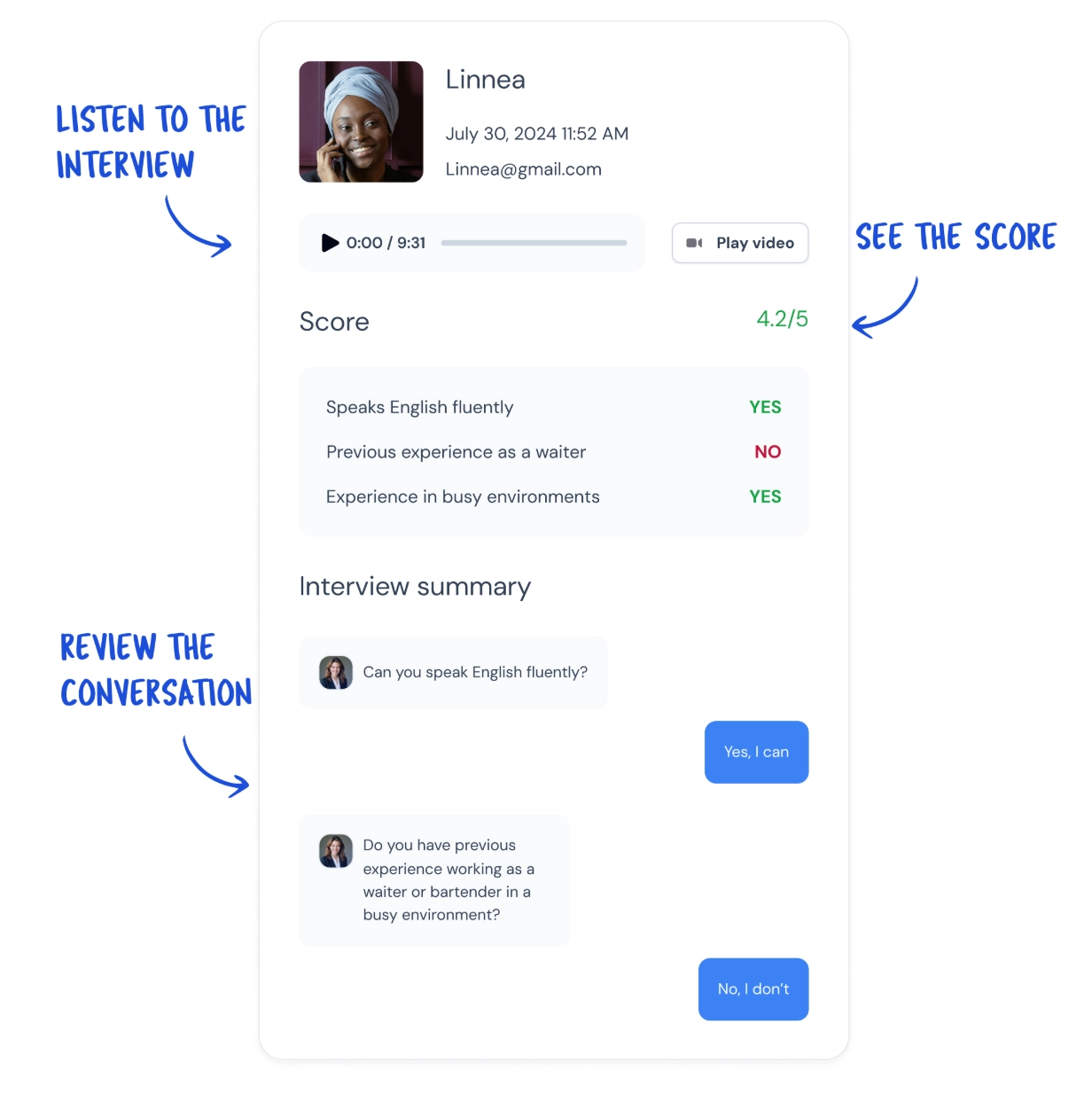
Skills assessment is one of the steps of the recruiting process. Here, AI also brings a lot of capabilities. For example, TalkScore Tests is a language testing software that leverages AI and is adapted to test the English proficiency of candidates and employees through natural, conversational means. It applies various questions, such as open-ended, listen-and-repeat exercises, and listen-and-speak training, so candidates or employees can respond by voice or video on platforms of their choice, such as Messenger, WhatsApp, and web.
While TalkPush is primarily a recruitment automation tool, its features indirectly aid in employee performance management by ensuring the recruitment of candidates with the required language skills, thereby enabling a more effective workforce.
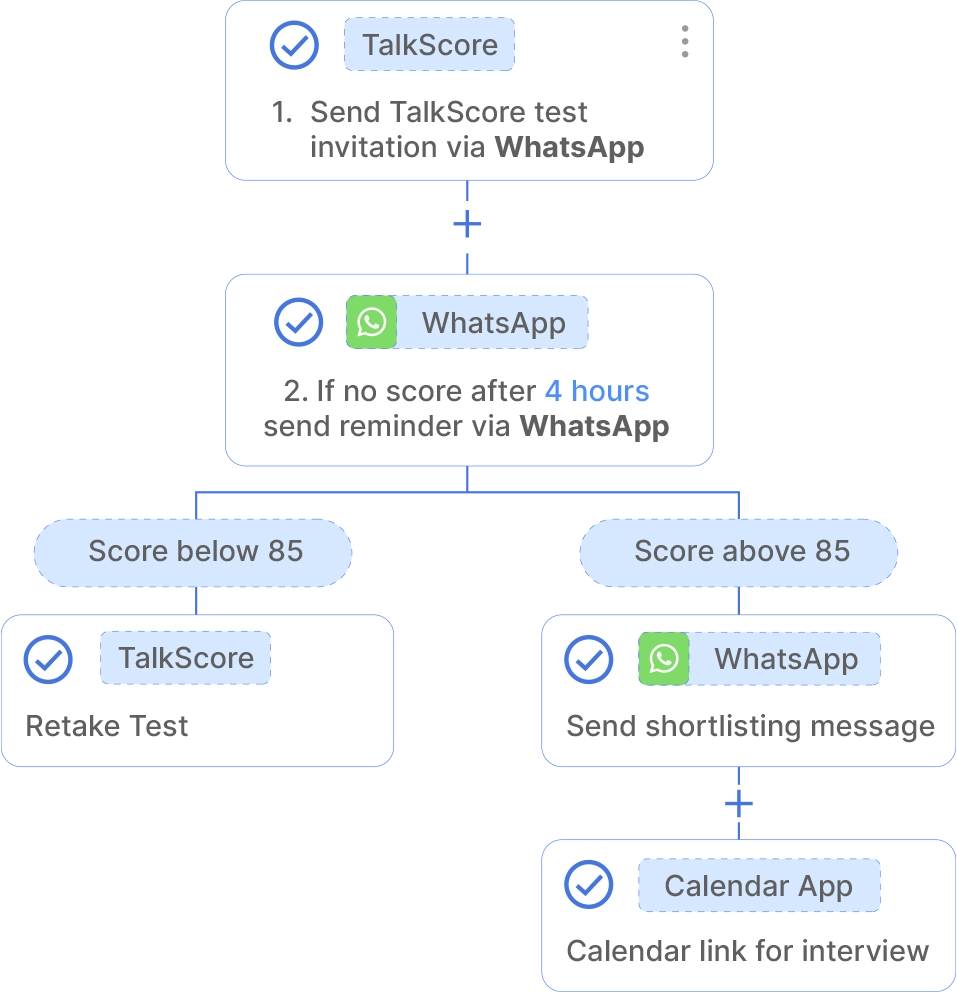
TalkScore skill testing process
Employee Support and Engagement
AI-powered virtual assistants are helping workers around the clock by answering their questions about payroll, benefits, and corporate procedures. This guarantees that workers receive prompt, correct responses while also lessening the administrative load on HR departments. Personalized text and voice communication increases employee engagement and job satisfaction.
Intercom is an empowerment platform meant to empower communication, built first for customer service but just as apt for internal training and team collaboration optimization. Its AI-powered features help organizations provide effortless, instant, accurate answers and eliminate the need for recurrent human input.
One of FinAI agent's prominent features is the ability to act as an internal help desk with automated support that sounds conversational and natural. Employees can ask policy or procedure questions and receive immediate, plain-English responses — no digging through outdated manuals or waiting for a response email. If the employee has trickier questions, Intercom automatically routes them to the right person, with ticketing and workflows integrated.
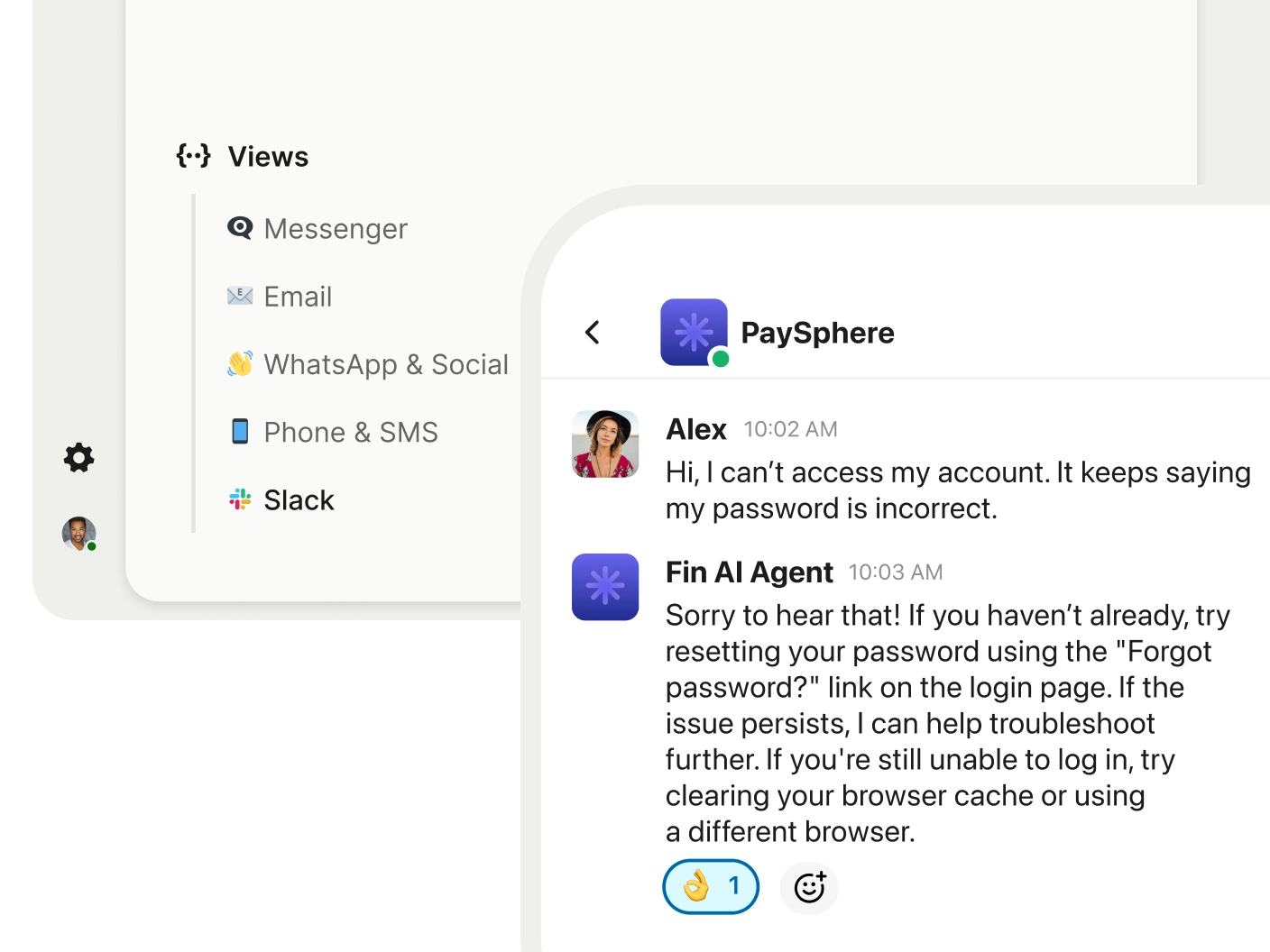
Intercom’s Agent Fin delivers instant, accurate answers on Slack, scaling AI-first employee service
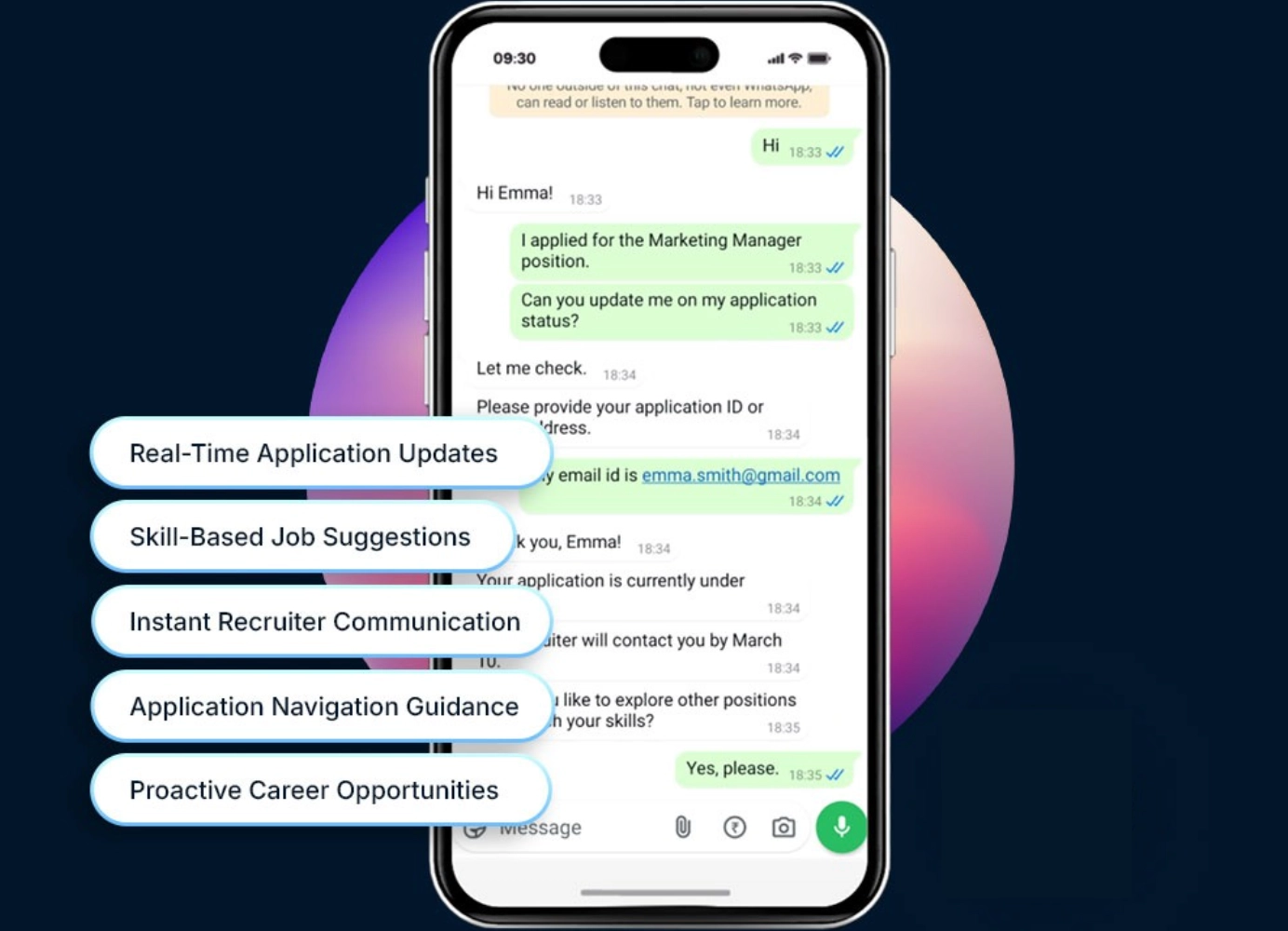
Another great example of solutions for employee support is Kin by Kinfolk. It is an AI-powered HR assistant that automates employee support and administrative tasks, enhancing engagement and productivity. It provides 24/7 assistance across multiple communication channels like Slack, Teams, email, SMS, and WhatsApp, ensuring employees receive timely support wherever they are. Key features include conversation management, advanced workflows, personalized support, and proactive communications.
Performance Management
Performance management is being smartly transformed with AI systems that collect and analyze feedback from different people across the organization to provide insights in real time. Reminders and tracking facts stay automated at any event, which may offer managers and personnel the opportunity to support them, stay synchronized on goals, spotlight performance improvement over time, and create a significant feedback loop.
Harper is an AI-powered HR generalist developed by Wisq that is designed to automate and enhance a variety of human resources processes within companies. Through the utilization of Wisq's Agentic AI Platform, Harper handles tasks such as policy compliance, performance management, and employee guidance. Capability-wise, Harper is trained on an HR curriculum that enables it to accurately respond to 94% of SHRM-CP exam questions and 12 times faster than a certified HR professional. It can learn instantly from a company's policies, content, and culture so that interactions reinforce organizational standards. Harper also actively surfaces insights from workforce interactions to help HR teams proactively nip potential problems.
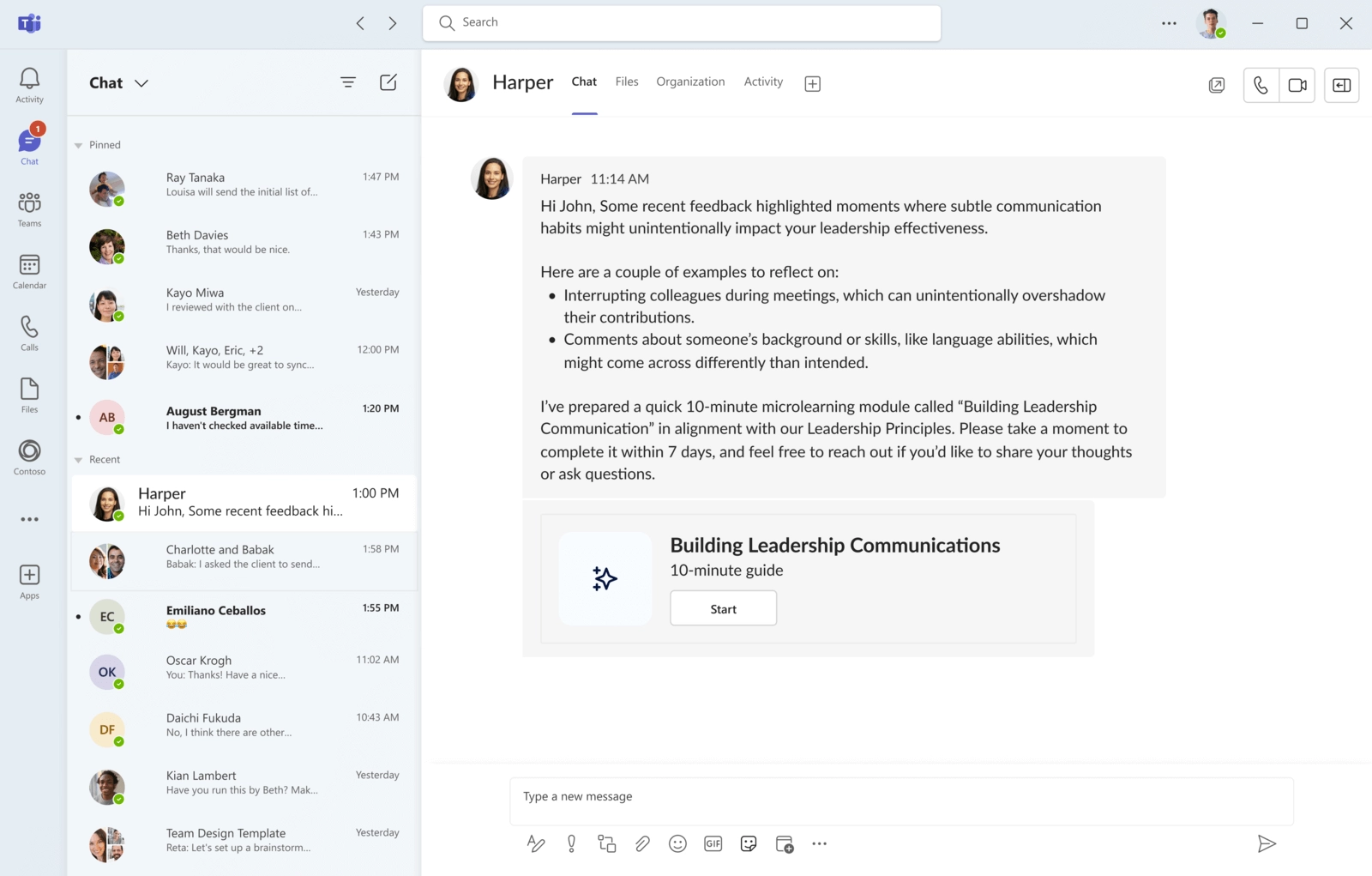
Harper provides insight into employee communication habits
Training and Development
From performance data, AI helpers can point out useful classes and work choices, helping workers grow and climb the company ladder.
Beam AI enhances employee training with AI-driven tools for personalized learning. The Training Module delivers role-specific, bite-sized content, while the Training Program tool aligns training with company goals. The Employee Training Developer streamlines planning and automates skill development.
Another good example is SpringsApps' AI learning agents, which enhance employee training by providing personalized learning experiences, adaptive content, and real-time feedback. They integrate with corporate Learning Management Systems (LMS) to automate assessments, track progress, and offer interactive learning through text and video-based AI assistants. These agents use AI-driven analytics to identify skill gaps and recommend targeted training.
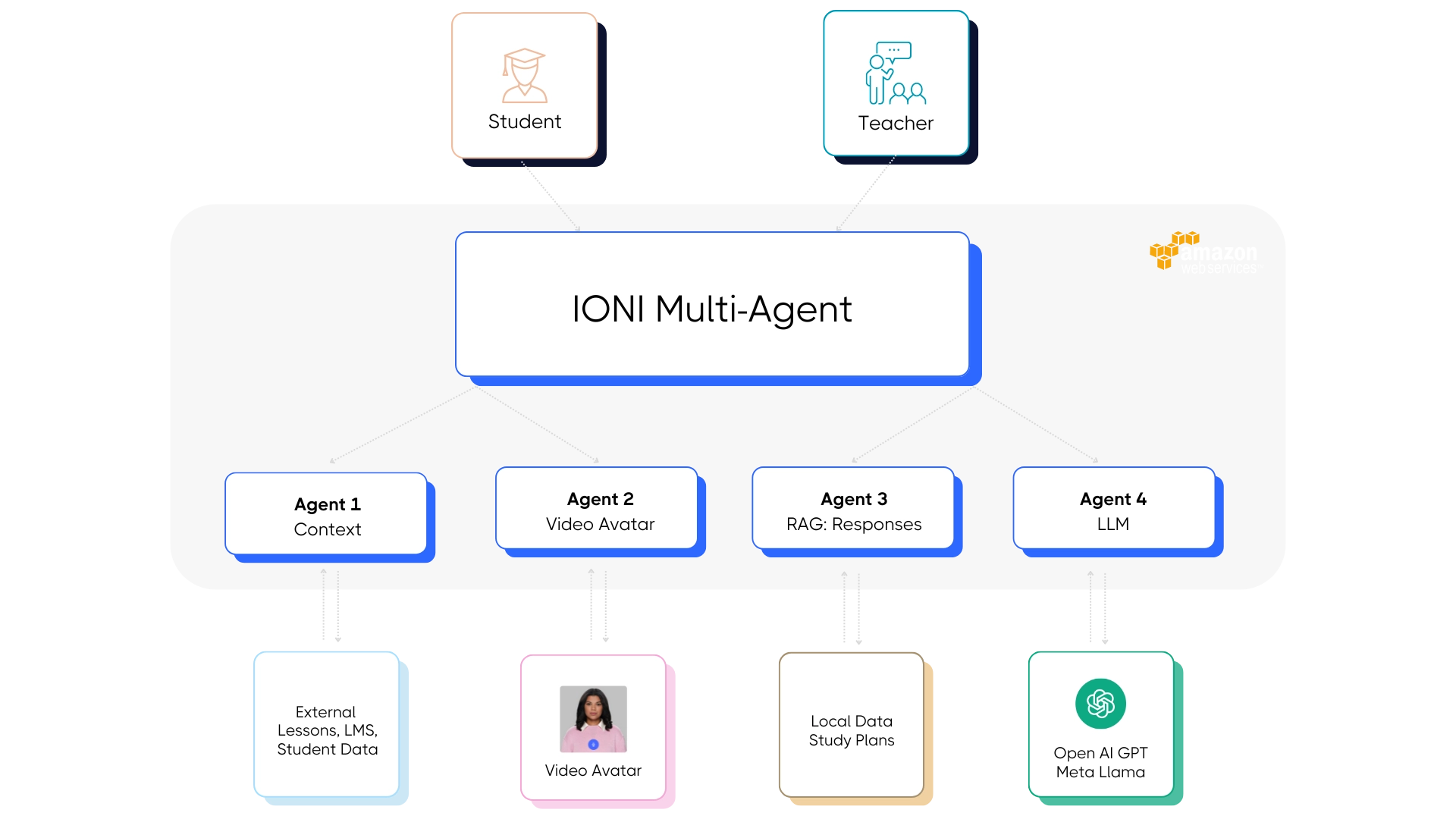
How SpringAI Agents Work
HR Analytics and Decision Support
AI agents are increasingly integrated into HR analytics and decision-making, transforming traditional HR practices into data-driven, strategic functions. AI agents easily process large amounts of employee data to recognize patterns and trends, allowing HR professionals to make informed recruitment, performance management, and employee retention decisions.
AHA! An AI-powered assistant enhances HR analytics and decision-making by integrating AI with workforce data. It provides insights, automates reporting, and supports making decisions in talent management, workforce planning, and compliance. The AI assistant connects to HR systems, offering personalized, data-driven recommendations while ensuring security and privacy. This enables HR leaders to optimize hiring, retention, and risk mitigation.
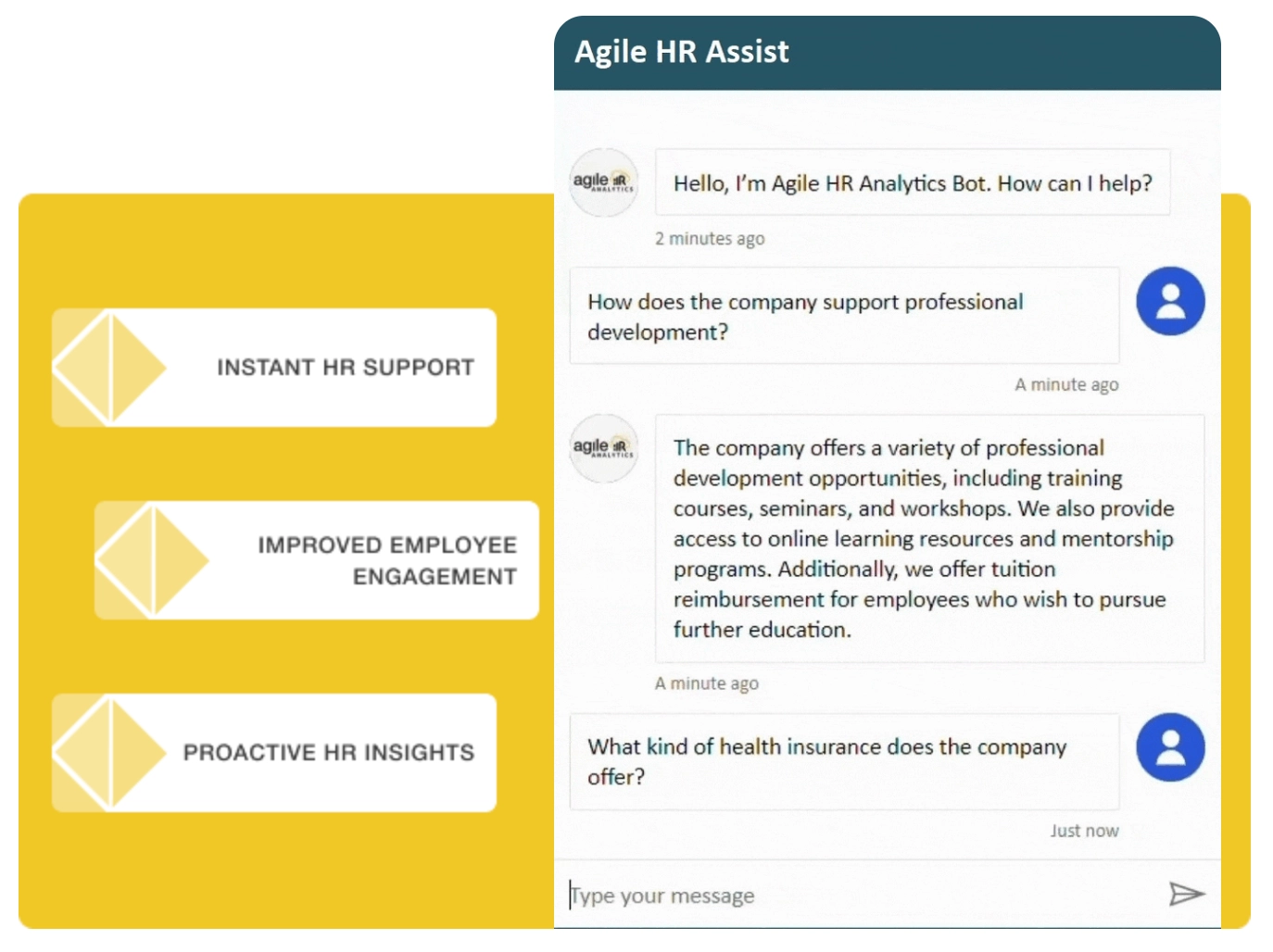
AHA! HR Assistant
In HR Analytics, Lyzr offers over 40 specialized AI agents to streamline various HR functions. They provide analytics and decision support by analyzing employee data and delivering actionable insights. These agents help HR professionals optimize workforce management, improve employee engagement, and enhance performance by identifying trends, monitoring key metrics, and offering recommendations to support data-driven decision-making.
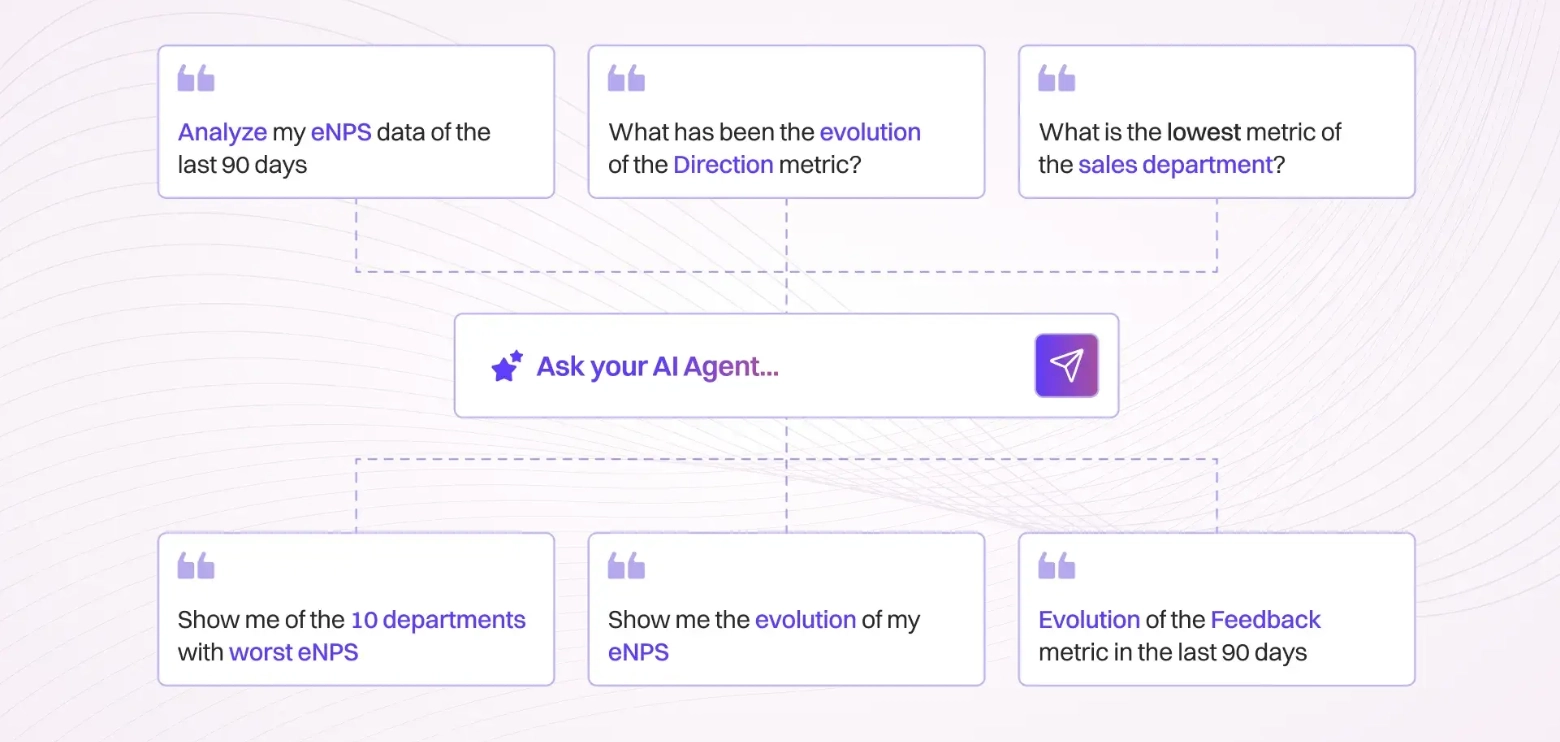
Lyzr People Analytics Solution
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
We are still at the beginning of the AI implementations within the HR industry. While the agents mentioned in this article are impressive, most still face technical limitations such as latency, poor handling of unstructured data (AI may misinterpret unstructured inputs like complex resumes, cover letters, or verbal explanations in interviews) and limited contextual understanding, where AI may fail to grasp industry-specific requirements, evolving job roles, or the broader company culture that influences hiring decisions.
There are still significant ethical considerations that companies must mitigate while using AI agents. Bias and fairness are at the top, as ensuring AI algorithms are free from prejudice and promote fair treatment across diverse workforces remains the main priority.
Privacy and data security are also to be considered as protecting employees’ sensitive information and maintaining compliance with global data protection regulations are crucial. Companies need to adopt strong cybersecurity measures to protect AI-driven HR systems.
Finally, there must be a balance between human touch and automation. AI can offer efficiency, but the need for genuine human connection in HR interactions remains essential. AI should support, but not replace, the empathetic and strategic roles that HR professionals play.
Future Trends & Conclusion
The future of conversational ambassadors in HR is encouraging, with AI shifting from simple automation to intelligent decision-making and predictive insights.
AI systems will get better at predicting employee needs and offering proactive support, resulting in hyper-personalization. Creating conversational agents that can detect and react to human emotions has the potential to improve virtual interactions and make digital conversations feel more human.
Integration with HR tech stacks has emerged as another big trend. Lower friction and better interoperability ensure more productivity powered by a unified digital experience for both employees and HR teams.
Adoption intensity is a key factor in unlocking the full potential of AI in Human Resources, and it will help HR practitioners remain conscious of its ethical implications as well as prepare for future evolution.
The future will see AI and human recruiters working together, with AI handling data-driven tasks and humans focusing on empathy, creativity, and strategic decision-making.
Looking to build an AI agent for HR or Recruiting?

Talk to Yuliya. She will make sure that all is covered. Don't waste time on googling - get all answers from relevant expert in under one hour.